Case report
A female newborn (3190 g) was transferred to our department on continuous infusion of prostaglandin on the 3rd day of life with prenatally diagnosed univentricular CHD with duct-dependent pulmonary circulation. On admission, the patient presented with moderate overall condition, tachypnoea, tachycardia, and percutaneous oxygen saturations above 90%. Transthoracic echocardiography confirmed the initial diagnosis of dextrocardia, single ventricle with double outlet, and subvalvular stenosis of the pulmonary artery. Additionally, imaging revealed an interrupted inferior vena cava with a continuation through the hemiazygos vein to the left superior vena cava, a left aortic arch, and a tortuous right-sided ductus arteriosus supplying pulmonary circulation (Supplementary Figure 1A). Further, there was suspicion of partial anomalous pulmonary venous drainage from the left pulmonary veins into the left superior vena cava without restriction, possibly with communication to the left atrium (Supplementary Figure 1(b) and (c)). Clinical presentation, along with echocardiographic evidence of moderate interatrial restriction (mean pressure gradient of 5 mmHg) and signs of pulmonary congestion on X-ray, suggested inadequate interatrial connection (Supplementary Figure 1D).
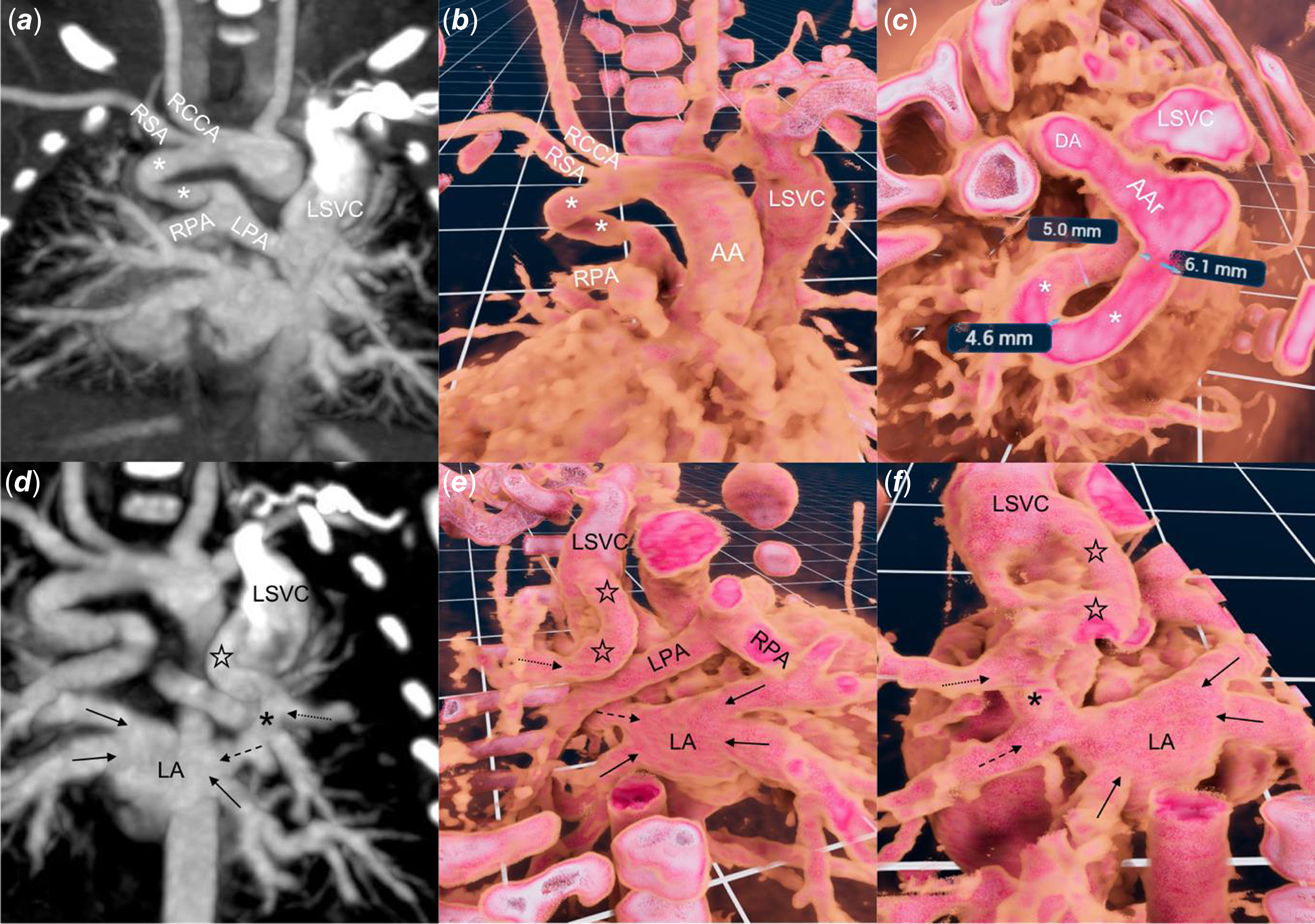
Figure 1. Standard two-dimensional ( a, d ) CT and three-dimensional ( b, c, e, f ) reconstruction with virtual reality software (VMersive, VR—Learning, Warsaw, Poland). ( a, b ) a right sided, tortuous and narrowed at the pulmonary end of ductus arteriosus (white asterix) supplies native pulmonary arteries. ( c ) wide along most of its length ductus arteriosus takes a 180° turn. ( d, e, f ) a vertical vein (black stars) joins the left superior vena cava and the left upper pulmonary vein (dotted arrow), which than, anterior to the right pulmonary artery, connects (black asterix) with the left middle pulmonary vein (dashed arrow) and together with three remaining veins (black arrows) drain to the left atrium. AA = Ascending aorta, AAr = Aortic Arch, LPA = Left Pulmonary Artery, RCCA = Right Common Carotid Artery, RSA = Right Subclavian Artery.
