Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Wolters, Felicitas
Lagaly, Gerhard
Kahr, Guenter
Nueesch, Rolf
and
Emmerich, Katja
2009.
A comprehensive characterization of dioctahedral smectites.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 1,
p.
115.
Galamboš, Michal
Kufčáková, Jana
Rosskopfová, Ol’ga
and
Rajec, Pavol
2010.
Adsorption of cesium and strontium on natrified bentonites.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry,
Vol. 283,
Issue. 3,
p.
803.
Emmerich, Katja
2010.
Advances in the characterization of industrial minerals.
p.
129.
Pentrák, Martin
Madejová, Jana
and
Komadel, Peter
2010.
Effect of chemical composition and swelling on acid dissolution of 2 : 1 clay minerals.
Philosophical Magazine,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 17-18,
p.
2387.
Ertem, Gözen
Steudel, Annett
Emmerich, Katja
Lagaly, Gerhard
and
Schuhmann, Rainer
2010.
Correlation Between the Extent of Catalytic Activity and Charge Density of Montmorillonites.
Astrobiology,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 7,
p.
743.
Moraes, D.S.
Angélica, R.S.
Costa, C.E.F.
Rocha Filho, G.N.
and
Zamian, J.R.
2010.
Mineralogy and chemistry of a new bentonite occurrence in the eastern Amazon region, northern Brazil.
Applied Clay Science,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 3,
p.
475.
Kogure, Toshihiro
and
Drits, Victor A.
2010.
Structural Change in Celadonite and Cis-Vacant Illite by Electron Radiation in Tem.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 4,
p.
522.
Zhu, Yun
Li, Yan
Lu, Anhuai
Wang, Haoran
Yang, Xiaoxue
Wang, Changqiu
Cao, Weizheng
Wang, Qinghua
Zhang, Xiaolei
Pan, Danmei
and
Pan, Xiaohong
2011.
Study of the Interaction Between Bentonite and a Strain of Bacillus Mucilaginosus.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 5,
p.
538.
Ganguly, Saheli
Dana, Kausik
Mukhopadhyay, Tapas Kumar
and
Ghatak, Sankar
2011.
Thermal degradation of alkyl triphenyl phosphonium intercalated montmorillonites.
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,
Vol. 105,
Issue. 1,
p.
199.
Lanson, Bruno
2011.
Layered Mineral Structures and their Application in Advanced Technologies.
p.
151.
Ganguly, Saheli
Dana, Kausik
Mukhopadhyay, Tapas Kumar
and
Ghatak, Sankar
2011.
Simultaneous Intercalation of Two Quaternary Phosphonium Salts Into Montmorillonite.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 1,
p.
13.
Kaufhold, Stephan
Dohrmann, Reiner
Stucki, Joseph W.
and
Anastácio, Alexandre S.
2011.
Layer Charge Density of Smectites — Closing the Gap Between the Structural Formula Method and the Alkyl Ammonium Method.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 2,
p.
200.
Sarkar, Madhuchhanda
Dana, Kausik
and
Ghatak, Sankar
2011.
Evolution of molecular structure and conformation of n-alkylammonium intercalated iron rich bentonites.
Journal of Molecular Structure,
Carrasco, F.
Gámez-Pérez, J.
Santana, O.O.
and
Maspoch, M.Ll.
2011.
Processing of poly(lactic acid)/organomontmorillonite nanocomposites: Microstructure, thermal stability and kinetics of the thermal decomposition.
Chemical Engineering Journal,
Vol. 178,
Issue. ,
p.
451.
Liu, Dong
Yuan, Peng
Liu, Hongmei
Cai, Jingong
Qin, Zonghua
Tan, Daoyong
Zhou, Qing
He, Hongping
and
Zhu, Jianxi
2011.
Influence of heating on the solid acidity of montmorillonite: A combined study by DRIFT and Hammett indicators.
Applied Clay Science,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 4,
p.
358.
Christidis, George E.
2011.
Layered Mineral Structures and their Application in Advanced
Technologies.
p.
237.
Bergaya, Faïza
Jaber, Maguy
and
Lambert, Jean‐François
2011.
Rubber‐Clay Nanocomposites.
p.
1.
Guerra, Denis L.
Silva, Weber L.L.
Oliveira, Helen C.P.
Viana, Rúbia R.
and
Airoldi, Claudio
2011.
Organofunctionalized Amazon smectite for dye removal from aqueous medium—Kinetic and thermodynamic adsorption investigations.
Journal of Hazardous Materials,
Vol. 186,
Issue. 1,
p.
675.
Vidal, Nuria
and
Volzone, Cristina
2012.
Influence of organobentonite structure on toluene adsorption from water solution.
Materials Research,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 6,
p.
944.
Joshi, Ghanshyam V.
Kevadiya, Bhavesh D.
Mody, Haresh M.
and
Bajaj, Hari C.
2012.
Confinement and controlled release of quinine on chitosan–montmorillonite bionanocomposites.
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 3,
p.
423.
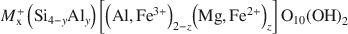 where x = ξ = 0.2–0.6, x = y+z, and y≪z, vary widely in composition and structure. The commonly used classification into five montmorillonite and two beidellite groups for the solid-solution sequence does not allow an unambiguous classification with respect to structural features and the resulting properties.
where x = ξ = 0.2–0.6, x = y+z, and y≪z, vary widely in composition and structure. The commonly used classification into five montmorillonite and two beidellite groups for the solid-solution sequence does not allow an unambiguous classification with respect to structural features and the resulting properties.