Introduction
Suicide is an important public health phenomenon, with a complex, multi-dimensional aetiology (WHO, 2021a). Approximately 703 000 people died by suicide in 2019, and this cause of death presents a global annual mortality rate of nine per 100 000 individuals, with different mortality time trends across countries (from fewer than two to more than 80 per 100 000) and age classes (WHO, 2021b). Moreover, suicide is one of the most important factors influencing the risk of death and years of life lost (YLL) among people affected by a mental disorder (Harris and Barraclough, Reference Harris and Barraclough1998; Nordentoft et al., Reference Nordentoft, Wahlbeck, Hällgren, Westman, Ösby, Alinaghizadeh, Gissler and Laursen2013; Walker et al., Reference Walker, McGee and Druss2015; Girardi et al., Reference Girardi, Schievano, Fedeli, Braggion, Nuti and Amaddeo2021). In fact, psychopathology is strongly associated with suicidal thoughts and behaviours, and it can precede these outcomes and increase their likelihood (for recent reviews, see Franklin et al., Reference Franklin, Ribeiro, Fox, Bentley, Kleiman, Huang, Musacchio, Jaroszewski, Chang and Nock2017; Ribeiro et al., Reference Ribeiro, Huang, Fox and Franklin2018; Guzmán et al., Reference Guzmán, Cha, Ribeiro and Franklin2019; for a modelling of potential mechanisms underpinning the relationship between mental disorders and suicide, see Mishara and Chagnon, Reference Mishara, Chagnon, O'Connor and Pirkis2016).
Research on the relationship between mental disorders and suicide is relevant, as it is widely assumed that estimates of suicide risk and definitions of high-risk patients according to individual characteristics may guide the clinical treatment of psychiatric patients. In this regard, a meta-review assessed the risks of all-cause and suicide mortality in people with mental disorders (Chesney et al., Reference Chesney, Goodwin and Fazel2014), concluding that the highest suicide risk was associated with borderline personality disorder, which presented a 45-fold increase in risk relative to the general population level. Suicide risk was also found to be strongly associated with anorexia nervosa in women (31-fold increase), depression (20-fold increase), bipolar disorder (17-fold increase), opioid use (14-fold increase) and schizophrenia (13-fold increase).
Nevertheless, some scholars have argued that the risk conferred by mental disorders is over-rated, because most observed associations have arisen from psychological autopsy studies (Pridmore, Reference Pridmore2015; Hjelmeland and Knizek, Reference Hjelmeland and Knizek2017). Such studies obtain information on decedents by suicide by interviewing individuals who were close to them, and they run the risk of introducing recall biases by priming informants to consider particular risk factors (e.g. mental disorders) that might explain the suicide (Cavanagh et al., Reference Cavanagh, Carson, Sharpe and Lawrie2003). On the other hand, studies using record linkage data (whereby mental health service use data are linked with suicide data at the individual level) may offer a more objective window into the relationship (Goldney, Reference Goldney2015; Haw and Hawton, Reference Haw and Hawton2015).
A recent meta-analysis provided a conservative estimate of the association between mental disorders and suicide risk by restricting the inclusion criteria to record linkage studies, exclusively (Too et al., Reference Too, Spittal, Bugeja, Reifels, Butterworth and Pirkis2019). The association was confirmed by the pooled results, revealing an eightfold increase in risk relative to the general population level. Notably, the time periods examined in the included studies ranged from 1973 (Webb et al., Reference Webb, Lichtenstein, Larsson, Geddes and Fazel2014) to 2012 (Høye et al., Reference Høye, Nesvåg, Reichborn-Kjennerud and Jacobsen2016); thus, more up-to-date evidence is urgently needed, also to determine whether recent advancements in psychiatric care can be linked to temporal variations in suicide mortality. Moreover, record linkage studies have only been conducted in six countries (i.e. Denmark, Sweden, Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, Norway), and their results are hardly generalisable, since their overall high heterogeneity (93.8–97.9%) can be mainly (50.5%) explained by the country of study (Too et al., Reference Too, Spittal, Bugeja, Reifels, Butterworth and Pirkis2019). As several factors may explain differences between countries (e.g. selection criteria, national legal systems, specificities of mental health care), data from under-studied countries are needed to improve access to high-quality mental health care and thereby prevent suicide.
Based on these premises, the present record linkage study investigated the relationship between suicide mortality and contact with mental health services among a population-based cohort of adult patients with a diagnosed mental disorder, who were in the care of a community mental health centre (CMHC) in Northeast Italy. Patients were observed over a 10-year period, from 2008 to 2018. Specifically, we aimed at estimating differences in suicide risk by age, gender, time elapsed since the first contact with the CMHC, calendar year of diagnosis and diagnostic category. To assess the impact of suicide mortality, we estimated the amount of potential life years lost. Moreover, since access to lethal means is relatively manageable (especially in in-patient clinical settings), we also aimed at estimating patterns in suicide modality.
Methods
The study was conducted in the Veneto Region (Northeast Italy, population 4.9 million). Recruitment and follow-up methods were previously described (Girardi et al., Reference Girardi, Schievano, Fedeli, Braggion, Nuti and Amaddeo2021). Briefly, we recruited all patients aged 18–84 years cared by CMHC in Veneto in 2008, who had received a psychiatric diagnosis in or prior to the year 2008. CMHC data included demographics, date of first contact with the psychiatric service and clinical diagnosis (according to the ICD-9CM). Diagnostic groups were defined as: schizophrenia and related disorders (ICD-9CM 295, 297, 298.1–298.9, 299); bipolar disorder (296.4–296.7); other affective disorders (296, 298.0, 300.4, 309.0, 309.1, 311); neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders (300, 306, 307.4, 307.8–307.9, 308, 316); borderline personality disorder (301.83); other personality disorders (301, 302, 312); substance use disorders (291–292, 303–305); and all other diagnoses (e.g. eating disorders, dementia, etc.).
