No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 October 2021
This paper introduces the Low Acoustic Noise and Turbulence (LANT) wind tunnel of the Sao Carlos School of Engineering, University of Sao Paulo (USP-EESC), Brazil. The closed-loop wind tunnel features several devices to improve flow uniformity, reduce swirl, and lower the background acoustic noise and turbulence, enabling stability and aeroacoustic experiments. The design criteria was based on the best practices reported, in particular for low turbulence wind tunnels. Yet, these criteria are conflicting and we discuss the decisions that had to be made and present flow quality results that were achieved. The 16-bladed axial fan with 13-blade stators is driven by a variable-speed electric motor. At the corners, 100 mm dense acoustic foam is installed on the vertical walls, floor and ceiling, and the turning vanes are filled with acoustic-absorbing material. The long settling chamber contains a 3.175 mm mesh hexagonal honeycomb and five fine mesh nylon screens, ending in a 7:1 area ratio short contraction. The 3-m long closed-working section has a 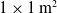 $1\times 1\ {\rm m}^2$
cross-section area. At 15 m/s the working section wall boundary layer is less than 100 mm thick, providing an area of at least
$1\times 1\ {\rm m}^2$
cross-section area. At 15 m/s the working section wall boundary layer is less than 100 mm thick, providing an area of at least 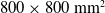 $800\times 800\ \mathrm{mm}^2$
where the streamwise flow uniformity was within 1%. In the 10–30 m/s flow speed range, the turbulence intensity ranged from 0.05% to 0.071% and the background acoustic noise level, obtained with an inflow microphone, ranged from 90 and 110 dB. A benchmark experiment on a flat plate boundary layer produced an almost perfect two-dimensional Blasius profile up to
$800\times 800\ \mathrm{mm}^2$
where the streamwise flow uniformity was within 1%. In the 10–30 m/s flow speed range, the turbulence intensity ranged from 0.05% to 0.071% and the background acoustic noise level, obtained with an inflow microphone, ranged from 90 and 110 dB. A benchmark experiment on a flat plate boundary layer produced an almost perfect two-dimensional Blasius profile up to 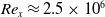 $Re_x \approx 2.5 \times 10^6$
. A beamforming benchmark experiment on aeroacoustics accurately identified the sound emitted by a cylinder immersed in the flow.
$Re_x \approx 2.5 \times 10^6$
. A beamforming benchmark experiment on aeroacoustics accurately identified the sound emitted by a cylinder immersed in the flow.