Introduction
Predicting the future evolution of the West Antarctic ice sheet (WAIS) is an area of active research with global implications. While local changes in flow behavior have regional effects on ice-sheet mass balance, the potential for global impacts arises through cryospheric influence on global sea level and ocean-circulation patterns. A majority of the ice in West Antarctica is tied up in the thick interior of the ice sheet, the discharge of which is dominated by internal deformation or slow basal motion leading to flow rates of meters to tens of meters per year. This interior basin feeds three main outlet systems, which deposit ice into the Weddell Sea, Pine Island Bay and Ross Sea, respectively. Much attention has been focused on the Ross Sea sector where the fast-moving Ross ice streams transport much of the grounded (non-floating) interior ice across the Siple Coast grounding line. Presently, ice flows at hundreds of meters per year in these streaming regions due to rapid basal sliding over, or deformation within, a well-lubricated subglacial till layer (Reference Blankenship, Bentley, Rooney and AlleyBlankenship and others, 1986; Reference AlleyAlley, 1989; Reference Engelhardt and KambEngelhardt and Kamb, 1998; Reference Tulaczyk, Kamb and EngelhardtTulaczyk and others, 2000a; Reference Kamb, Alley and BindschadlerKamb, 2001). Variations in this ice-drainage system have occurred at least since the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) (Reference Alley and BindschadlerAlley and Bindschadler, 2001). Despite a grounding-line advance to nearly the continental-shelf edge during the last glaciation and a subsequent ∼1300km retreat, the ice streams maintained their characteristically low-elevation, low-slope surface profiles and existed in roughly their present locations (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999; Reference Anderson, Shipp, Alley and BindschadlerAnderson and Shipp, 2001).
The acceleration of ice from the inland region into the ice streams leads to a local thinning of the ice sheet. Ice-stream models that calculate a basal thermal budget for current conditions locally predict an associated increase in the basal thermal gradient that would dewater and strengthen the subglacial sediments to satisfy the local freezing tendency(Reference Hulbe and MacAyealHulbe and MacAyeal, 1999; Reference Tulaczyk, Kamb and EngelhardtTulaczyk and others, 2000b). Removal of the basal lubricant in Reference Tulaczyk, Kamb and EngelhardtTulaczyk and others’ (2000b) model slows the rapid ice motion and introduces unsteadiness that mimics the observed variability in the ice-stream system. Local thermal budgets have been used to argue that the ice streams are on the edge of the freeze/thawboundary and that the post-glacial-maximum grounding-line retreat is on the brink of reversing itself (Reference Clarke and MarshallClarke and Marshall, 1998;personal communication from S. Vogel and S. Tulaczyk, 2001). With more regional basal freezing, slowing and thickening of the ice streams would likely follow, accompanied by a grounding-line readvance.
However, field observations indicate substantial melting beneath the thicker inland ice (Reference Engelhardt and KambEngelhardt and Kamb, 1997, Reference Engelhardt and Kamb1998; Reference Tulaczyk, Kamb and EngelhardtKamb, 2001). That meltwater may supply lubrication and move latent heat downstream, thus satisfying local basal-thermal deficits. Based on the presence of a 410 m debris-rich ice layer at the base of Ice Stream C (personal communication from H. Engelhardt, 2001), it is apparent that a sub-ice-stream system of widespread, thin, interconnected, ice-contact braided channels (Reference Walder and FowlerWalder and Fowler, 1994; Reference Catania and PaolaCatania and Paola, 2001) was transporting regional water to balance the negative local budget for an extended period prior to the slow-down of the ice stream ∼150 years ago (Reference Retzlaff and BentleyRetzlaff and Bentley, 1993; personal communication from S. Vogel and S. Tulaczyk, 2001; possible explanations for the slow-down are discussed by Reference Anandakrishnan, Alley, Jacobel, Conway, Alley and BindschadlerAnandakrishnan and others (2001) and Reference Whillans, Bentley, van der Veen, Alley and BindschadlerWhillans and others (2001)). Not only is the frozen-on layer too thick to have formed since Ice Stream C slowed, but the underlying sediments are still soft and are hence not yet dewatered (Reference Kamb, Alley and BindschadlerKamb, 2001). A linked regional water system is therefore required. Similar debris-rich layers are found at the bases of Ice Stream D andWhillans Ice Stream (personal communication from H. Engelhardt, 2001).