In view of the complex anatomy, a contrast CT was performed to plan the initial stage of palliation (Figure 1(a) and (d)). A three-dimensional dataset was analysed in virtual reality using dedicated software (VMersive, Warsaw, Poland). The imaging confirmed a left-sided aortic arch with a right-sided ductus arteriosus that narrowed at the pulmonary end (Figure 1(b) and (c); Supplementary Video 1). The left superior pulmonary vein drained into the vertical vein, which had a connection with the left superior vena cava and continued into the left atrium through the left middle pulmonary vein. (Figure 1(e) and (f); Supplementary Video 1). After a multidisciplinary discussion, we opted for percutaneous first-stage palliation, enlargement of the atrial communication, and stenting of the ductus arteriosus, to offer a less invasive approach (excluding sternotomy and cardiopulmonary bypass) suitable for a fragile newborn.
Under general anaesthesia and guided by ultrasound, vascular access was obtained through the left internal jugular vein and the right femoral artery. A 4 Fr angiographic catheter was advanced through the ductus arteriosus to the left pulmonary artery. Angiography in the late venous phase revealed an unobstructed anomalous pulmonary vein drainage from the left upper pulmonary vein to the left superior vena cava, with faint contrast flow between the left upper and middle veins with the latter emptying into the left atrium (Figure 2(a), Supplementary Video 1). Subsequently, hand contrast injections in the vertical vein and the upper and lower pulmonary veins were performed (Figure 2(b), (c) and (d)). Over a 0.014” floppy wire, a catheter was advanced from the left superior vena cava, through the vertical vein, to the left atrium and oriented towards the narrow interatrial communication (Figure 2(e)). Using transthoracic echocardiography and fluoroscopy guidance, the restrictive interatrial communication was crossed downstream and static atrial septoplasty using a 10 x 30 mm Tyshak II balloon (NuMed) was performed. The catheter was inflated twice, with a clear indentation on the first attempt and full expansion during the second (Figure 2(f), Supplementary Figure 1E, Supplementary Video 1). Haemodynamic measurements showed a mean left atrial pressure of 8 mmHg, with a mean gradient across the atrial septum of 1 mmHg. Transthoracic echocardiography confirmed unrestrictive flow through the interatrial communication (Supplementary Figure 1F).
