Article contents
On the Complexity of the Classification Problem for Torsion-Free Abelian Groups of Finite Rank
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 January 2014
Extract
In this paper, we shall discuss some recent contributions to the project [15, 14, 2, 18, 22, 23] of explaining why no satisfactory system of complete invariants has yet been found for the torsion-free abelian groups of finite rank n ≥ 2. Recall that, up to isomorphism, the torsion-free abelian groups of rank n are exactly the additive subgroups of the n-dimensional vector space ℚn which contain n linearly independent elements. Thus the collection of torsion-free abelian groups of rank at most n can be naturally identified with the set S (ℚn) of all nontrivial additive subgroups of ℚn. In 1937, Baer [4] solved the classification problem for the class S(ℚ)of rank 1 groups as follows.
Let ℙ be the set of primes. If G is a torsion-free abelian group and 0 ≠ x ϵ G, then the p-height of x is defined to be
hx(p) = sup{n ϵ ℕ ∣ There exists y ϵ G such that pny = x} ϵ ℕ ∪{∞}; and the characteristic χ (x) of x is defined to be the function
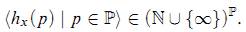
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Association for Symbolic Logic 2001
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by