Record linkage between patient and mortality information was performed by a standardised anonymisation process that assigned each subject a unique code and allowed record linkage between electronic records, with no possibility of retrieving patients’ identities. Subjects were followed-up for overall mortality and cause of death from 2008 (year of recruitment of the cohort), until 31 December 2018. Cause of death was coded according to the ICD-10. Suicides (ICD10 X60–X84) were classified as poisoning (X60–X69); hanging, strangulation/suffocation (X70); drowning (X71); suicide by firearm (X72–X74); jumping (X80); or unspecified/other.
The study variables were summarised in frequency tables. Categorical variables were compared using a χ 2 test. Statistical significance was assumed at the 5% level. The cumulative mortality risk curves were estimated by Fine and Gray cumulative incidence estimator, considering suicide and other causes of death as competitive events; the estimation was performed by diagnostic group and equality across groups was tested by a log-rank test.
For all observed deaths – and separately for deaths from suicide – we computed YLL as the difference between the subject's age at death and the current life (at the year of reference) expectancy for the general population, with respect to the subject's age and sex, as provided by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT). For each diagnostic group, we also calculated the average YLL from suicide and all causes, and the relative percentage contribution of suicide to overall YLL.
The effects of age, gender, time elapsed since the first contact with a psychiatric service, calendar year of diagnosis and diagnostic category on the suicide mortality rate were estimated as mortality rate ratios (MRR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), obtained using Poisson regression. Since patients diagnosed before the start of the follow-up can be subjected to self-selection bias or other time-related dynamics, their influence in the analysis was assessed by means of a sensitivity analysis performed on the same Poisson regression model but including only subjects with a first diagnosis in the year 2008.
A multinomial logistic regression was estimated to assess differences in suicide modality, including suicide modality as the dependent variable and testing the significance of the covariates’ effect using an analysis of variance based on the likelihood ratio test. The results were reported in terms of odds ratios (OR) with 95% CIs with respect to the reference category.
