No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 March 2019
The structural aspects of the precipitation of MgFa in LiF have been studied in LiF crystals containing up to 3 wt. % MgFs. The precipitate particles appear to be rodlike, having a sawtooth morphology. The rods lie in two directions on matrix planes which are close to but not precisely {111}LIF.
The lattice orientation relationship between MgF2 and LiF has been established by X-ray techniques as
(111)LIF‖(100)MgF2
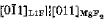
Laue photographs of slowly cooled crystals show diffuse X-ray scattering effects which are associated with the precipitation process.
Excellent matching of atoms at the interfaces between the precipitate and matrix is postulated on the basis of a hard-sphere atomic model. The results suggest that phase coherency obtains during the early stages of growth, and that growth is controlled by dislocation interfaces.
Rapid quenching retains all MgF2 in solution. Upon subsequent aging a transition structure forms which is based essentially on the LiF lattice but with a cell size of 8.20 Å, roughly double that of LiF. With further aging the transition structure is replaced by the normal MgF2 tetragonal structure.
Supported by the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the United States Department of Defense, Contract No. SD-68, and by the National Science Foundation, Contract No. GP519.