Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 January 2019
We study the problem of choosing the best subset of 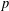 $p$ features in linear regression, given
$p$ features in linear regression, given  $n$ observations. This problem naturally contains two objective functions including minimizing the amount of bias and minimizing the number of predictors. The existing approaches transform the problem into a single-objective optimization problem. We explain the main weaknesses of existing approaches and, to overcome their drawbacks, we propose a bi-objective mixed integer linear programming approach. A computational study shows the efficacy of the proposed approach.
$n$ observations. This problem naturally contains two objective functions including minimizing the amount of bias and minimizing the number of predictors. The existing approaches transform the problem into a single-objective optimization problem. We explain the main weaknesses of existing approaches and, to overcome their drawbacks, we propose a bi-objective mixed integer linear programming approach. A computational study shows the efficacy of the proposed approach.