The cohort data were built using SAS Enterprise Guide 6.1, and YLL was estimated via the ‘Epi’ and ‘popEpi’ packages in R (Carstensen and Plummer, Reference Carstensen and Plummer2011; Plummer and Carstensen, Reference Plummer and Carstensen2011). Since all analyses were carried out on routinely collected anonymised records, the study was exempt from approval by the local ethics committee.
Results
Overall, 54 350 CMHC patients were recruited (41.9% male, median age 48 years). Distribution by diagnostic group was as follows: 23.9% schizophrenia and related disorders; 3.6% bipolar syndrome; 30.2% other affective disorders; 17.8% neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders; 0.8% borderline personality disorder; 8.4% other personality disorders; 2.1% substance use disorders; and 13.2% other diagnoses.
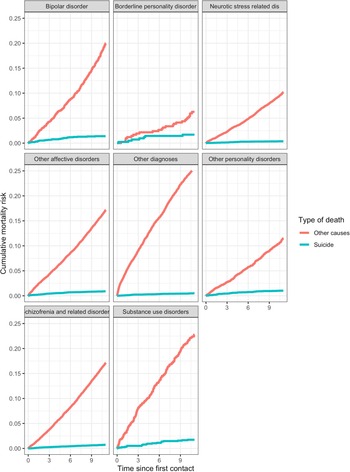
A total of 9176 deaths were registered among the cohort subjects over the 10-year follow-up period (531 638 person-years). The overall mortality risk (both for suicide and other causes) differed by diagnostic group (log-rank test p < 0.001) with a high mortality risk for non-suicidal causes among patients with a diagnosis of substance use disorders or bipolar disorders; patients with borderline personality disorders reported a mortality risk for suicide closed to that for other causes, while for the other groups the difference in risk was more marked (Fig. 1).
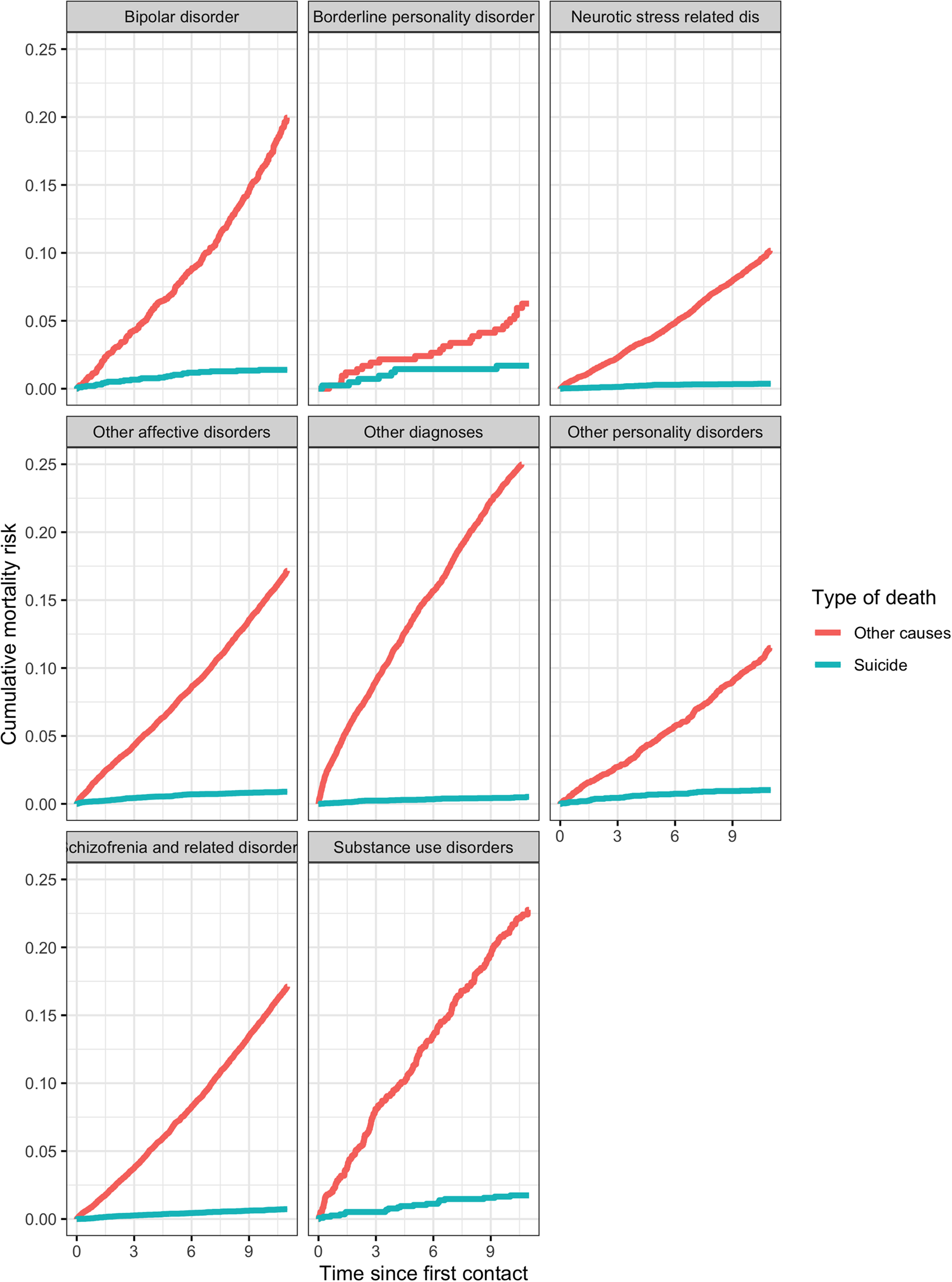
Fig. 1. Cumulative mortality risk estimated by Fine and Gray cumulative incidence estimator by diagnostic group for suicide mortality and other causes.
Out of the entire deaths amount, 407 were from suicide (61.1% male, mean age at death 52.2 years). With respect to overall deaths, decedents from suicide were younger and more likely to be male and diagnosed with bipolar disorder, other affective disorder, or a personality disorder (Table 1).
Table 1. Main characteristics of decedents from suicide and other causes in a cohort of 54 350 community mental health centre patients in the Veneto Region (Italy)
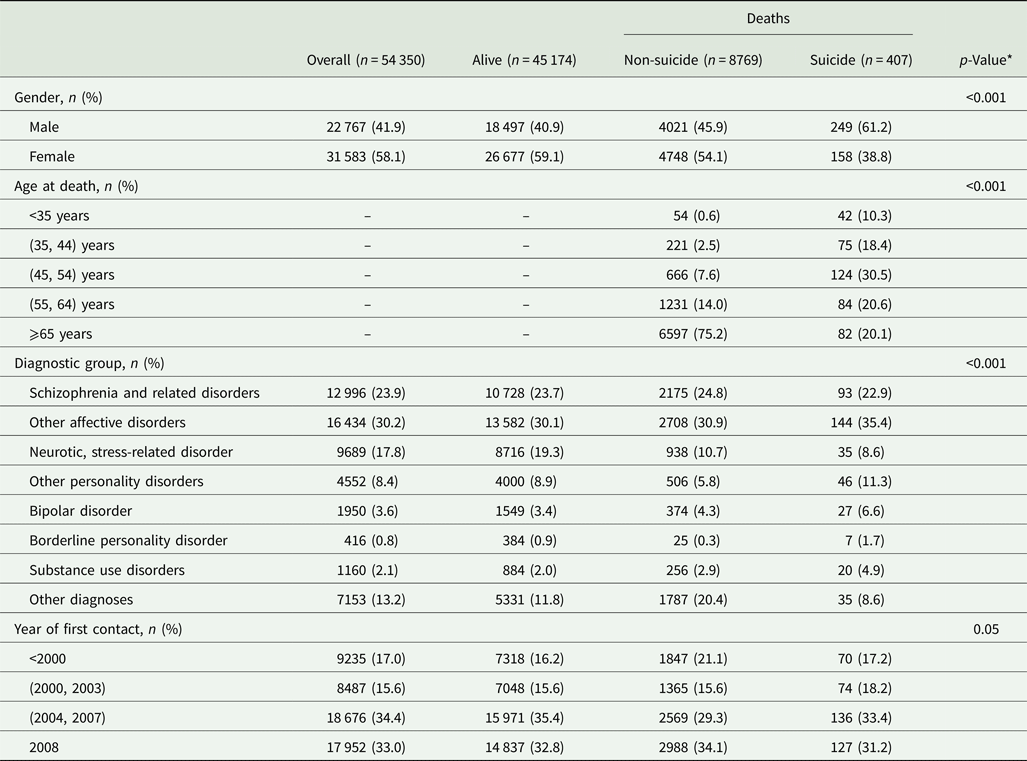
* p-Value related to the χ 2 test between comparison among deaths amount due to suicide and non-suicide.
Despite representing only 4.4% of all registered deaths, deaths from suicide accounted for 8.7% of all YLL, amounting to 12 845 YLL with a mean of 31.5 YYL per decedent. The share of all YLL represented by suicide was larger among patients with bipolar disorder (11.5%), borderline personality disorder (27.2%) and a substance use disorder (12.1%) (Table 2).
