No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
11. A Brief Discussion on Fu Hao
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 March 2015
Abstract
(N.B. A version of this paper has now been published in Kaogu 1983.6:537-41.)
Fu Hao 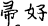 (or Fu Zi
(or Fu Zi 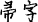 ) appears in the oracle-bone inscriptions from Anyang. The name is often seen in Period I inscriptions (from the time of Wu Ding) and occasionally in Period IV inscriptions (from the time of Wu Yi and Wen Ding). The two are separated by four kings (Zu Geng, Zu Jia, Lin Xin, and Kang Ding), perhaps by as much as one hundred years. Does the Fu Hao in both periods refer to the same person? How can we explain this phenomenon?
) appears in the oracle-bone inscriptions from Anyang. The name is often seen in Period I inscriptions (from the time of Wu Ding) and occasionally in Period IV inscriptions (from the time of Wu Yi and Wen Ding). The two are separated by four kings (Zu Geng, Zu Jia, Lin Xin, and Kang Ding), perhaps by as much as one hundred years. Does the Fu Hao in both periods refer to the same person? How can we explain this phenomenon?
In the oracle-bone records of people and their activities there are cases where one figure is active in different periods. These names are often also place names, and these figures possess a populace and products. These names are probably what is termed “Clan-Territory titles” 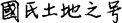 (a term found in the Gu shi kao, as quoted in the “Zheng yi”
(a term found in the Gu shi kao, as quoted in the “Zheng yi”  commentary to the Zuo zhuan
commentary to the Zuo zhuan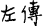 ). Based on their clan name they served hereditarily as officials. These clan names occur in historical literature, as in “In the past, our former kings were for generations Lords of Millet (Hou Ji
). Based on their clan name they served hereditarily as officials. These clan names occur in historical literature, as in “In the past, our former kings were for generations Lords of Millet (Hou Ji 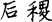 ), serving under the Yü
), serving under the Yü 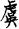 and Xia
and Xia  “(Guo yü
“(Guo yü “Zhou Yü”
“Zhou Yü” 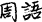 ); or “The Zhong
); or “The Zhong  and Li
and Li 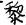 clans generation after generation ordered heaven and earth, … the Sima clan for generation after generation was in charge of the history of Zhou” (Shi ji
clans generation after generation ordered heaven and earth, … the Sima clan for generation after generation was in charge of the history of Zhou” (Shi ji , “Taishigong zixu”
, “Taishigong zixu”  ).
).
- Type
- Session III: Tomb Number Five at Anyang and Fu Zi
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Society for the Study of Early China 1986


