To the Editor
With great interest, we read the article by Olarinmoye et al. titled ‘Molecular detection of rabies virus strain with N-gene that clustered with China lineage 2 co-circulating with Africa lineages in Monrovia, Liberia: first reported case in Africa’ [Reference Olarinmoye1]. Two technical issues should be considered.
First, the full-length of the nucleoprotein (N) and the glycoprotein (G) gene should get sequenced to perform sequence analysis on the proteins. The replacement of the amino acid in comparison with other rabies viruses should be further investigated.
Second, the result of phylogenetic analysis, ‘the rabies virus (RABV) strain (MF765758) detected clustered with China lineage 2 RABVs of dogs (99% homology to KU963489 and DQ666322)’, is not comprehensive and need further analysis. Based on the partial N gene sequence (MF765758), we Blast it in the NCBI GenBank (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). The partial of 15 nucleoprotein (N, 554-nt) genes retrieved from the NCBI GenBank database. Multiple alignments of sequences were performed using CLUSTAL X 2.1 [Reference Larkin2], and the aligned sequences were used to infer the phylogenetic tree by maximum likelihood (ML) methods using MEGA X [Reference Kumar3]. Apart from the two RABV strains of China lineage 2 (KU963489 and DQ666322), the France RABV strain, CVS (GU992321), the India RABV strains, RAB5 and RAB7 (KF535200 and KF535201), had very close resemblance (99% homology) with Monrovia RABV sequence MH765758. The phylogenetic analysis revealed them to be the same lineage (Fig. 1). China RABV strains KU963489 (or SN2-62-CanineCHINA2005) and DQ666322 (or Jiangsu_Yc63) were not pandemic strains in China [Reference Zhao4]. The phylogenetic analysis would be more comprehensive and accurate if RABV strains from India and France were added.
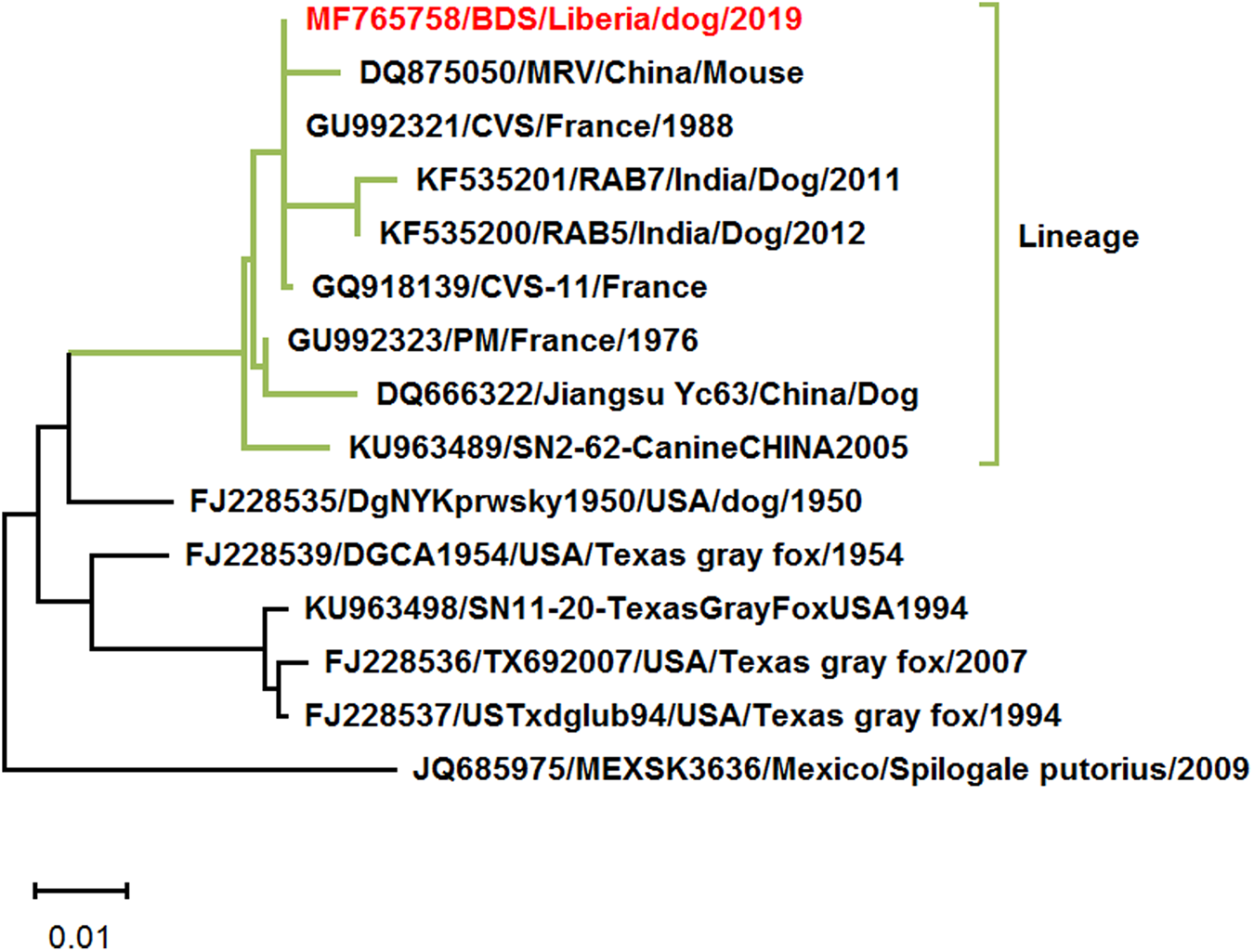
Fig. 1. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree on the partial N gene of rabies viruses. This analysis involved 15 nucleotide sequences. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X.
It is worth noting that the relationship between Liberia strain (MH765758), India strains (KF535200 and KF535201), China strains (KU963489, DQ666322 and DQ875050) and France RABV strains (GU992321 and GQ918139) should be further investigated.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31472176, 31802202) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number 2016YFD0500401).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.



