Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Every norm  $\mathcal{V}$ on
$\mathcal{V}$ on 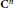 ${{\text{C}}^{\text{n}}}$ induces two norm numerical ranges on the algebra
${{\text{C}}^{\text{n}}}$ induces two norm numerical ranges on the algebra 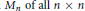 ${{M}_{n}}\,\text{of}\,\text{all}\,\text{n}\,\times \,\text{n}$ complex matrices, the spatial numerical range
${{M}_{n}}\,\text{of}\,\text{all}\,\text{n}\,\times \,\text{n}$ complex matrices, the spatial numerical range
 $$W\left( A \right)=\left\{ {{x}^{*}}Ay:x,y\in {{\text{C}}^{n}},{{v}^{D}}\left( x \right)=v\left( y \right)={{x}^{*}}y=1 \right\},$$
$$W\left( A \right)=\left\{ {{x}^{*}}Ay:x,y\in {{\text{C}}^{n}},{{v}^{D}}\left( x \right)=v\left( y \right)={{x}^{*}}y=1 \right\},$$
where  ${{\mathcal{V}}^{D}}$ is the norm dual to
${{\mathcal{V}}^{D}}$ is the norm dual to  $\mathcal{V}$, and the algebra numerical range
$\mathcal{V}$, and the algebra numerical range
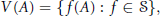 $$V\left( A \right)=\left\{ f\left( A \right):f\in S \right\},$$
$$V\left( A \right)=\left\{ f\left( A \right):f\in S \right\},$$
where  $S$ is the set of states on the normed algebra
$S$ is the set of states on the normed algebra 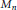 ${{M}_{n}}$ under the operator norm induced by
${{M}_{n}}$ under the operator norm induced by  $\mathcal{V}$. For a symmetric norm
$\mathcal{V}$. For a symmetric norm  $\mathcal{V}$, we identify all linear maps on
$\mathcal{V}$, we identify all linear maps on 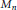 ${{M}_{n}}$ that preserve either one of the two norm numerical ranges or the set of states or vector states. We also identify the numerical radius isometries, i.e., linear maps that preserve the (one) numerical radius induced by either numerical range. In particular, it is shown that if
${{M}_{n}}$ that preserve either one of the two norm numerical ranges or the set of states or vector states. We also identify the numerical radius isometries, i.e., linear maps that preserve the (one) numerical radius induced by either numerical range. In particular, it is shown that if  $\mathcal{V}$ is not the
$\mathcal{V}$ is not the 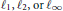 ${{\ell }_{1}},{{\ell }_{2}},\,\text{or}\,{{\ell }_{\infty }}$ norms, then the linear maps that preserve either numerical range or either set of states are “inner”, i.e., of the form
${{\ell }_{1}},{{\ell }_{2}},\,\text{or}\,{{\ell }_{\infty }}$ norms, then the linear maps that preserve either numerical range or either set of states are “inner”, i.e., of the form 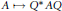 $A\mapsto {{Q}^{*}}AQ$, where
$A\mapsto {{Q}^{*}}AQ$, where 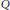 $Q$ is a product of a diagonal unitary matrix and a permutation matrix and the numerical radius isometries are unimodular scalar multiples of such inner maps. For the
$Q$ is a product of a diagonal unitary matrix and a permutation matrix and the numerical radius isometries are unimodular scalar multiples of such inner maps. For the 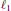 ${{\ell }_{1}}$ and the
${{\ell }_{1}}$ and the 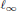 ${{\ell }_{\infty }}$ norms, the results are quite different.
${{\ell }_{\infty }}$ norms, the results are quite different.