No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Given a matrix 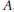 $A$, let
$A$, let 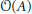 $\mathcal{O}\left( A \right)$ denote the orbit of
$\mathcal{O}\left( A \right)$ denote the orbit of 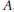 $A$ under a certain group action such as
$A$ under a certain group action such as
(1)  $U\left( m \right)\,\otimes U\left( n \right)$ acting on
$U\left( m \right)\,\otimes U\left( n \right)$ acting on 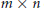 $m\,\times \,n$ complex matrices
$m\,\times \,n$ complex matrices 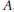 $A$ by
$A$ by 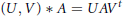 $(U,\,V)\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{V}^{t}}$,
$(U,\,V)\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{V}^{t}}$,
(2)  $O\left( m \right)\otimes O\left( n \right)$ or
$O\left( m \right)\otimes O\left( n \right)$ or 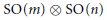 $\text{SO(}m\text{)}\,\otimes \,\text{SO(}n\text{)}$ acting on
$\text{SO(}m\text{)}\,\otimes \,\text{SO(}n\text{)}$ acting on 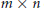 $m\,\times \,n$ real matrices
$m\,\times \,n$ real matrices 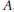 $A$ by
$A$ by 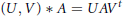 $(U,\,V)\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{V}^{t}}$,
$(U,\,V)\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{V}^{t}}$,
(3) 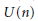 $U(n)$ acting on
$U(n)$ acting on 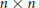 $n\,\times \,n$ complex symmetric or skew-symmetric matrices
$n\,\times \,n$ complex symmetric or skew-symmetric matrices 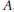 $A$ by
$A$ by 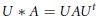 $U\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{U}^{t}}$,
$U\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{U}^{t}}$,
(4) 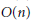 $O(n)$ or
$O(n)$ or 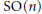 $\text{SO(n)}$ acting on
$\text{SO(n)}$ acting on 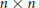 $n\,\times \,n$ real symmetric or skew-symmetric matrices
$n\,\times \,n$ real symmetric or skew-symmetric matrices 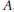 $A$ by
$A$ by 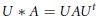 $U\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{U}^{t}}$.
$U\,*\,A\,=\,UA{{U}^{t}}$.
Denote by
1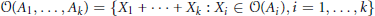 $$\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})\,=\,\{{{X}_{1\,}}+\cdot \cdot \cdot +\,{{X}_{k}}\,:\,{{X}_{i}}\,\in \,\mathcal{O}({{A}_{i}}),i\,=\,1,\ldots ,k\}$$
$$\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})\,=\,\{{{X}_{1\,}}+\cdot \cdot \cdot +\,{{X}_{k}}\,:\,{{X}_{i}}\,\in \,\mathcal{O}({{A}_{i}}),i\,=\,1,\ldots ,k\}$$
the joint orbit of the matrices 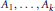 ${{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}}$. We study the set of diagonals or partial diagonals of matrices in
${{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}}$. We study the set of diagonals or partial diagonals of matrices in 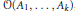 $\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})$, i.e., the set of vectors
$\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})$, i.e., the set of vectors 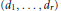 $({{d}_{1}},\ldots {{d}_{r}})$ whose entries lie in the
$({{d}_{1}},\ldots {{d}_{r}})$ whose entries lie in the 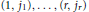 $(1,\,{{j}_{1}}),\ldots ,(r,\,{{j}_{r}})$ positions of a matrix in
$(1,\,{{j}_{1}}),\ldots ,(r,\,{{j}_{r}})$ positions of a matrix in 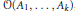 $\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})$ for some distinct column indices
$\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})$ for some distinct column indices 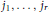 ${{j}_{1}},\ldots ,{{j}_{r}}$. In many cases, complete description of these sets is given in terms of the inequalities involving the singular values of
${{j}_{1}},\ldots ,{{j}_{r}}$. In many cases, complete description of these sets is given in terms of the inequalities involving the singular values of 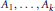 ${{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}}$. We also characterize those extreme matrices for which the equality cases hold. Furthermore, some convexity properties of the joint orbits are considered. These extend many classical results on matrix inequalities, and answer some questions by Miranda. Related results on the joint orbit
${{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}}$. We also characterize those extreme matrices for which the equality cases hold. Furthermore, some convexity properties of the joint orbits are considered. These extend many classical results on matrix inequalities, and answer some questions by Miranda. Related results on the joint orbit 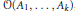 $\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})$ of complex Hermitian matrices under the action of unitary similarities are also discussed.
$\mathcal{O}({{A}_{1}},\ldots ,{{A}_{k}})$ of complex Hermitian matrices under the action of unitary similarities are also discussed.