While this basal water system has the potential to maintain the long-term persistence
![]() of the ice streams (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999; Reference Anderson, Shipp, Alley and BindschadlerAnderson and Shipp, 2001; Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others, 2002), the rapid variability
of the ice streams (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999; Reference Anderson, Shipp, Alley and BindschadlerAnderson and Shipp, 2001; Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others, 2002), the rapid variability
![]() within this same hydrologic system (e.g. Reference Alley, Anandakrishnan, Bentley and LordAlley and others, 1994; Reference Engelhardt and KambEngelhardt and Kamb, 1997) may allow for the marked unsteadiness observed in the glaciologic data (e.g. Reference Retzlaff and BentleyRetzlaff and Bentley, 1993; Reference Bindschadler and VornbergerBindschadler and Vornberger, 1998; Reference Fahnestock, Scambos, Bindschadler and KvaranFahnestock and others, 2000). Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others (2002) used numerical flowline sensitivity simulations along Ice Stream D to estimate its past and present “health” based on the total basal thermal budget of the combined inland-catchment and ice-stream regions. The experimental results suggested that there is enough latent heat available in the modern basal water system to keep the ice stream away from the critical edge of freezing to its bed, thereby allowing for additional thinning and grounding-line retreat. Furthermore, a majority of the experiments predicted that the ice-stream bed was close to freezing at the LGM configuration and that postglacial climate changes increased basal lubrication greatly beginning sometime between 10 and 13 kyr, in close agreement with the onset of deglaciation (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999). We extend this modeling effort to flowlines alongIce Stream A,Whillans Ice Stream and Ice Stream C.
within this same hydrologic system (e.g. Reference Alley, Anandakrishnan, Bentley and LordAlley and others, 1994; Reference Engelhardt and KambEngelhardt and Kamb, 1997) may allow for the marked unsteadiness observed in the glaciologic data (e.g. Reference Retzlaff and BentleyRetzlaff and Bentley, 1993; Reference Bindschadler and VornbergerBindschadler and Vornberger, 1998; Reference Fahnestock, Scambos, Bindschadler and KvaranFahnestock and others, 2000). Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others (2002) used numerical flowline sensitivity simulations along Ice Stream D to estimate its past and present “health” based on the total basal thermal budget of the combined inland-catchment and ice-stream regions. The experimental results suggested that there is enough latent heat available in the modern basal water system to keep the ice stream away from the critical edge of freezing to its bed, thereby allowing for additional thinning and grounding-line retreat. Furthermore, a majority of the experiments predicted that the ice-stream bed was close to freezing at the LGM configuration and that postglacial climate changes increased basal lubrication greatly beginning sometime between 10 and 13 kyr, in close agreement with the onset of deglaciation (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999). We extend this modeling effort to flowlines alongIce Stream A,Whillans Ice Stream and Ice Stream C.
Model Description
As presented in Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others (2002), the Pennsylvania State University/University of Chicago flowline model (Reference Cutler, MacAyeal, Mickelson, Parizek and ColganCutler and others, 2000; Reference ParizekParizek, 2000) is computationally fast enough to allow multiple simulations varying key parameters through the appropriate parameter space over glacial–interglacial cycles on existing computers. The two-dimensional (vertical and along-flow) finite-element model incorporates Hermitian-polynomial interpolation functions across 20 km elements (based on Reference MacAyealMacAyeal,1997). Ice dynamics is modeled with a diffusion formulation of the thin-ice approximation (Reference HutterHutter, 1983) in which only the vertical shear stress drives ice deformation. At the scale used here, intra-element longitudinal stresses are negligible in the force balance (Reference Whillans and vander VeenWhillans and Van der Veen, 1993). The flowlines are chosen to run along ice-stream center lines, thereby minimizing transverse stresses. Strain rate is set proportional to the third power of stress (Reference Budd and JackaBudd and Jacka, 1989). Sliding is parameterized as linear in basal shear stress with an adjustable prefactor set higher for the thin, low-surface-slope ice streams (e.g. region between onset and grounding line (g.l.) in Fig. 2a) and lower for the thicker inland ice (e.g. region between divide and onset in Fig. 2a) in order to simulate the effects of changing geology and to reconstruct reasonable LGM and modern profiles. Thermal subroutines account for both ice and bedrock. Within the ice, horizontal and vertical advection, vertical diffusion and viscous dissipation are included. Because we are interested in ≤ O(100)kyr time-scales, heat flow in the bedrock is simulated using vertical diffusion with a prescribed thermal-gradient boundary condition(generated by the regional geothermal flux) 1120m below the ice (see Fig. 2a). The rock layer provides thermal inertia for temperature variations that reach the ice–bedrock interface. Following Reference Le Meur and HuybrechtsLe Meur and Huybrechts (1996), isostatic depression is calculated with an elastic lithosphere and relaxed asthenosphere.
