No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 March 2019
Quantitative phase analysis (QPA) methods which employ only one diffraction line for each phase arc generally unreliable due to the influence of systematic errors such as preferred orientation and extinction. Gazzara and Messier (1977) proposed a multi-line QPA method using normalised line intensities for line j of phase i,
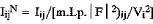
where Iij = measured Bragg intensity, m = multiplicity, Lp = Lorentz-polarisation factor, |F| = structure amplitude and Vi = cell volume. The method proposed here is a refinement of the Gazzara-Messier procedure. Phase compositions are calculated directly from the mean normalised Intensity 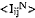 for resolved lines which span the 2θ range of the instrument. The method makes use of the variance in
for resolved lines which span the 2θ range of the instrument. The method makes use of the variance in 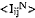 to estimate standard deviations for the phase compositions. Test results are given for binaries of corundum-quartz and corundum-ceria.
to estimate standard deviations for the phase compositions. Test results are given for binaries of corundum-quartz and corundum-ceria.