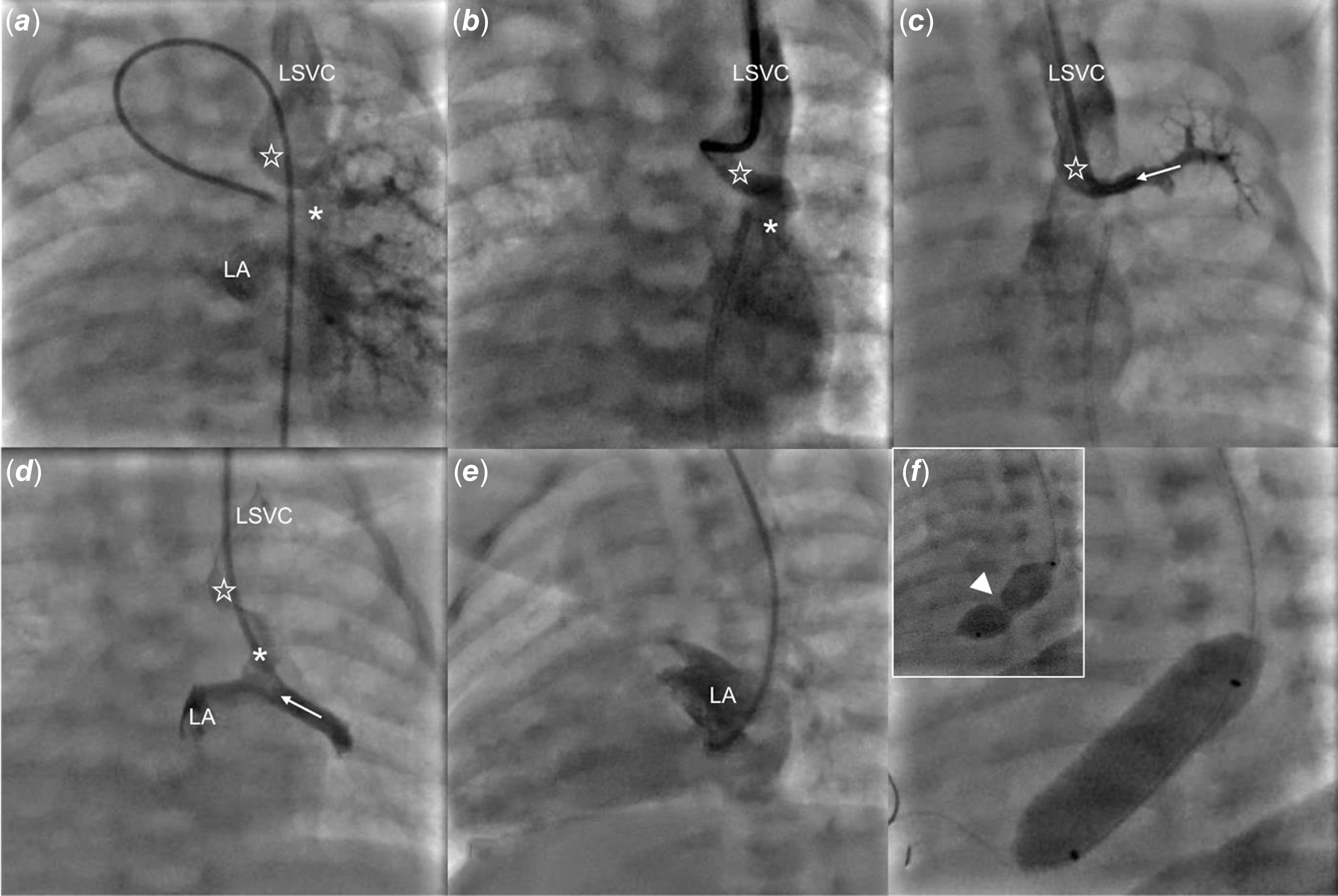
Figure 2. Percutaneous static balloon atrialseptoplasty. ( a ) a late phase of angiography from the left pulmonary artery shows contrast return from the left lung to the left superior vena cava (LSVC) via a vertical vein (empty star) and to the left atrium (LA). ( b ) a hand contrast injection to the vertical vein (empty star) through a catheter advanced from the LSVC. ( c ) angiography from the left upper pulmonary vein (white dotted arrow) shows contrast return via the vertical vein (empty star) to the LSVC. ( d ) an angiography through the catheter advanced further through a connection (asterix) between the left upper and middle (white arrow) veins shows simultaneous contrast flow to the left atrium and LSVC. ( e ) an angiography from the LA with minimal flow across the inter-atrial septum to the right atrium. ( f ) arrowhead points to the indentation on the balloon catheter at the beginning of inflation that vanished with complete balloon expansion.
