Introduction
Infective endocarditis (IE) is a complex disease with a high mortality and morbidity [Reference Delahaye1]. Hospital administrative registries are cornerstones in epidemiological studies of IE [Reference Schmidt2, Reference Erichsen, Gislason and Bruun3]. Many administrative healthcare registries are based on discharge diagnoses coded according to the International Classification of diseases, Tenth revision (ICD-10) [Reference Schmidt2, Reference Tan4]. Data from such registries are essential tools in increasing the epidemiological knowledge of IE. Nationwide registries have not only proved valuable in observational studies but also in registry-supported randomised controlled clinical trials. Moreover, the use of nationwide registries to examine preventive strategies of IE has been debated in scientific communities [Reference Jolly5, 6]. A prerequisite is, however, that the IE diagnosis in the administrative registries is reliable.
A recent validation study of the cardiovascular diagnoses in the Danish National Patient Registry (DNPR) found a positive predictive value (PPV) of 82% for IE [Reference Sundbøll7]. However, because the IE population is heterogeneous and the minimum period of in-hospital intravenous antibiotic treatment in Denmark is 2 weeks [Reference Habib8], the PPV may be lower in patients with shorter hospital stays. We, therefore, examined the PPV of IE according to the length of hospital stay.
Methods
The Danish National Health Service provides free universal tax-supported health care. Denmark is a homogenous country, divided into five regions, all with similar demographic and socioeconomic characteristics [Reference Henriksen9]. We identified patients from the Central Denmark Region, specifically from the Aarhus University Hospital and from two regional hospitals (Herning and Randers) in the period from 1 January 2010 to 31 December 2012. The DNPR and its research potential have been described in details previously [Reference Schmidt2].
The current study is a post-hoc analysis of a previous validation study [Reference Sundbøll7]. In brief, we identified a random sample of 100 patients diagnosed with first-time primary or secondary diagnoses of IE in the DNPR. IE was identified by the following ICD-10 codes: DI33.x, DI38.x and DI39.8. We excluded outpatients in this post-hoc analysis.
A medical record review was considered as the reference standard against which the ICD-10 codes were validated. Three physicians reviewed discharge summaries from the medical records and if the diagnosis of IE was not clear from the discharge summary, the full medical record was reviewed. If the reviewing physician was uncertain if the diagnosis was consistent with the medical record, an independent physician reviewed the medical record so that consensus could be reached. This decision was based on clinical findings (e.g. fever, malaise, vascular and immunologic phenomena) and paraclinical criteria (positive blood culture and positive echocardiography). Hence, the Duke criteria were inherent to the validation process, albeit not strictly followed [Reference Sundbøll7].
We retrieved information on the type of admission (primary or secondary diagnoses) and admission length that was calculated as the total number of days admitted to hospital for IE including the admission and discharge dates. We accounted for transfer between departments, as IE patients discharged from one department still were considered to be hospitalised for IE if they were admitted to another department for IE within <24 h. We ascertained information from the DNPR on whether transesophageal echocardiography (TEE, procedure code: UXUC81) or positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scan (procedure codes: WDIPSFAXX, WDLPSFAXX and WDTCPXYXX) were performed during admission. However, the recordings themselves were not accessible. In addition, information on implantation of a prosthetic heart valve (procedure codes: KFKD, KFMD, KFGE and KFJF) or a cardiac implantable electronic device (procedure codes: BFCA0 and BFCB0) at any time before the IE admission was obtained.
Statistical analyses
The PPV and 95% confidence interval were computed using the Wilson score method [Reference Wilson10]. First, we stratified by admission lengths <2 and ⩾2 weeks. Admission lengths ⩾2 weeks were also separated into 2 to <4 weeks, ⩾4 to <6 weeks and ⩾6 weeks. Third, we repeated the PPV calculation in patients who had a TEE or a PET/CT scan conducted during admission and in patients with a previous prosthetic valve or a cardiac implantable electronic device.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Danish Data Protection Agency (record number: 1-16-02-1-08) and the Chairs of participating departments as part of quality insurance.