The local basal heat budget is calculated as the sum of the geothermal and frictional heat flow “into” the ice–bedrock interface minus the heat conduction “out” from the interface and into the ice. Excess heat goes to melting while a deficit goes to freezing. Based on salt-tracer measurements in boreholes on Whillans Ice Stream (Reference Engelhardt and KambEngelhardt and Kamb, 1997), it is assumed that a throughgoing hydrologic system links the thermal states of inland and ice-stream beds on time-scales much shorter than the time-step sizes for either the dynamic or the longer thermodynamic routines. (Given observed flow rates of 7.5 mms–1 and a 20 km horizontal nodal spacing, a parcel of water could travel across an element in approximately one simulated month.) Therefore, latent heat entering the hydrologic system due to up-glacier melting is instantly available to locations with a negative thermal budget such that the sum of heat along the flowline is a measure of ice-stream “health”. While the complex and largely unobserved basal water system has been reduced to this one-dimensional idealization, thermal effects due to the lateral transfer of water into the ice stream are likely minimal as present borehole observations show that the interstream ridges are frozen to their beds (Reference Engelhardt and KambEngelhardt and Kamb, 1997; personal communication from H. Engelhardt, 2001).
Surface air temperatures are initialized with modern values along each flowline. Throughout the duration of each simulation, these temperatures are adjusted for elevation change (using an annual-average adiabatic lapse rate for West Antarctica of 5.1 ˚Ck m – 1 (Reference Fortuin and OerlemansFortuin and Oerlemans, 1990)) and climate change (using the 10–90 kyr Byrd Station’s ice-isotopic record, dated by Reference Blunier and BrookBlunier and Brook (2001), converted to temperature change at 0.6% OC–1, extended across the glacial cycle using Byrd Station’s modern –28°C at 0–10 kyr and a linear trend to this value at 90–130 kyr as displayed in Figure 3a). Sea-level changes affecting elevation, grounding-line flotation thickness and lithospheric loading are taken from SPECMAP (Reference Imbrie, Berger, Imbrie, Hays, Kukla and SaltzmanImbrie and others, 1984). The accumulation-rate parameterization assumes a 55% decrease for a 10°C cooling, initialized from local modern values (Reference HuybrechtsHuybrechts, 1992). These follow the approach that was used to model Ice Stream D in Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others (2002).
Ice-Stream Simulations
Eleven simulations for each ice stream considered here (Ice Stream A, Whillans Ice Stream and Ice Stream C) follow the respective flow paths displayed in Figure 1. Each simulation begins with a thermal spin-up from 300 to 130 kyr under modern conditions and initially linear temperature gradients between specified surface temperature and initially thawed bed (Fig.2a). Because the model does not treat ice-shelf dynamics, the flotation thickness is assigned at the modern grounding line throughout the spin-up period.

Fig. 1. Flowline-model domains, from divides down Ice Stream A,Whillans Ice Stream (B) and Ice Stream C and across the Ross embayment to the continental-shelf edge, BEDMAP dataset (sponsored by the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research and coordinated by the British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge, U. K.).
From 130 to 27.8 kyr, floatingiceis artificially grounded on a very slippery bed that offers almost no resistance to flow in the “shelf” zone between the modern grounding line and ice front (Fig. 2a). The ice-stream domain for basal-thermal-budget calculations spans the zone between the onset region and the location where the ice has reached the local flotation thickness.

Fig. 2. (a) Initial conditions including isotherms along flowline through Ice Stream C; (b) LGM (22.1kyr); and (c) modern ice-sheet reconstructions with basal melting, eighth simulation on Ice Stream C (Table 1).
