Volume 19 - Issue 73 - January 1915
Other
Index
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. i-ii
-
- Article
- Export citation
Notices of the Aëronautical Society of Great Britain
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Obituary
Reginald Jordan Alston
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Major Alfred Herbert Tyler, R.E.
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Major Raleigh, R.F.C.
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 3-4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Death of the Late Mr. E. T. Busk and the Posthumous Award to him of the Gold Medal of the Aeronautical Society
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 5-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
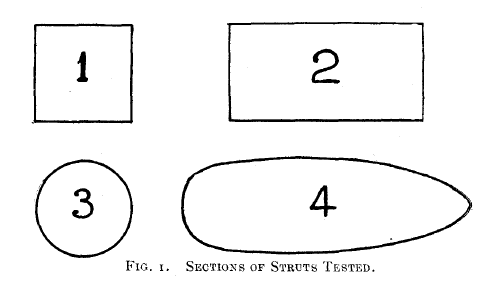
The Resistance of Inclined Struts in a Uniform Air Current
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 7-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flapping Flight
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 13-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the Flight of Albatrosses and Gannets
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 22-29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Other
The Royal Flying Corps on Active Service
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 30-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Royal Flying Corps
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 32-33
-
- Article
- Export citation
List of British Fatalities
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 33
-
- Article
- Export citation
New Books and Publications
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 34
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reviews
Books on the Great War. F. W. T. Lange and W. T. Berry. (London: Grafton and Co. 1915. pp. 55. Price 2s. 6d. net.) - Aircraft in War. Eric Stuart Bruce. (London: Hodder and Stoughton. 1914. pp. 77. Illus. Price is. net.) - Aircraft in the German War. H. Massac Buist. (London: Methuen and Co., Ltd. 1914. pp. 128. Illus. Price is. net.) - The Mastery of the Air. W. J. Claxton. (London: Blackie and Son. 1914. pp. 258. Illus. Price 2s. 6d.) - Modern Weapons of War, by Land, Sea and Air. Cyril Hall. (London: Blackie and Son. 1915. pp. 192. Illus. Price 2s. 6d.) - "The Times" History of the War. Vol. II., Part 18. " Military Aeronautics and the British Air Service." pp. 173–196. Illus. (London: " The Times." 1914. Price 7d. net.) - " T.P.'s Journal," Great Deeds of the Great War. Edited by T. P. O'Connor. Vol. I., No. 8. pp. 199–202. Illus. Vol. I, No. 9. pp. 231-234. Illus. (London: " The Daily Telegraph." 1914. Price 3d. per number.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, pp. 34-37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stability and Equilibrium of Floating Bodies. Bernard C. Laws. (London: Constable and Co. 1914. pp. 251. Figs. Price 10s. 6d. net.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Discoveries and Inventions of the Twentieth Century. Edward Cressy. (London : George Routledge and Sons, Ltd. 1914. pp. 398. Illus. Price 7s. 6d. net.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 37
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Essays of an Aviator. (London: "Aeronautics." 1914. pp. 45. Price 2s. 6d.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flight without Formulae. Com. Duchenc. Translated from the French by John H. Ledeboer, B.A. (London: Longmans, Green and Co. 1914. pp. 211. Figs. Price 7s. 6d.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 38
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Aeroplane. C. Grahamc-White and Harry Harper. (London: T. C. and E. C. Jack. 1914. pp. 280. Illus., 16 plates. Price 3s. 6d. net.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 38
-
- Article
- Export citation
All the World's Aircraft. By Fred. T. Jane. Sixth year of issue. (London : Sampson, Low, Marston and Co. 1914. pp. 202 + 19b + 14c + 19d. Illus. Price 21s. net.)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2016, p. 39
-
- Article
- Export citation