Intimations of death often cause symptoms or syndromes of mental or emotional disorder, of which anxiety and depression are the most common. It is entirely appropriate, therefore, for mental health services to be involved with those who care for the dying in whatever setting (Reference Spiess, Northcott and OffsaySpiess et al, 2002). Old age psychiatrists have recognised their more direct role in caring for dying patients for some time (Reference Black and JolleyBlack & Jolley, 1990, Reference Black and Jolley1991). A particular impetus has emerged behind the notion of palliative care in dementia (Reference Hughes, Robinson and VolicerHughes et al, 2005). This is a field in which the literature is burgeoning (Reference Robinson, Hughes and VolicerRobinson et al, 2005) but where there is no generally agreed way in which services should be provided (Reference Hughes, Robinson and HughesHughes & Robinson, 2006). Before considering particular issues that arise in palliative care in dementia, there are two immediate questions: first, in the context of dementia, what is palliative care and, second, is there a need for it?
What is palliative care?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has defined palliative care as:
‘an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial and spiritual’ (World Health Organization, 2002).
However, a difficult problem emerges in the context of dementia since it is often not seen as a life-threatening illness. Palliative care can be regarded as a spectrum (Reference Addington-HallAddington-Hall, 1998). At one end, the palliative care approach equates to good-quality, person-centred dementia care. At the other, the terminal stages of dementia may well require specialist palliative care (involving more detailed knowledge and skills, for example in pain relief).
In between, palliative interventions (which in cancer care could involve palliative radiotherapy for bone pain) might comprise the raft of pharmacological and psychosocial approaches used to treat the behavioural and psychological signs of dementia.
One conceptual and practical issue concerns whether these potential components of care in dementia can (and should) be usefully packaged together under the umbrella of ‘palliative care’. A reasonable response might be that if conceptual packaging in this way leads to improvements in patient care, perhaps through advance care planning, then the enterprise would seem worthwhile.
Is there a need for improved palliative care in dementia?
There is compelling evidence that the care of people with dementia, especially towards the end of their lives, is less than optimal (Reference Ballard, Fossey and ChithramohanBallard et al, 2001a ). Retrospective case-note studies demonstrate inadequate palliative care in both psychiatric and acute hospital wards (Reference Lloyd-WilliamsLloyd-Williams, 1996; Reference Sampson, Gould and LeeSampson et al, 2006). Life expectancy is more emphatically curtailed by dementia than it is by other psychiatric syndromes (Reference Jolley and BaxterJolley & Baxter, 1997). Yet the evidence for suboptimal care persists, especially in the terminal phase (Reference Wilden and WrightWilden & Wright, 2002), with studies in the USA and Israel confirming the somewhat dismal picture (Reference Mitchell, Kiely and HamelMitchell et al, 2004; Reference Aminoff and AdunskyAminoff & Adunsky, 2006).
In a retrospective survey of carers in England, Reference McCarthy, Addington-Hall and AltmannMcCarthy et al(1997) reported a host of common symptoms and signs experienced by people with dementia in the last year of life: confusion (83%), urinary incontinence (72%), pain (64%), low mood (61%), constipation (59%) and loss of appetite (57%). The study found similar frequencies of such symptoms in cancer patients, but people with dementia experienced the symptoms for longer. Out of 170 people with dementia in the same study, none had died in a hospice. In a study of presenile dementia, the proportion of people dying in their own home decreased from 25% in 1985–91 to 15% in 1992–98; the proportion dying in residential or nursing homes increased from 14 to 32% during the same period (Reference Kay, Forster and NewensKay et al, 2000).
Given the evidence of inadequate levels of care in both long-term institutions and hospitals, and given that people with dementia do not seem to gain access to specialist palliative care services, the implication is that there are needs for palliative care – particularly in the last year of life – that are not being met.
Efficacy of palliative care in dementia
This situation might be easily rectified if there were a straightforward model of how palliative care should be provided in dementia. Not only, however, is there no single model but the scientific evidence for the efficacy of palliative care in advanced dementia is lacking. Reference Sampson, Ritchie and LaiSampson et al(2005) undertook a systematic review and concluded that the evidence of efficacy was equivocal. Their initial research yielded 885 studies, of which only 49 met the criteria for further scrutiny. Of these, 30 were review articles and, of the remaining 19 papers, only four fulfilled the criteria for review of the complete paper (Table 1). However, even these four studies have deficiencies in terms of methodology.
Table 1 Studies of efficacy of palliative care in advanced dementia (adapted from Reference Sampson, Ritchie and LaiSampson et al, 2005)
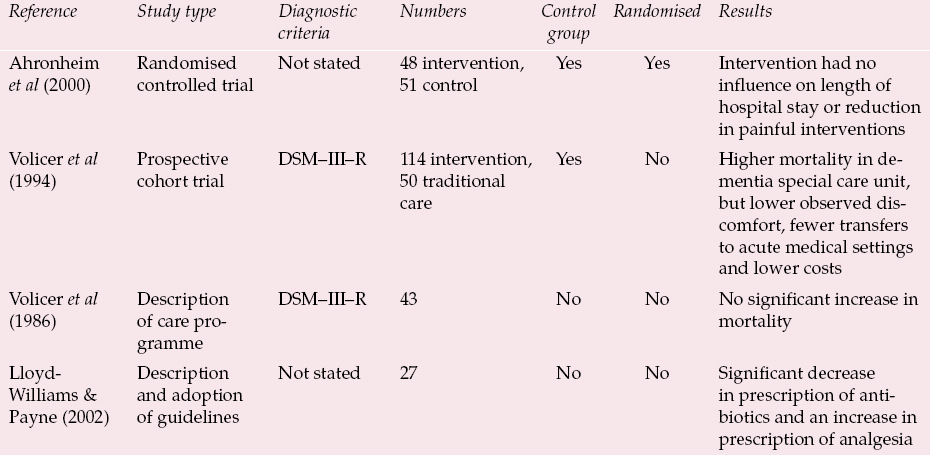
| Reference | Study type | Diagnostic criteria | Numbers | Control group | Randomised | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Ahronheim, Morrison and MorrisAhronheim et al(2000) | Randomised controlled trial | Not stated | 48 intervention, 51 control | Yes | Yes | Intervention had no influence on length of hospital stay or reduction in painful interventions |
| Reference Volicer, Collard and HurleyVolicer et al(1994) | Prospective cohort trial | DSM–III–R | 114 intervention, 50 traditional care | Yes | No | Higher mortality in dementia special care unit, but lower observed discomfort, fewer transfers to acute medical settings and lower costs |
| Reference Volicer, Rheaume and BrownVolicer et al(1986) | Description of care programme | DSM–III–R | 43 | No | No | No significant increase in mortality |
| Reference Lloyd-Williams and PayneLloyd-Williams & Payne (2002) | Description and adoption of guidelines | Not stated | 27 | No | No | Significant decrease in prescription of antibiotics and an increase in prescription of analgesia |
In the studies in which the methodology was less rigorous, there seemed to be some benefit in terms of the palliative approach: better symptom control and more analgesia, fewer putatively unnecessary interventions (i.e. transfer to acute hospitals and use of antibiotics), with lower costs (Table 1). Such benefits require closer scrutiny. However, the study with the best methodology (a randomised controlled trial by Reference Ahronheim, Morrison and MorrisAhronheim et al, 2000) failed to demonstrate any influence of the palliative care approach on the care of patients with dementia in an acute hospital.
The relative paucity of good-quality evidence can be excused because of the difficulty of the task. The lack of effect in the study of Reference Ahronheim, Morrison and MorrisAhronheim et al(2000) was blamed on uncertainties over prognosis and the difficulties involved in altering care plans already instituted by a medical team. There is a more general problem about how to assess outcomes in end-of-life care in people with dementia.
Much of the research comes from the USA. In particular, Ladislav Volicer's group in Boston have been able to build up a picture of how a hospice or palliative care approach might be useful in a special care unit for dementia (Reference Volicer and HurleyVolicer & Hurley, 1998). This has largely been achieved by showing benefits in particular areas (e.g. the management of fever or discomfort) and it may be that research needs to be more focused to show greater efficacy. The possibility remains, therefore, that palliative care can be provided in innovative ways with discernible benefits for people with dementia and their carers, despite the current dearth of evidence. For instance, again in the USA, Reference Shega, Levin and HoughamShega et al(2003) described in a preliminary report how community support from an early stage was helpful for pain control and complying with patients’ wishes and choice of place of death. These results suggest that there is likely to be a variety of ways to provide palliative care to people with dementia, from specialist long-term care units to community support (Reference Hughes, Robinson and VolicerHughes et al, 2005). Furthermore, there needs to be methodologically rigorous research to support such developments.
Predicting death in dementia
In the USA, where Medicare funding for a stay in a hospice requires a predicted survival of under 6 months, a number of studies have focused on predictors of death in dementia (Reference Volicer, Hurley and FabiszewskiVolicer et al, 1993; Reference Hanrahan, Raymond and McGowanHanrahan et al, 1999; Reference Schonwetter, Han and SmallSchonwetter et al, 2003). Many of the putative predictors have proved inaccurate. Nevertheless, Reference Sachs, Shega and Cox-HayleySachs et al(2004) suggest three markers of severity that at least imply that discussions about hospice enrolment might be appropriate. The first is Functional Assessment Staging (FAST; Reference Reisberg, Sclan and FranssenReisberg et al, 1994), where the person is non-ambulatory, has lost meaningful conversation and is dependent for most activities of daily living (i.e. stage 7C), especially when this is combined with complications such as weight loss of 10% or more, recurrent infections and multiple pressure sores; the second is hip fracture or pneumonia in advanced dementia (Reference Morrison and SiuMorrison & Siu, 2000a ) and the third the need for artificial feeding (Reference Grant, Rudberg and BrodyGrant et al, 1998).
In the UK, the precise prediction of death in dementia is less of an issue but there is still the need to discuss matters with families. The timing of such discussions will be a matter of clinical judgement. For instance, some people with dementia might wish to make advance decisions – about palliative care and where they wish to die – soon after diagnosis. Where such discussions have not taken place at an early stage, prognostic indicators might be a useful way to prompt appropriate conversations (Reference Coventry, Grande and RichardsCoventry et al, 2005).
Physical health in advanced dementia
The physical health of people with advanced dementia need increasing consideration as the condition progresses and there are specific symptoms and signs associated with dying (Reference Regnard, Huntley and HughesRegnard & Huntley, 2006). General levels of functioning need attention, and the right amount of support should be provided to allow as much independence as possible while still maintaining the person's dignity. Genuinely interesting activities or complementary therapies may be useful (e.g. Reference James, Mackenzie and Mukaetova-LadinskaJames et al, 2006; but see also Reference Cayton, Hughes, Louw and SabatCayton, 2006, against ‘doll therapy’). In the final stages of dementia, weight loss and loss of muscle and muscle strength become apparent. In part this reflects reduced food intake but the degree of weight loss often seems greater than can be explained in this way. It is important to look for ways to treat this general debility, which may include feeding approaches, in order to avoid deterioration by negligence. Low metabolic rate and physical inactivity can mean a state of physiological homoeostasis, in which the body weight is low but constant, which must be distinguished from progressive starvation (Reference HofferHoffer, 2006). Even so, people approaching death with dementia can show continued loss of weight and body mass (Reference Thomas, O'Brien, Jacoby and OppenheimerThomas & O'Brien, 2002). At the same time there are potential problems from contractures and skin integrity, which is compromised by poor diet and lack of mobility. Hence, there are requirements for physiotherapy and good nursing.
Similarly, both bladder and bowel function are compromised in advanced dementia. Incontinence of urine is common, which itself threatens skin integrity, causing discomfort. Advice from a continence specialist will often be helpful. Constipation, which can sometimes lead to impaction or overflow incontinence, can occur when the diet or fluid intake are poor, or when medication slows bowel transit times. Immobility and reduced awareness of the call to stool make matters worse. Constipation itself impedes bladder function. Discomfort, pain or toxicity can follow. The person may become more confused or more agitated. A common sign of constipation is the tendency to lean to the side. Vigilance and prophylaxis, with good nursing observations and medical review, will help to avoid the worst consequences of both incontinence and constipation (Reference Regnard, Huntley and HughesRegnard & Huntley, 2006).
Pain
There is considerable concern that people with severe dementia might be in pain that is neither detected nor adequately treated. Several large studies have suggested that pain is common in older people generally. Reference Ferrell, Ferrell and OsterweilFerrell et al(1990) found that 71% of 92 nursing home residents had pain some of the time, 47% had intermittent pain and 24% reported of constant pain. Only 15% of those with pain had received analgesic medication in the previous 24 h. The mean score on the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) was 20.7. In a study of almost 50 000 nursing home residents, over 25% had daily pain, of whom 25% received no analgesia (Reference Won, Lapane and GambassiWon et al, 1999). However, people with moderately severe cognitive impairment (equivalent to a MMSE score of less than 19) and those with moderate to severe communication difficulties were excluded.
