No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 March 2025
In this article, the authors consider the boundedness on Triebel–Lizorkin spaces for the d-dimensional Calderón commutator defined by 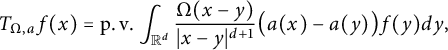 $$ \begin{align*}T_{\Omega,a}f(x)=\mathrm{p.\,v.}\int_{\mathbb{R}^d}\frac{\Omega(x-y)}{|x-y|^{d+1}}\big(a(x)-a(y)\big)f(y){d}y,\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}T_{\Omega,a}f(x)=\mathrm{p.\,v.}\int_{\mathbb{R}^d}\frac{\Omega(x-y)}{|x-y|^{d+1}}\big(a(x)-a(y)\big)f(y){d}y,\end{align*} $$ $\Omega $ is homogeneous of degree zero, integrable on
$\Omega $ is homogeneous of degree zero, integrable on 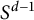 $S^{d-1}$ and has a vanishing moment of order one, a is a Lipschitz function on
$S^{d-1}$ and has a vanishing moment of order one, a is a Lipschitz function on 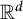 $\mathbb {R}^d$. The authors proved that if
$\mathbb {R}^d$. The authors proved that if 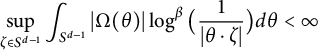 $$ \begin{align*}\sup_{\zeta\in S^{d-1}}\int_{S^{d-1}}|\Omega(\theta)|\log ^{\beta} \big(\frac{1}{|\theta\cdot\zeta|}\big)d\theta<\infty\end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*}\sup_{\zeta\in S^{d-1}}\int_{S^{d-1}}|\Omega(\theta)|\log ^{\beta} \big(\frac{1}{|\theta\cdot\zeta|}\big)d\theta<\infty\end{align*} $$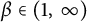 $\beta \in (1,\,\infty )$, then
$\beta \in (1,\,\infty )$, then 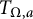 $T_{\Omega ,a}$ is bounded on Triebel–Lizorkin spaces
$T_{\Omega ,a}$ is bounded on Triebel–Lizorkin spaces 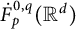 $\dot {F}_{p}^{0,q}(\mathbb {R}^d)$ for
$\dot {F}_{p}^{0,q}(\mathbb {R}^d)$ for 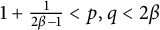 $1+\frac {1}{2\beta -1}<p,q<2\beta $.
$1+\frac {1}{2\beta -1}<p,q<2\beta $.
The research was supported by the NNSF of China under grants #12271483, #11971295, and #11771399.