Original Articles
The Coccidae of South Africa–iv.*
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 95-128
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mosquito Notes
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 129-137
-
- Article
- Export citation
On some African Delphacidae (Homoptera)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 139-144
-
- Article
- Export citation
Insects Injurious to Economic Crops in the Zanzibar Protectorate
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 145-155
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the Use of Experimental Plots when studying Forest Insects
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 157-160
-
- Article
- Export citation
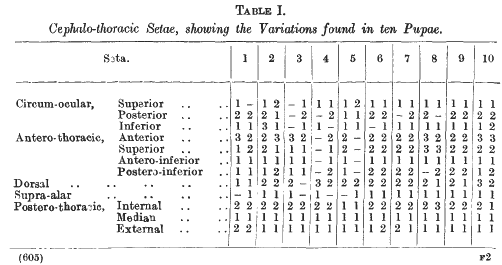
The Chaetotaxy of the Pupa of Stegomyia fasciata
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 161-169
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new Hispid Beetle injurious to the Oil Palm in the Gold Coast
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 171-174
-
- Article
- Export citation
Observations on Scale-Insects (Coccidae).—VI
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 175-207
-
- Article
- Export citation
Miscellaneous
Collections received
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. 209-210
-
- Article
- Export citation
Front matter
BER volume 10 issue 2 Cover, Front matter and Errata
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2009, pp. f1-f8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation