Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 January 2016
Suppose k is a positive integer and 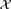 ${\cal X}$ is a k-fold packing of the plane by infinitely many arc-connected compact sets, which means that every point of the plane belongs to at most k sets. Suppose there is a function f(n) = o(n2) with the property that any n members of
${\cal X}$ is a k-fold packing of the plane by infinitely many arc-connected compact sets, which means that every point of the plane belongs to at most k sets. Suppose there is a function f(n) = o(n2) with the property that any n members of 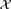 ${\cal X}$ determine at most f(n) holes, which means that the complement of their union has at most f(n) bounded connected components. We use tools from extremal graph theory and the topological Helly theorem to prove that
${\cal X}$ determine at most f(n) holes, which means that the complement of their union has at most f(n) bounded connected components. We use tools from extremal graph theory and the topological Helly theorem to prove that 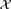 ${\cal X}$ can be decomposed into at most p (1-fold) packings, where p is a constant depending only on k and f.
${\cal X}$ can be decomposed into at most p (1-fold) packings, where p is a constant depending only on k and f.