Table 2. Total number (YLL) and average number of years of life lost (mYLL) for the entire cohort and for suicide by diagnostic group
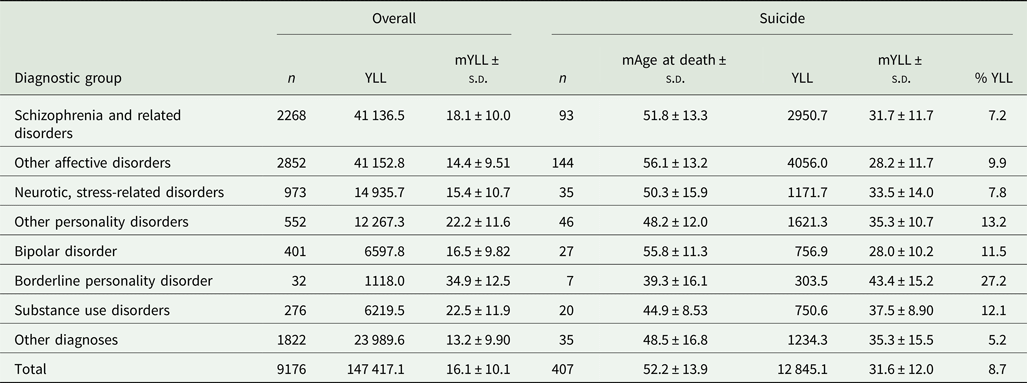
For the suicide group, the median age (mAge) at death and the percentage of years of life lost due to suicide (%YLL) is reported.
The Poisson regression determined that the female suicide mortality rate was half that of males (MRR 0.45; 95% CI 0.37–0.55). Overall, the suicide mortality rate also peaked among subjects aged 45–54 years (MRR 1.56; 95% CI 1.09–2.23) and in the 2 months following first contact with the psychiatric service (MRR10.4; 95% CI 5.30–20.3). However, the rate decreased as further time elapsed since first contact. In addition, patients with more recent diagnoses had a lower mortality risk. Patients affected by neurotic/stress-related and somatoform disorders showed the lowest suicide rates; the highest rates were registered by subjects diagnosed with bipolar disorder, borderline personality disorder and a substance use disorder (Table 3). The sensitivity analysis based on patients diagnosed during the year 2008 broadly confirmed the previous results (online Supplementary Table S2), showing only a slight reduction in the suicidal risk in the first 2 months following first contact with the psychiatric service.
Table 3. Mortality rates and mortality rate ratios (MRR) for suicide estimated by the Poisson regression model and relative 95% confidence interval (95%CI)
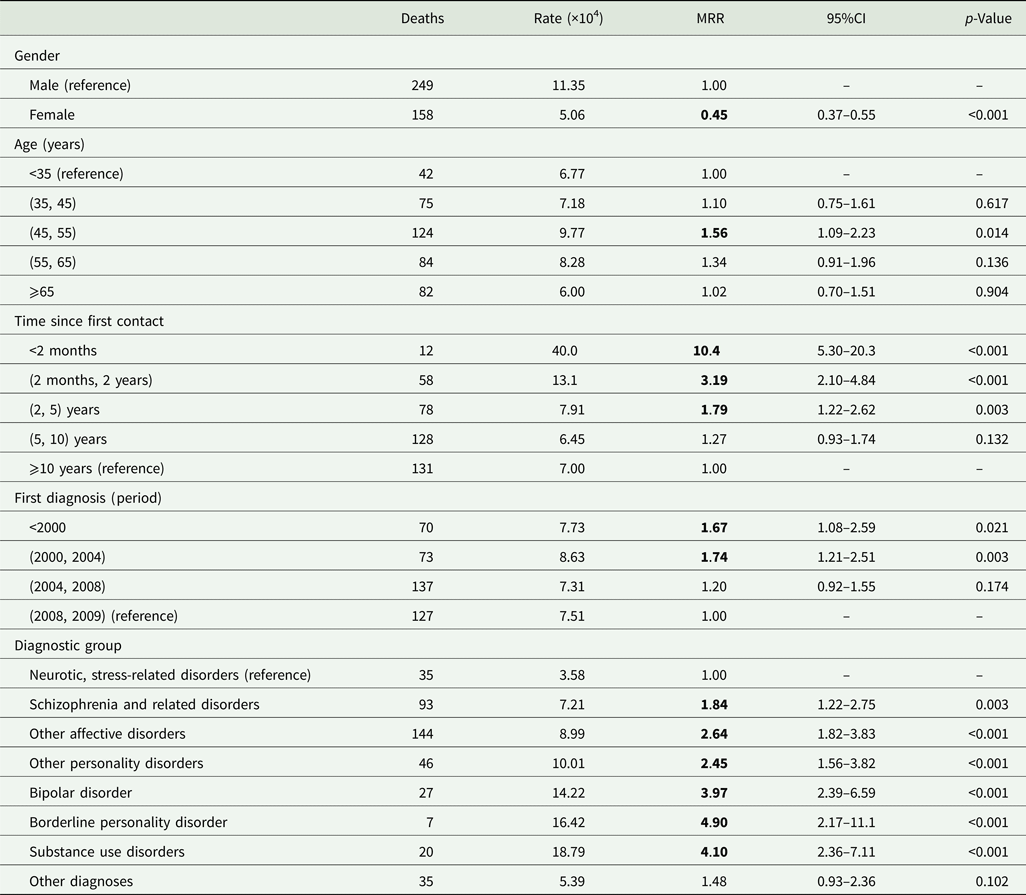
Bold values denote statistical significance at the p < 0.05 level.