Results
Of the 100 medical records, 92 were available for review (see study flowchart in the Fig.1). In 84 of patients (91%), IE was the primary diagnosis. The median admission length was 31 days (25 and 75 percentiles: 13–45 days). The Table 1 shows characteristics of the included patients. The majority of the patients had an admission length of ⩾2 weeks. The PPV was 65% for admission lengths <2 weeks and 90% for admission lengths ⩾2 weeks. The PPV was consistently high when stratifying by submission lengths ⩾2 weeks: 88% for 2 to <4 weeks, 93% for 4 to <6 weeks and 89% for ⩾6 weeks. No overall differences in the PPVs were observed between patients with or without a prosthetic heart valve or a cardiac implantable electronic device.
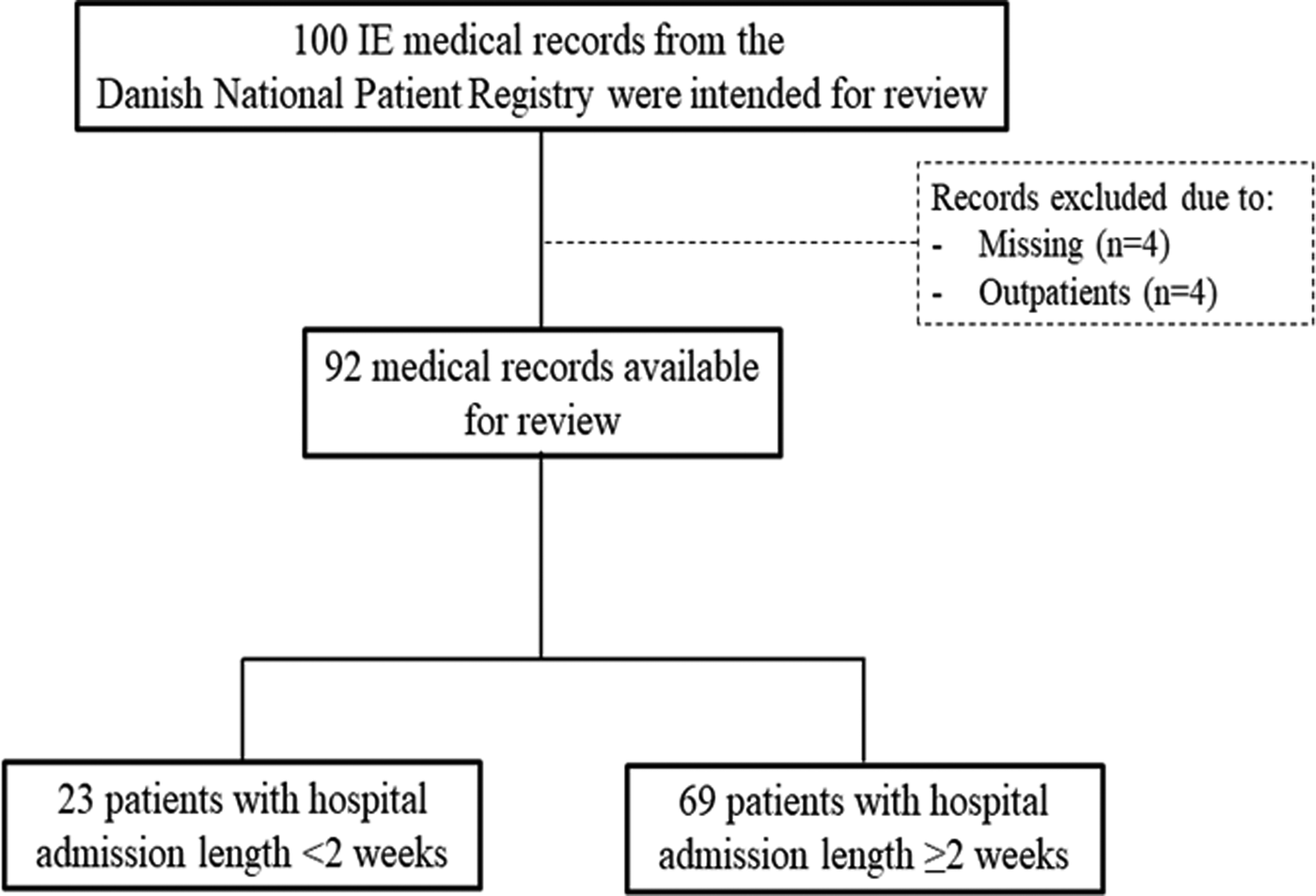
Fig. 1. Flow chart of the study cohort selection process.