Subsequently, two Onyx stents (5 × 26 mm and 5 × 12 mm; Medtronic, Warsaw) were successfully implanted through a 5/6 Fr sheath into the long, tortuous ductus arteriosus, starting from the pulmonary end. The procedure was completed without complications. Heparin infusion administered for 24 hours was switched to aspirin. A control chest X-ray revealed moderately increased, symmetrical pulmonary artery flow, leading to transient infusion of dopamine (5 μg/kg/min). Transthoracic echocardiography showed laminar flow across the interatrial communication, a mean gradient of 2 mmHg, good systemic ventricular contractility, and unobstructed flow through the stented ductus arteriosus (Supplementary Video 1).
The patient was extubated on the second day post-intervention, and enteral feeding was initiated and well-tolerated by the patient. On the third day after the procedure, the patient was transferred from the ICU to the cardiology ward. Over the subsequent days, we managed pulmonary over-circulation with intravenous and later oral medications. In the second week of observation, the patient was discharged with a weight of 3690 g and, percutaneous oxygen saturations ranging from 86 to 92%.
Discussion
Patients with heterotaxy syndrome, single ventricular physiology, and anomalies of pulmonary venous return face high early surgical mortality and poor long-term outcomes. Reference Agarwal, Varghese, Jesudian and Moses1 Single ventricle circulation with a restrictive interatrial septum carries significant mortality and morbidity risks without adequate decompression. Reference Moszura, Dryżek and Góreczny2,Reference Gossett, Rocchini, Lloyd and Graziano3 Transcatheter interventions offer the advantage of delaying surgical repair beyond the fragile newborn period when patients and cardiovascular structures are larger.
Balloon atrial septoplasty is the preferred method for addressing restrictive atrial communication, and eliminating the need for cardiopulmonary bypass. Reference Moszura, Góreczny and Dryżek4 Accessing the atrial septum via the jugular vein is challenging due to its anatomical orientation. This procedure is typically performed via femoral or umbilical venous access. In cases where femoral access is not feasible, transhepatic puncture or azygos vein access, especially in the presence of an interrupted inferior vena cava, can be considered. Reference Beyazal and Orun5,Reference Neves, Ferreiro, Fontes and Pedra6 Balloon atrial septoplasty through the azygos vein has been documented in two left isomerism cases. Reference Beyazal and Orun5 The transjugular approach for atrial communication dilatation, especially in newborns, is infrequent, with only one reported case in a newborn and two described in infants with less complex defects. Reference Padhi, Bakshi and Londhe7–Reference Mackie, Aiyagari and Zampi9
Accurate imaging is paramount in complex cases. CT scans processed into a virtual reality three-dimensional model offer precise anatomical visualisation and facilitate intervention simulation, which has the potential to enhance procedural planning. Reference Szeliga, Kołcz, Piwowarczyk and Góreczny10 This innovative approach played a pivotal role in ensuring a smoother procedure, aiding in the anticipation of the challenging catheter course and ultimately contributing to the success of the intervention.
In our case, the presence of a vein connecting the left pulmonary veins to the superior vena cava and the left atrium allowed for straightforward crossing of the restrictive interatrial communication downstream from the left atrium to the right atrium, and provided stable support for the balloon during the procedure. To minimise the risk of damaging pulmonary veins or the left superior vena cava during catheter pullback, we opted for a static balloon dilatation of the communication.
While there is one report of a similar approach, to our knowledge this is the first example of utilisation of jugular venous access for atrial septoplasty in a newborn with such a complex cardiac anomaly Reference Neves, Ferreiro, Fontes and Pedra6 . This procedure, in our opinion, would not have been as easily achievable without the integration of multi-modal imaging, particularly three-dimensional VR modelling, in the pre-procedure planning.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047951123004341.
Acknowledgements
To Anna Grondalski from the Pomeranian Medical University of Szczecin for editing the text.
Financial support
Virtual Reality project is supported by the Jagiellonian University Medical College internal grant No. N41/DBS/001219.
Competing interests
None.
Ethical Standards
The research does not involve human experimentation.





