Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Let 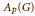 ${{A}_{p}}\left( G \right)$ be the Figa-Talamanca, Herz Banach Algebra on
${{A}_{p}}\left( G \right)$ be the Figa-Talamanca, Herz Banach Algebra on  $G$; thus
$G$; thus 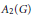 ${{A}_{2}}\left( G \right)$ is the Fourier algebra. Strong Ditkin
${{A}_{2}}\left( G \right)$ is the Fourier algebra. Strong Ditkin 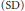 $\left( \text{SD} \right)$ and Extremely Strong Ditkin
$\left( \text{SD} \right)$ and Extremely Strong Ditkin 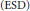 $\left( \text{ESD} \right)$ sets for the Banach algebras
$\left( \text{ESD} \right)$ sets for the Banach algebras 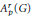 $A_{P}^{r}\left( G \right)$ are investigated for abelian and nonabelian locally compact groups
$A_{P}^{r}\left( G \right)$ are investigated for abelian and nonabelian locally compact groups  $G$. It is shown that
$G$. It is shown that 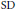 $\text{SD}$ and
$\text{SD}$ and 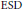 $\text{ESD}$ sets for
$\text{ESD}$ sets for 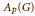 ${{A}_{p}}\left( G \right)$ remain
${{A}_{p}}\left( G \right)$ remain 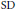 $\text{SD}$ and
$\text{SD}$ and 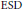 $\text{ESD}$ sets for
$\text{ESD}$ sets for 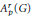 $A_{P}^{r}\left( G \right)$, with strict inclusion for
$A_{P}^{r}\left( G \right)$, with strict inclusion for 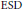 $\text{ESD}$ sets. The case for the strict inclusion of
$\text{ESD}$ sets. The case for the strict inclusion of 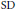 $\text{SD}$ sets is left open.
$\text{SD}$ sets is left open.
A result on the weak sequential completeness of 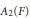 ${{A}_{2}}\left( F \right)$ for
${{A}_{2}}\left( F \right)$ for 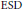 $\text{ESD}$ sets
$\text{ESD}$ sets  $F$ is proved and used to show that Varopoulos, Helson, and Sidon sets are not
$F$ is proved and used to show that Varopoulos, Helson, and Sidon sets are not 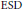 $\text{ESD}$ sets for
$\text{ESD}$ sets for 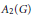 ${{A}_{2}}\left( G \right)$, yet they are such for
${{A}_{2}}\left( G \right)$, yet they are such for 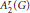 $A_{2}^{r}\left( G \right)$ for discrete groups
$A_{2}^{r}\left( G \right)$ for discrete groups  $G$, for any
$G$, for any 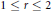 $1\,\le \,r\,\le \,2$.
$1\,\le \,r\,\le \,2$.
A result is given on the equivalence of the sequential and the net definitions of 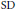 $\text{SD}$ or
$\text{SD}$ or 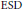 $\text{ESD}$ sets for
$\text{ESD}$ sets for  $\sigma $-compact groups.
$\sigma $-compact groups.
The above results are new even if  $G$ is abelian.
$G$ is abelian.