From ∼27.8 to 12.9 kyr, the grounding line is fixed at the continental shelf edge (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999). From ∼ 12.9kyr to the present, the grounding line is marched back from the LGM extent (e.g. Fig. 2b) to the modern position (e.g. Fig. 2c) at varying rates matching the “swinging gate” constrained by distributed geologic evidence (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999).Throughout the last 27.8 kyr, all regions beyond the assigned grounding line are fixed as ice-free, thereby eliminating the need to include ice-shelf dynamics or specify a calving law in these data-driven simulations. In this way, errors associated with ignoring longitudinal stresses near the grounding line are minimized. We then determine what model conditions immediately preceded the known grounding-line retreat to help infer whether modern conditions are consistent with those that accompanied retreat.
Sensitivity experiments conducted on each flowline tested reasonable ranges of the geothermal flux, basal sliding conditions and accumulation rate on domains divided into three distinct basal regions (see Fig. 2a): “sheet” (divide to fixed modern onset region for sliding and thermal-budget calculations), “from stream” (modern onset to modern grounding line for sliding calculations and variable region from modern onset to assigned grounding-line position for thermal-budget calculations) and “shelf” (variable region between the modern grounding line and ice front (assigned grounding line) during the period spanning ∼130–27.8 kyr (27.8 kyr–present) for sliding). All runs permit sliding in the “stream” and “shelf” zones regardless of the local thermal conditions at the bed. Along with the “shelf” sliding enhancement between the modern and assigned grounding lines (130kyr–present), this promotes thin, flat ice-stream profiles (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999; Reference Anderson, Shipp, Alley and BindschadlerAnderson and Shipp, 2001), thereby encouraging modeled basal freeze-on by increasing the thermal gradient within the ice. In addition, all artificial melt generated at the slope breaks between sliding regimes is completely removed from the thermal budget. The steep surface slopes that are generated at these locations lead to anomalously high local driving stresses that produce added meltwater. By removing this excess heat, we eliminate the melting bias from the simulations, driving the ice streams even closer to the freeze-on threshold. While strain heating within the ice column also increases at these nick points, the net effect across these transition zones in nature and model is comparable. Because the transition occurs more gradually in nature than in the model, excess simulated strain heating at the artificial nick point is compensated by a modeled shortfall immediately down-glacier. (Inclusion of longitudinal stresses in the force-balance calculations would smooth out the nick points and lead to more uniform meltwater production across the transition regions (Reference Price, Bindschadler, Hulbe and BlankenshipPrice and others, 2002).) Sliding in the “sheet” domain occurs only where the local basal temperature reaches the pressure-melting point. For calculations of available basal water only, the sheet region is assumed to be twice as wide as the stream based on modern observations (Reference JoughinJoughin and others, 1999).
Results
Meltwater is produced throughout the climate cycle, though its effect on the energy budget of each ice stream varies during the cycle. In 31of the 33 simulations conducted here, enough meltwater is produced along each flowline to prohibit freeze-on of the modern ice streams (see Table 1). The tendency to shut-down is observed only on Ice Stream C when the regional geothermal flux is reduced to 60mWm−2. During the LGM, basal melting is restricted to bedrock overdeepenings beneath the ice-stream catchments (e.g. Fig. 2b). The quantity of LGM meltwater production is insufficient to balance the freezing tendencies of the ice streams for all but one parameter configuration. The lower accumulation rates during the last glaciation act to warm the bed in these simulations, but the colder temperatures and reduced frictional heating from decreased flow speeds simply cool the bed more. While data support streaming flow throughout the LGM, it persists in the simulations only when we increase the regional geothermal flux to 100mWm−2. The simulated shut-down of all ice streams may be due to the omission of flow convergence from sheet to stream, which results in somewhat thinner inland ice (cf. modern profiles in Fig. 2a and c) and an underestimation of upstream basal melting. Somewhat thicker LGM inland ice may have fed slightly thicker and slower ice streams, which in turn would have contributed to the LGM grounding-line advance. Similar to the findings for Ice Stream D (Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others, 2002), several experiments predict that sufficient lubrication for thawed basal conditions out to the grounding line is restored sometime between 10 and 13 kyr (e.g. Fig. 3b and c).
Table 1. Thermal-budget simulations for flowlines A, B and C


Fig. 3. (a) 130 kyr temperature forcing. (b–d) History of basal heat budget, for eighth simulation (Table 1): flowline A (b); flowline B (c); and flowline C (d). Total heat budgets are calculated assuming catchment sheet is twice as wide as stream. In each simulation, the sharp negative imbalance 2 7.8 kyr is a result of the initial assignment of the flotation thickness at the LGM grounding line and should not be interpreted as a physical phenomenon.
