Article contents
The arc space of horospherical varieties and motivic integration
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 June 2013
Abstract
For an arbitrary connected reductive group 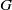 $G$, we consider the motivic integral over the arc space of an arbitrary
$G$, we consider the motivic integral over the arc space of an arbitrary 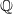 $ \mathbb{Q} $-Gorenstein horospherical
$ \mathbb{Q} $-Gorenstein horospherical 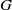 $G$-variety
$G$-variety 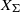 ${X}_{\Sigma } $ associated with a colored fan
${X}_{\Sigma } $ associated with a colored fan 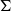 $\Sigma $ and prove a formula for the stringy
$\Sigma $ and prove a formula for the stringy 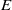 $E$-function of
$E$-function of 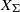 ${X}_{\Sigma } $ which generalizes the one for toric varieties. We remark that, in contrast to toric varieties, the stringy
${X}_{\Sigma } $ which generalizes the one for toric varieties. We remark that, in contrast to toric varieties, the stringy 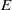 $E$-function of a Gorenstein horospherical variety
$E$-function of a Gorenstein horospherical variety 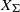 ${X}_{\Sigma } $ may be not a polynomial if some cones in
${X}_{\Sigma } $ may be not a polynomial if some cones in 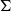 $\Sigma $ have nonempty sets of colors. Using the stringy
$\Sigma $ have nonempty sets of colors. Using the stringy 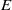 $E$-function, we can formulate and prove a new smoothness criterion for locally factorial horospherical varieties. We expect that this smoothness criterion holds for arbitrary spherical varieties.
$E$-function, we can formulate and prove a new smoothness criterion for locally factorial horospherical varieties. We expect that this smoothness criterion holds for arbitrary spherical varieties.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s) 2013
References
- 10
- Cited by


