Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Let ℝ denote the real line. Let {Tt}tєℝ be a measure preserving ergodic flow on a non atomic finite measure space (X, ℱ, μ). A nonnegative function φ on ℝ is called a weight function if ∫ℝ φ(t)dt = 1. Consider the weighted ergodic averages
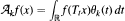
of a function f X —> ℝ, where {θk} is a sequence of weight functions. Some sufficient and some necessary and sufficient conditions are given for the a.e. convergence of Akf, in particular for a special case in which
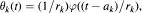
where φ is a fixed weight function and {(ak, rk)} is a sequence of pairs of real numbers such that rk > 0 for all k. These conditions are obtained by a combination of the methods of Bellow-Jones-Rosenblatt, developed to deal with moving ergodic averages, and the methods of Broise-Déniel-Derriennic, developed to deal with unbounded weight functions.