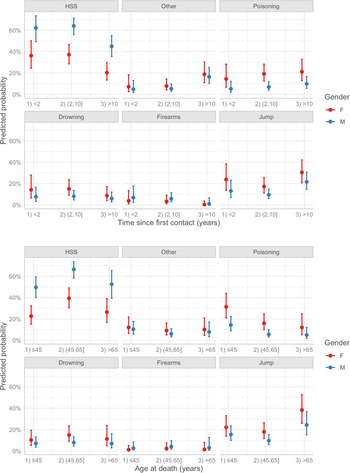
The most common suicide modality was hanging (47%), followed by jumping (18%), poisoning (13%) and drowning (10%); suicide from a firearm was rare (4%). Online Supplementary Table S2 shows that suicide modality was influenced by gender, age at death and time since first contact with the psychiatric service. In fact, as reported in online Supplementary Table S4, females were more likely to engage in poisoning (OR 4.75; 95% CI 2.43–9.29), jumping (OR 3.11; 95% CI 1.73–5.61), drowning (OR 3.18; 95% CI 1.55–6.52) and other methods (OR 2.54; 95% CI 1.21–5.32), rather than hanging. In addition, after 10 years had elapsed since the first contact with the psychiatric service, patients reported an increased frequency of jumping (OR 3.23; 95% CI 1.70–6.15) and other methods for suicide (OR 4.40; 95% CI 2.00–9.68), relative to hanging. Younger people (<45 years) showed a higher frequency of poisoning (OR 3.39; 95% CI 1.67–6.87) and jumping (OR 2.14; 95% CI 1.09–4.19) than patients aged 45–65 years; a significantly higher frequency of jumping also was observed among older patients (OR 3.18; 95% CI 1.54–6.57). The predicted probabilities by suicide modality, gender, age at death and time since first contact were shown in Fig. 2 highlighting the previously reported differences in terms of probability: hanging, strangulation and suffocation were the most common modalities of suicide for both genders. They significantly decreased with the time since first contact, while the probability related to the ‘jump’ modality increased with the age at death, especially among females.
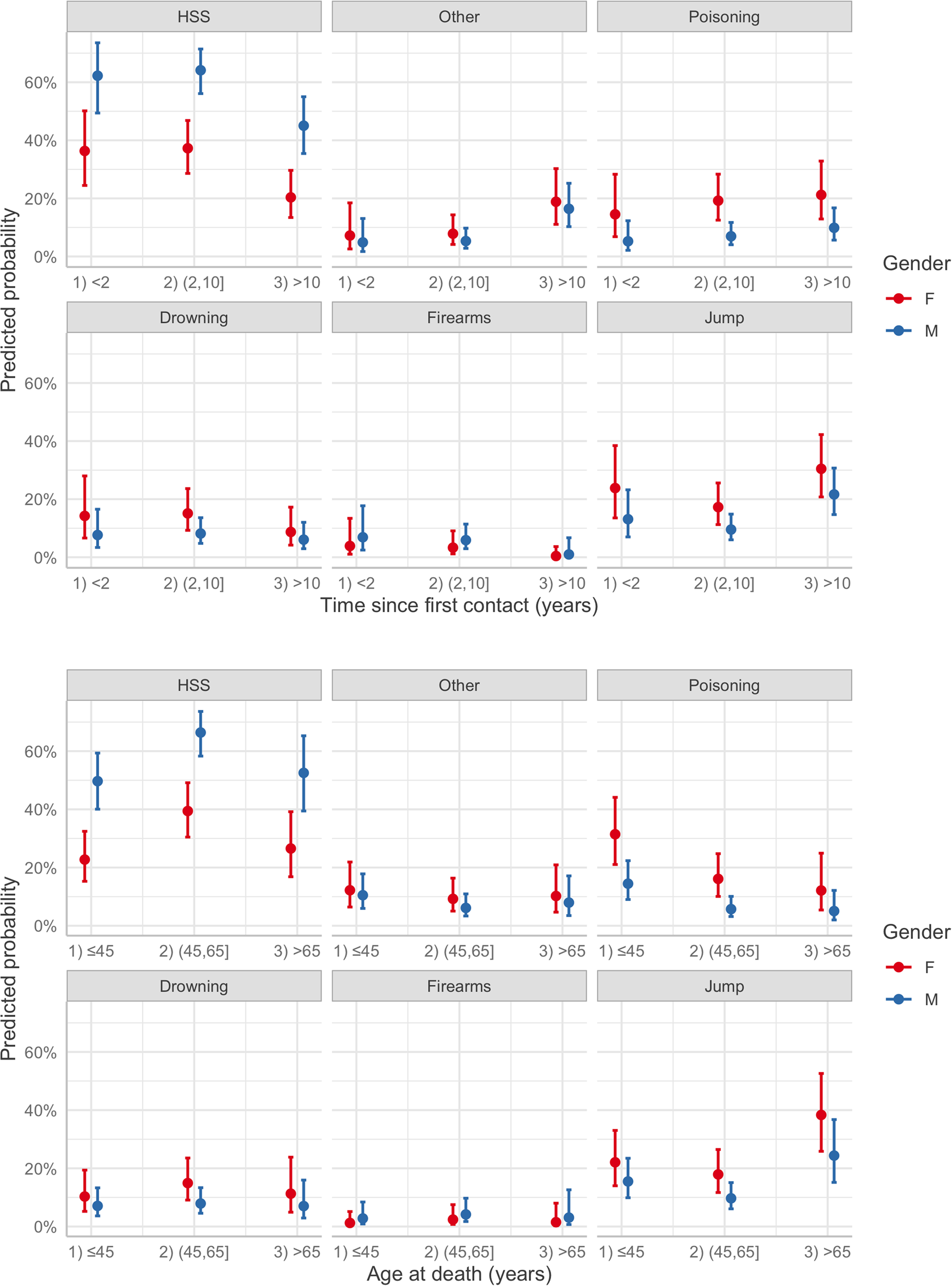
Fig. 2. Predicted probability of suicidal modality estimated by multinomial regression model for combinations of age of death, gender and time since first contact. HSS, hanging, strangulation and suffocation.
Discussion
The present 10-year cohort study showed that, in Northeast Italy, the suicide mortality crude rate for CMHC patients was approximately 7.66 per 10 000, representing a tenfold higher rate than that of the general Italian population (WHO, 2021b). Overall, the observed mortality rate that accounted for 8.7% of all YLL among subjects deserves close attention.
