Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
We prove a nonvanishing result for families of 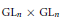 $\text{G}{{\text{L}}_{n}}\times \text{G}{{\text{L}}_{n}}$ Rankin–Selberg
$\text{G}{{\text{L}}_{n}}\times \text{G}{{\text{L}}_{n}}$ Rankin–Selberg 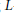 $L$-functions in the critical strip, as one factor runs over twists by Hecke characters. As an application, we simplify the proof, due to Luo, Rudnick, and Sarnak, of the best known bounds towards the Generalized Ramanujan Conjecture at the infinite places for cusp forms on
$L$-functions in the critical strip, as one factor runs over twists by Hecke characters. As an application, we simplify the proof, due to Luo, Rudnick, and Sarnak, of the best known bounds towards the Generalized Ramanujan Conjecture at the infinite places for cusp forms on 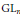 $\text{G}{{\text{L}}_{n}}$. A key ingredient is the regularization of the units in residue classes by the use of an Arakelov ray class group.
$\text{G}{{\text{L}}_{n}}$. A key ingredient is the regularization of the units in residue classes by the use of an Arakelov ray class group.