Article contents
Decomposability of von Neumann Algebras and the Mazur Property of Higher Level
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
The decomposability number of a von Neumann algebra 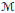 $\mathcal{M}$ (denoted by
$\mathcal{M}$ (denoted by 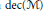 $\text{dec}\left( \mathcal{M} \right)$) is the greatest cardinality of a family of pairwise orthogonal non-zero projections in
$\text{dec}\left( \mathcal{M} \right)$) is the greatest cardinality of a family of pairwise orthogonal non-zero projections in 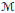 $\mathcal{M}$. In this paper, we explore the close connection between
$\mathcal{M}$. In this paper, we explore the close connection between 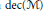 $\text{dec}\left( \mathcal{M} \right)$ and the cardinal level of the Mazur property for the predual
$\text{dec}\left( \mathcal{M} \right)$ and the cardinal level of the Mazur property for the predual 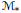 ${{\mathcal{M}}_{*}}$ of
${{\mathcal{M}}_{*}}$ of 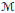 $\mathcal{M}$, the study of which was initiated by the second author. Here, our main focus is on those von Neumann algebras whose preduals constitute such important Banach algebras on a locally compact group
$\mathcal{M}$, the study of which was initiated by the second author. Here, our main focus is on those von Neumann algebras whose preduals constitute such important Banach algebras on a locally compact group 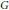 $G$ as the group algebra
$G$ as the group algebra 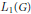 ${{L}_{1}}(G)$, the Fourier algebra
${{L}_{1}}(G)$, the Fourier algebra 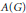 $A(G)$, the measure algebra
$A(G)$, the measure algebra 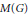 $M(G)$, the algebra
$M(G)$, the algebra 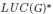 $LUC{{(G)}^{*}}$, etc. We show that for any of these von Neumann algebras, say
$LUC{{(G)}^{*}}$, etc. We show that for any of these von Neumann algebras, say 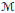 $\mathcal{M}$, the cardinal number dec
$\mathcal{M}$, the cardinal number dec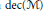 $(\mathcal{M})$ and a certain cardinal level of the Mazur property of
$(\mathcal{M})$ and a certain cardinal level of the Mazur property of 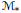 ${{\mathcal{M}}_{*}}$ are completely encoded in the underlying group structure. In fact, they can be expressed precisely by two dual cardinal invariants of
${{\mathcal{M}}_{*}}$ are completely encoded in the underlying group structure. In fact, they can be expressed precisely by two dual cardinal invariants of 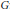 $G$: the compact covering number
$G$: the compact covering number 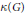 $\kappa (G)$ of
$\kappa (G)$ of 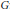 $G$ and the least cardinality
$G$ and the least cardinality 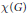 $\mathcal{X}(G)$ of an open basis at the identity of
$\mathcal{X}(G)$ of an open basis at the identity of 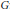 $G$. We also present an application of the Mazur property of higher level to the topological centre problem for the Banach algebra
$G$. We also present an application of the Mazur property of higher level to the topological centre problem for the Banach algebra 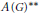 $A{{(G)}^{**}}$.
$A{{(G)}^{**}}$.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2006
References
- 10
- Cited by