The risk of suicide was also associated with sociodemographic and clinical factors. Specifically, suicide mortality was highest among patients aged 45–54 years, in line with global estimations, which show that more than half of global suicides (58%) occur before the age of 50 years (WHO, 2021b). Moreover, our data showed that the suicide mortality rate was significantly higher in male patients, relative to female patients. Within the context of suicide research, gender differences in suicidal behaviour rates are referred to as the ‘gender paradox’ (Canetto and Sakinofsky, Reference Canetto and Sakinofsky1998), which describes the general phenomenon that, in most Western countries, females have a higher rate of suicidal ideation, yet a lower rate of suicide mortality, relative to males. While the gender paradox may seem to be a mere artefact of data collection driven by cultural expectations about gender (e.g. under-reporting of non-fatal suicide behaviours in males), it has been repeatedly confirmed by meta-analytic studies (Miranda-Mendizabal et al., Reference Miranda-Mendizabal, Castellví, Parés-Badell, Alayo, Almenara, Alonso, Blasco, Cebrià, Gabilondo, Gili, Lagares, Piqueras, Rodríguez-Jiménez, Rodríguez-Marín, Roca, Soto-Sanz, Vilagut and Alonso2019) and the global age-standardised suicide rate (12.6 and 5.4 per 100 000 for males and females, respectively; WHO, 2021b). A putative explanation for this holds that males may use or have easier access to more violent and lethal means for suicide (Windfuhr and Kapur, Reference Windfuhr, Kapur, O'Connor, Platt and Gordon2011). While data on suicide attempts were not available in the present study, our results confirm gender differences in suicide mortality in the clinical population, as well.
Regarding the type of diagnosis, patients with borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder and substance use disorders displayed the highest risk of suicide and lost the greatest number of life years. Surprisingly, the suicide rate for psychosis spectrum disorders did not differ from the overall rate (7.21 v. 7.66 per 10 000) and the rate ratio for suicide mortality showed less than a twofold increase over the reference category (i.e. neurotic, stress-related disorders). While this moderate increase is in line with some reports (Lawrence et al., Reference Lawrence, Almeida, Hulse, Jablensky and Holman2000), further attention is needed, since high heterogeneity between previous studies of suicide risk among psychosis spectrum patients has been reported, also due to the type of comparison group, the mental disorder classification and the inclusion of older people (Too et al., Reference Too, Spittal, Bugeja, Reifels, Butterworth and Pirkis2019). Notably, the mental disorder classification applied in the present study (i.e. ICD-9) involves broader diagnostic criteria for psychosis spectrum disorders than the current ones (e.g. ICD-11; DSM-5). For example, ICD-9 included ‘latent schizophrenia’, a relatively less severe diagnosis that today would be recorded as a personality disorder (borderline and/or schizotypal) or, in younger individuals, as an attenuated psychotic syndrome (Lingiardi and Boldrini, Reference Lingiardi and Boldrini2019).
Conversely, subjects with substance use disorders reported a higher suicide risk and the highest crude mortality rate. Numerous biopsychosocial mechanisms may contribute to the increased risk of suicide amongst these patients, including (i) the influence of substance use on cognition and behaviour, which may result in disinhibition and impulsivity; (ii) pain, distress and psychiatric conditions, which increase the likelihood of both substance use disorders and suicide; and (iii) unemployment, social isolation and marginalisation as a result of a substance use disorder (Pompili et al., Reference Pompili, Serafini, Innamorati, Dominici, Ferracuti, Kotzalidis, Serra, Girardi, Janiri, Tatarelli, Sher and Lester2010; Shustov et al., Reference Shustov, Tuchina, Fedotov and Novikov2016; Esang and Ahmed, Reference Esang and Ahmed2018; Bohnert and Ilgen, Reference Bohnert and Ilgen2019). With respect to the latter, the social isolation and marginalisation of individuals with a substance use disorder may be strongly related to the laws and policies applied to condemn and/or pursue consumers of psychoactive substances. The environment in which individuals with a substance use disorder purchase illegal substances can be highly traumatic, and the frequency of traumatic experiences (e.g. violence, detention, usury, social isolation) in a given substance market is likely to be closely related to the laws that govern that market (Perrone et al., Reference Perrone, De Bei and Cristofari2020). In turn, traumatic experiences are well-known as both distal (Zatti et al., Reference Zatti, Rosa, Barros, Valdivia, Calegaro, Freitas, Ceresér, da Rocha, Bastos and Schuch2017) and proximal (O'Connor and Kirtley, Reference O'Connor and Kirtley2018) risk factors for suicide. Notably, in Italy, during the analysed time period, strong prohibitionist national policies were applied regarding the use and possession of psychoactive substances (Ronconi and Camposeragna, Reference Ronconi and Camposeragna2021). Legislation and collective regulations may exert a significant influence on psychopathology (with respect to suicide, see e.g. Knipe et al., Reference Knipe, Metcalfe, Fernando, Pearson, Konradsen, Eddleston and Gunnell2014; Kim et al., Reference Kim, Koo, Lee, Won and Song2019; Cai et al., Reference Cai, Canetto, Chang and Yip2021), and more research is needed to estimate the potential impact of different drug policies on clinical outcomes (including suicide) among individuals with a substance use disorder. Researchers working in the growing field of legal epidemiology (Burris et al., Reference Burris, Cloud and Penn2020) are particularly well positioned to address this issue.
On the other hand, in the present study, patients with borderline and other personality disorders lost more life years by suicide than by any other disease category, suggesting that they tended to commit suicide at an earlier age. This finding is not surprising, since personality disorders typically onset during adolescence (Newton-Howes et al., Reference Newton-Howes, Clark and Chanen2015) – several years earlier than most other mental disorders (e.g. schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depressive disorders), which typically onset by mean age 24 years (de la Fuente-Tomas et al., Reference de la Fuente-Tomas, Sánchez-Autet, García-Álvarez, González-Blanco, Velasco, Martínez, Garcia-Portilla and Bobes2019). Specific efforts to reduce early suicidality in individuals with a personality disorder are strongly needed. Treatments for personality disorders are usually offered relatively late in the course of the disorder, and are often characterised by therapeutic nihilism (Snowden and Kane, Reference Snowden and Kane2003; Sheehan et al., Reference Sheehan, Nieweglowski and Corrigan2016). In contrast, intervention during the early stages of a personality disorder (i.e. in adolescence) might help to decrease the persistence and/or severity of the personality disorder and prevent the cascading of secondary psychopathology, psychosocial disability and suicidality (Chanen and Thompson, Reference Chanen and Thompson2018).
