Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 September 2013
Let 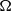 $\Omega $ be the set of unit vectors and
$\Omega $ be the set of unit vectors and 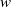 $w$ be a radial weight on the plane. We consider the weighted directional maximal operator defined by
$w$ be a radial weight on the plane. We consider the weighted directional maximal operator defined by 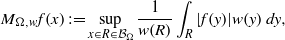 $$\begin{eqnarray*}{M}_{\Omega , w} f(x): = \sup _{x\in R\in \mathcal{B} _{\Omega }}\frac{1}{w(R)} \int \nolimits \nolimits_{R} \vert f(y)\vert w(y)\hspace{0.167em} dy,\end{eqnarray*}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray*}{M}_{\Omega , w} f(x): = \sup _{x\in R\in \mathcal{B} _{\Omega }}\frac{1}{w(R)} \int \nolimits \nolimits_{R} \vert f(y)\vert w(y)\hspace{0.167em} dy,\end{eqnarray*}$$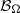 ${ \mathcal{B} }_{\Omega } $ denotes the set of all rectangles on the plane whose longest side is parallel to some unit vector in
${ \mathcal{B} }_{\Omega } $ denotes the set of all rectangles on the plane whose longest side is parallel to some unit vector in 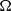 $\Omega $ and
$\Omega $ and 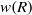 $w(R)$ denotes
$w(R)$ denotes 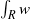 $\int \nolimits \nolimits_{R} w$. In this paper we prove an almost-orthogonality principle for this maximal operator under certain conditions on the weight. The condition allows us to get the weighted norm inequality
$\int \nolimits \nolimits_{R} w$. In this paper we prove an almost-orthogonality principle for this maximal operator under certain conditions on the weight. The condition allows us to get the weighted norm inequality 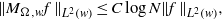 $$\begin{eqnarray*}\Vert {M}_{\Omega , w} f\mathop{\Vert }\nolimits_{{L}^{2} (w)} \leq C\log N\Vert f\mathop{\Vert }\nolimits_{{L}^{2} (w)} ,\end{eqnarray*}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray*}\Vert {M}_{\Omega , w} f\mathop{\Vert }\nolimits_{{L}^{2} (w)} \leq C\log N\Vert f\mathop{\Vert }\nolimits_{{L}^{2} (w)} ,\end{eqnarray*}$$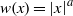 $w(x)= \vert x\hspace{-1.2pt}\mathop{\vert }\nolimits ^{a} $,
$w(x)= \vert x\hspace{-1.2pt}\mathop{\vert }\nolimits ^{a} $, 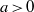 $a\gt 0$, and when
$a\gt 0$, and when 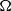 $\Omega $ is the set of unit vectors on the plane with cardinality
$\Omega $ is the set of unit vectors on the plane with cardinality 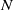 $N$ sufficiently large.
$N$ sufficiently large.