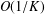 $O(1/K)$ CONVERGENCE RATE OF THE ALTERNATING DIRECTION METHOD OF MULTIPLIERS IN A COMPLEX DOMAIN
$O(1/K)$ CONVERGENCE RATE OF THE ALTERNATING DIRECTION METHOD OF MULTIPLIERS IN A COMPLEX DOMAINPublished online by Cambridge University Press: 30 August 2018
We focus on the convergence rate of the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) in a complex domain. First, the complex form of variational inequality (VI) is established by using the Wirtinger calculus technique. Second, the 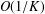 $O(1/K)$ convergence rate of the ADMM in a complex domain is provided. Third, the ADMM in a complex domain is applied to the least absolute shrinkage and selectionator operator (LASSO). Finally, numerical simulations are provided to show that ADMM in a complex domain has the
$O(1/K)$ convergence rate of the ADMM in a complex domain is provided. Third, the ADMM in a complex domain is applied to the least absolute shrinkage and selectionator operator (LASSO). Finally, numerical simulations are provided to show that ADMM in a complex domain has the 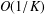 $O(1/K)$ convergence rate and that it has certain advantages compared with the ADMM in a real domain.
$O(1/K)$ convergence rate and that it has certain advantages compared with the ADMM in a real domain.