The World Health Organization (WHO, 2021a) recently recommended measures to ‘identify, assess, manage, and follow-up anyone affected by suicidal behaviors, from an early stage’. In line with this recommendation, the present results may also help to inform clinicians and policymakers on when to increase efforts to prevent suicide in help-seeking individuals. Specifically, we found that suicide mortality was highest within the 2 months following the first contact with a CMHS, and decreased as further time elapsed. This finding can be interpreted in at least two ways: (1) contact with a CMHS and psychosocial and/or pharmacological treatments are effective in reducing suicidality, and their effect increases over time; and (2) some help-seeking individuals make first contact with a CMHS when their clinical condition is already so severe as to lead to suicide soon thereafter (Cosci and Fava, Reference Cosci and Fava2013; de la Fuente-Tomas et al., Reference de la Fuente-Tomas, Sánchez-Autet, García-Álvarez, González-Blanco, Velasco, Martínez, Garcia-Portilla and Bobes2019), and clinical treatments at this stage may be insufficient to prevent this dramatic outcome. With respect to the latter explanation, meta-analytic data have shown that a great number of individuals experience years of untreated mental illness before seeking treatment from mental health services, though they often seek help in a different context (Perkins et al., Reference Perkins, Gu, Boteva and Lieberman2005; Ghio et al., Reference Ghio, Gotelli, Marcenaro, Amore and Natta2014; Penttilä et al., Reference Penttilä, Jääskeläinen, Hirvonen, Isohanni and Miettunen2014; Souaiby et al., Reference Souaiby, Gaillard and Krebs2016). For example, a systematic review of the pathways to care for patients with first-episode psychosis showed that, for the vast majority, first contact was with a physician, and frequently within a hospital emergency department (ED) (Anderson et al., Reference Anderson, Fuhrer and Malla2010). Recent findings from the same geographical area of the present study showed that approximately half of all patients who went on to develop a mental disorder between the ages of 15–24 contacted an ED three to four times on average, before contacting a CMHS (Solmi et al., Reference Solmi, Della Rocca, Cianci, Giacometti, Alexopulos, Granziol, Favaro, Fusar-Poli, Zoleo and Cremonese2020). Regarding suicide behaviours, a review of more than 40 studies (Luoma et al., Reference Luoma, Martin and Pearson2002) found that up to 3–4 suicide victims had contact with a primary care provider in the year of their suicide; in contrast, only about two out of every ten suicide victims had contact with an in-patient or out-patient mental health clinic in the year before death (Walby et al., Reference Walby, Myhre and Kildahl2018). Several reasons might account for the apparent barriers to mental healthcare, directing subjects at risk of (or already presenting with) a mental disorder towards a general physician or ED, instead of a CMHS. First, self-stigma, overall stigma and discrimination, in particular, have been shown to correlate with a longer duration of untreated illness (Kular et al., Reference Kular, Perry, Brown, Gajwani, Jasini, Islam, Birchwood and Singh2019). Subjects may be prone to avoiding clinical contexts associated with ‘mental health’, they may minimise their functional impairment or unspecific symptoms, and they may wait to seek help until they manifest acute signs or symptoms. Thus, specific efforts are urgently needed to destigmatise mental health settings, in order to meet international recommendations aimed at reducing the duration of untreated illness to a maximum of 3 months (Bertolote and McGorry, Reference Bertolote and McGorry2005). Moreover, the adoption of early intervention approaches integrating primary (e.g. general practitioners and EDs) and secondary (e.g. CMHS and psychiatric wards) care settings (Fusar-Poli et al., Reference Fusar-Poli, McGorry and Kane2017; Arango et al., Reference Arango, Díaz-Caneja, McGorry, Rapoport, Sommer, Vorstman, McDaid, Marín, Serrano-Drozdowskyj and Freedman2018) may be necessary to prevent suicide outcomes among individuals with a mental disorder.
Finally, regarding suicide modality, the present study found that the majority of suicidal patients ended their life via hanging (47%), whereas suicide from a firearm was rare (4%). This trend contradicts the findings of studies from the United States, showing that the most common suicide modality is by firearm (44.6%) – usually involving a handgun (61.3% of firearm suicides) (Persons et al., Reference Persons, Hefti and Nashelsky2019). Notably, the laws regulating access and exposure to firearms are extremely severe in Italy, compared to those in the United States. In Italy, there are 11.9 guns per 100 people; in the United States, this figure rises to 88.8 guns per 100 inhabitants (King, Reference King2010). Interestingly, studies aimed at comparing more v. less severe firearm state legislations in the United States have shown that legislations that limit access and exposure to handguns significantly reduce not only the rate of suicide by firearm, but also the overall suicide rate (Anestis and Anestis, Reference Anestis and Anestis2015; Kaufman et al., Reference Kaufman, Morrison, Branas and Wiebe2018). Although we cannot compare the overall suicide mortality rate registered in the present study to those of countries with more relaxed firearm legislation, our data on suicide modality suggest that national legislation that limits access and exposure to handguns may play a vital role in preventing suicides. Furthermore, limiting access to means of suicide is one of the strongest recommendations provided by the World Health Organization for suicide prevention (WHO, 2021a). Accordingly, and based on the results of the present study, clinicians should also maintain particular caution with respect to poisoning in both female and younger patients, and for jumping amongst both elderly patients and those with long-lasting contact with mental health services.