Table 1. Positive predictive value of infective endocarditis in the Danish National Patient Registry

PPV, positive predictive value; CI, confidence interval; IE, infective endocarditis; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; PET/CT, positron emission tomography/computed tomography; CIED, cardiac implantable electronic device; IQR, interquartile range.
a Calculated using Wilson score method.
Discussion
Our study had three findings. First, the PPV of IE in the DNPR was higher for patients with an admission length ⩾2 weeks compared with patients with an admission length <2 weeks. Second, the PPV did not differ in patients undergoing TEE or PET/CT. Third, the PPV was similar for patients with and without a prosthetic heart valve or a cardiac implantable electronic device.
The validity of the IE diagnosis was unknown in Danish registries until 2016 where the PPV overall was estimated to 82% [Reference Sundbøll7]. Since the diagnosis of IE is highly complex especially among patients with a prosthetic heart valve or a cardiac implantable electronic device, further analyses were warranted [Reference Habib, Thuny and Avierinos11]. We identified a high PPV for the IE diagnosis with admission length ⩾2 weeks, but also that restriction beyond 2 weeks of admission did not increase the PPV further. This is in line with clinical practice where IE is treated with intravenous antibiotics for 4–6 weeks in left-sided IE and 2 weeks in right-sided IE [Reference Habib8]. The full treatment period is carried out in hospital in Denmark. A forthcoming randomised clinical trial (Partial Oral Treatment of Endocarditis (POET), ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01375257) will clarify whether 2 weeks of intravenous antibiotics followed by oral antibiotics will be sufficient for treating IE. If national treatment guidelines will be changed followed by the results of POET, the PPV of the IE diagnosis may change with varying admission length.
The diagnosis of IE in patients with a prosthetic heart valve or a cardiac implantable electronic device may be challenging since echocardiography can be complicated by shadowing and artefacts in these patients and TEE is an option to overcome these issues. The finding that the PPV was similar for patients with and without a cardiac implantable electronic device and a prosthetic heart valve is important for all future studies in these high-risk populations with poor outcome and a mortality rate between 20 and 40% [Reference Habib8, Reference Habib, Thuny and Avierinos11].
Combining the IE diagnosis code with admission length ⩾2 weeks, our IE algorithm has almost the same high PPV as the diagnosis of myocardial infarction in the DNPR [Reference Madsen12]. Further, the PPV of the IE algorithm seems higher than stroke, however lower than e.g. the diagnoses of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter [Reference Wildenschild13, Reference Rix14].
Our study has limitations. First, the Duke criteria [Reference Habib8] were not assessed formally as part of the confirmation. Second, data collection was only made in one region of Denmark. However, due to the homogeneity of the country, these results are most likely generalisable to other parts of the country [Reference Henriksen9]. Further, our results may be transferable to other countries with similar healthcare structure. Third, our data synthesis is made from 2010 to 2012 and the accuracy of the IE algorithm before and after this period is not clarified in this study.
In conclusion, the IE diagnosis in the DNPR was reliable for patients with admission length ⩾2 weeks and also applied to patients with prosthetic heart valves or cardiac implantable electronic devices.
Acknowledgements
None.
Financial support
None reported.
Conflict of interest
None.