Discussion and Conclusions
With the recent slowing and thickening of Whillans Ice Stream and the local freezing tendencies inferred from measured borehole temperature profiles and observed basal debris layers within several ice streams, it has been theorized that the modern ice streams are cooling at depth and consuming their lubricant viabasal freezing. However, conservative numerical simulations along Ice Stream A, Whillans Ice Stream and Ice Stream C suggest that meltwater production inland and within bedrock lows can overcome the local freezing tendency along the modern ice streams. Previous work concluded the same for Ice Stream D (Reference Parizek, Alley, Anandakrishnan and ConwayParizek and others, 2002). Using a semi-empirical technique, Reference Joughin, Tulaczyk and EngelhardtJoughin and others (2003) reached a similar conclusion, increasing confidence in the results.
The LGM ice streams were likely slower than their modern counterparts as indicated by lower LGM accumulation rates combined with data suggesting ice-stream geometries similar to today’s (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999; Reference Anderson, Shipp, Alley and BindschadlerAnderson and Shipp, 2001). The modeled LGM reduction in production of lubricating basal meltwater is consistent with these observations. Furthermore, many of the simulations indicate that regional basal melting initially exceeded freezing sometime between 10 and 13 kyr, in accord with the on set of deglaciation (Reference Conway, Hall, Denton, Gades and WaddingtonConway and others, 1999). It is not hard to imagine a resulting feedback mechanism for retreat: additional lubrication leading to faster ice flow, thinning in the Ross embayment, and ultimately flotation and retreat of the grounding line.
Both model and data suggest further thinning and grounding-line retreat are thermally viable, via a through going basal meltwater system (e.g. personal communication from H. Engelhardt, 2001; Reference Kamb, Alley and BindschadlerKamb, 2001; cf. Reference Joughin and TulaczykJoughin and Tulaczyk, 2002). Local variability within the hydrologic system promotes either lubrication or freeze-on, depending on the local melt-water flow pattern. Therefore, observed short-term variability within the ice-stream system is likely to persist amidst continued ice streaming along the Siple Coast.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) Graduate Student Researchers Program Fellowship (to B. R. Parizek). This material is based in part upon work supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation under grants including Nos. 0126187 and 9814774.We are grateful to S. Anandakrishnan, R. A. Bindschadler, H. B. Conway, D. R. MacAyeal and M. Fahnestock for their contributions. Critical reviews by M. J. Sharp and an anonymous referee helped improve the clarity of the manuscript. Additional thanks to the Scientific Editor, H. Engelhardt, for his constructive remarks. Special thanks to H. H. Parizek for her encouragement throughout this research effort.


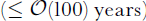 , asynchronous discharge variations with evolving lateral boundaries. Amidst this variability, a ∼1300 km grounding-line retreat has occurred since the Last Glacial Maximum. Numerical studies of Ice Stream D (Parizek and others, 2002) indicate that a proposed thermal-regulation mechanism (Clarke and Marshall, 1998; Hulbe and MacAyeal, 1999; Tulaczyk and others, 2000a, b), which could buffer the West Antarctic ice sheet against complete collapse, may be over-ridden by latent-heat transport within melt-water from beneath inland ice. Extending these studies to Ice Stream A, Whillans Ice Stream and Ice Stream C suggests that further grounding-line retreat contributing to sea-level rise is possible thermodynamically However, the efficiency of basal water distribution may be a constraint on the system. Because local thermal deficits promote basal freeze-on (especially on topographic highs), observed short-term variability is likely to persist.
, asynchronous discharge variations with evolving lateral boundaries. Amidst this variability, a ∼1300 km grounding-line retreat has occurred since the Last Glacial Maximum. Numerical studies of Ice Stream D (Parizek and others, 2002) indicate that a proposed thermal-regulation mechanism (Clarke and Marshall, 1998; Hulbe and MacAyeal, 1999; Tulaczyk and others, 2000a, b), which could buffer the West Antarctic ice sheet against complete collapse, may be over-ridden by latent-heat transport within melt-water from beneath inland ice. Extending these studies to Ice Stream A, Whillans Ice Stream and Ice Stream C suggests that further grounding-line retreat contributing to sea-level rise is possible thermodynamically However, the efficiency of basal water distribution may be a constraint on the system. Because local thermal deficits promote basal freeze-on (especially on topographic highs), observed short-term variability is likely to persist.