Limitations and future directions
The present study suffered from some limitations due to the nature of the data collected. First, a dilution effect of the observed suicide risk may have been present. Specifically, the cohort included subjects diagnosed by CMHC before the data linkage with the regional mortality database in 2008. Consequently, all individuals who had accessed a CMHC prior to 2008 and committed suicide prior to 2008 were lost, and this may have increased the risk of underestimation. However, a sensitivity analysis including only patients who made first contact with a CMHC in 2008 confirmed, with a reduced power, the results. Second, fatal suicide attempt was the only suicide-related variable considered, providing no room for suicidal ideation and non-fatal suicide attempts, which are clearly important risk factors for suicide mortality (World Health Organization, 2015; Hubers et al., Reference Hubers, Moaddine, Peersmann, Stijnen, van Duijn, van der Mast, Dekkers and Giltay2018). Third, we did not consider other relevant suicide predictors, such as socioeconomic status at the time of diagnosis (Arensman et al., Reference Arensman, Larkin, McCarthy, Leitao, Corcoran, Williamson, McAuliffe, Perry, Griffin and Cassidy2019); work history (Milner et al., Reference Milner, Spittal, Pirkis and LaMontagne2013; Azevedo Da Silva et al., Reference Azevedo Da Silva, Younès, Leroyer, Plancke, Lemogne, Goldberg, Rivière and Melchior2019); financial, legal or acute stressful life events; and psychosocial disability (Erlangsen et al., Reference Erlangsen, Banks, Joshy, Calear, Welsh, Batterham and Salvador-Carulla2021). Expanding the analyses to include these factors would increase the precision of the estimates and be strongly recommended for future studies. Fourth, our estimates were necessarily conservative, given that individuals with a mental disorder who did not seek support from public mental health services were not included in the record linkage. Moreover, the analysed data were exclusively collected in CMHCs; therefore, individuals who received a diagnosis of mental disorder in inpatient facilities were not included in the cohort. However, in Italy, a percentage between 93 and 97% of patients accessing inpatient facilities also accessed CMHCs (Lora, Reference Lora2009). For this reason, we are confident that such limitation has little or no impact on the generalisability of our findings. Fifth, due to the nature of the data collected, we could not estimate the comorbidity between different mental disorders, and thus future cohort studies may benefit from stratifying suicidal risk according to comorbidity profiles. As clinicians apply categorical diagnosis as part of their routine practice, further investigation of the relationship between different or comorbid mental disorders and suicide mortality is important. However, comorbidity is more often a diagnostic tool than a clinical reality, and future research may benefit from an emphasis on transdiagnostic dimensions (e.g. early traumatic experiences, common etiological factors) (Glenn et al., Reference Glenn, Kleiman, Cha, Deming, Franklin and Nock2018). Moreover, the observed diagnoses of mental disorders were limited to those registered at baseline. These diagnoses may have changed over time, and we were unable to determine whether the individuals included in this study had any symptoms at the time of their death or had different symptoms than those diagnosed when they were included in the cohort. In addition, we were unable to determine what type of treatments the patients included in the cohort received during the follow-up period. These are limitations that commonly affect the broad field of suicide risk factor studies. As argued by Franklin et al. (Reference Franklin, Ribeiro, Fox, Bentley, Kleiman, Huang, Musacchio, Jaroszewski, Chang and Nock2017), most studies test whether single isolated factors measured at one moment predict suicide-related outcomes over the course of years or even decades. They suggest that, to provide more relevant clinical evidence, future studies should include short follow-up intervals (in the order of minutes, hours or days), with repeated analysis or continuous measurement of constructs (e.g. rapid increases or decreases in depressive symptoms, rather than major depressive disorders), a focus on novel risk factors, and the application of risk algorithms to combine risk factors in a complex but replicable manner (Franklin et al., Reference Franklin, Ribeiro, Fox, Bentley, Kleiman, Huang, Musacchio, Jaroszewski, Chang and Nock2017). Finally, the presented results derived from a population of a wealthy and catholic Italian region, with historically low unemployment rates and a public health system integrated with local health units (Toniolo et al., Reference Toniolo, Mantoan and Maresso2012; ISTAT, 2020). Therefore, the generalisation of the results can be limited to similar populations, since socio-demographic characteristics modified the suicidal risk (Agerbo et al., Reference Agerbo, Gunnell, Bonde, Mortensen and Nordentoft2007). However, some of the present findings, especially those related to the time since first contact with mental health services (Chung et al., Reference Chung, Hadzi-Pavlovic, Wang, Swaraj, Olfson and Large2019) and to the different risk ratios according to different mental disorders diagnoses, are in line with evidence from other Western countries (Qin and Nordentoft, Reference Qin and Nordentoft2005).
Conclusions
The present estimates could not confirm the direct causal mechanisms of heightened suicide risk, but it identified patterns that suggest opportunities for the development of suicide prevention strategies (for reviews, see Pirkis et al., Reference Pirkis, Too, Spittal, Krysinska, Robinson and Cheung2015; Milner et al., Reference Milner, Witt, Pirkis, Hetrick, Robinson, Currier, Spittal, Page and Carter2017; Doupnik et al., Reference Doupnik, Rudd, Schmutte, Worsley, Bowden, McCarthy, Eggan, Bridge and Marcus2020). As the suicide mortality rates were found to be higher in the first 2 months following first contact with a CHMS, suicide preventive interventions should be promptly implemented for help-seeking individuals at their very first contact with mental health services. Special attention is also needed for males, patients aged 45–54 years, and patients diagnosed with borderline personality disorder, a substance use disorder and bipolar disorder. Finally, when seeking to limit access to means of suicide, clinicians should give particular attention to the modalities of hanging, poisoning (particularly among both female and younger patients) and jumping (particularly among both elderly patients and patients with long-lasting contact with mental health services).
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S2045796021000792
Data
Raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request without undue reservation.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
Since all analyses were carried out on routinely collected anonymised records, the study was exempt from approval by the local ethics committee.