Reference Ferrell, Ferrell and RiveraFerrell et al(1995) studied 217 nursing home residents with frank dementia (mean MMSE score 12.1, s.d. = 7.9) and found that 62% complained of pain. Excluded from the study, however, were 70 residents with whom communication was too difficult. In a retrospective case-note audit of people with dementia, Reference Lloyd-WilliamsLloyd-Williams (1996) found pain and breathlessness to be the most common symptoms, which were variably palliated.
There is some evidence that clinicians do not always recognise pain in people with dementia (Reference Cook, Niven and DownsCook et al, 1999) or that they under-treat it. Reference Morrison and SiuMorrison & Siu (2000a ), in a prospective cohort study of older people following hip fractures, concluded that those who were unable to report their pain received less analgesia. The most potentially disturbing finding was that those without cognitive impairment received three times the amount of opioid analgesia than those with advanced dementia. Reference Feldt, Ryden and MilesFeldt et al(1998) had similarly found that people with cognitive impairment received less analgesia post-operatively. Reference Closs, Barr and BriggsCloss et al (2004a ) reported similar findings in nursing homes in Leeds, where the mean MMSE score was 15 (s.d. = 9). One possibility, however, is that pain might be perceived differently in dementia (Reference Scherder, Slaets and DeijenScherder et al, 2003, Reference Scherder, Oosterman and Swaab2005).
These findings have led to a growth of interest in pain assessment tools. Self-report scales have proved useful in people with mild to moderate dementia who can still communicate (Reference Closs, Barr and BriggsCloss et al, 2004b ). For severe dementia there are now numerous observational scales, but two recent reviews have cast doubt on the robustness of their psychometric properties (Reference Herr, Coyne and KeyHerr et al, 2006; Reference Zwakhalen, Hamers and Abu-SaadZwakhalen et al, 2006). Observational pain tools might pick up not only pain but also distress, of which pain might be just one cause (Reference Regnard, Reynolds and WatsonRegnard et al, 2007). The relationship between pain, distress, agitation and other behavioural and psychological signs of dementia needs to be carefully considered (Reference Cipher and CliffordCipher & Clifford, 2004). It is difficult to be certain about the true prevalence of pain because of intrinsic problems with the assessment of pain in people with severe dementia.
The WHO's pain relief ladder is a useful way to guide treatment (World Health Organization, 2006). It suggests stepped care (Fig. 1) from non-opioid drugs (e.g. paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) to weak and then strong opioids, with adjuvant analgesics (e.g. neuropathic agents or psychotropic medication) being added at any step (Reference Regnard, Huntley and HughesRegnard & Huntley, 2006). Given the real possibility of side-effects, non-pharmacological therapies, from heat or massage to transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation or acupuncture, might also be tried. There is evidence that such a stepped care approach can be effective (Reference Lloyd-Williams and PayneLloyd-Williams & Payne, 2002).
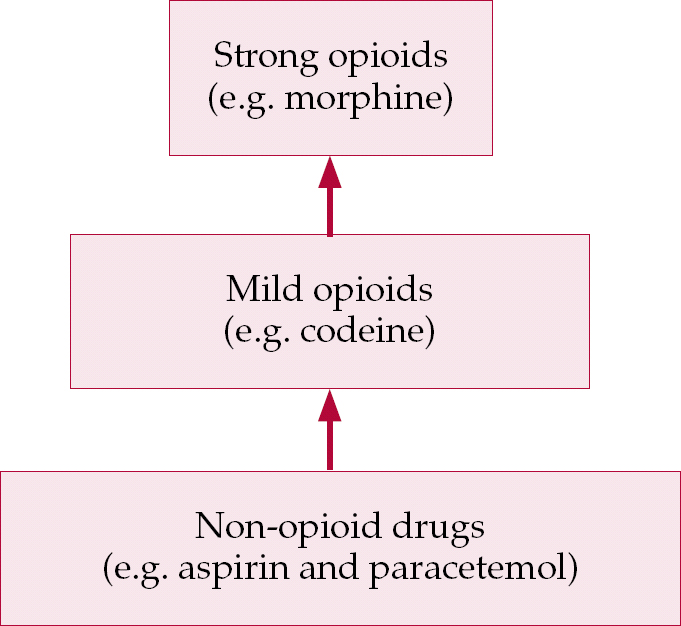
Fig. 1 A three-step hierarchy of drugs for pain relief (based on World Health Organization, 2006).
Infections and fevers
For a variety of reasons, including impaired immunological responses and immobility, people with advanced dementia are vulnerable to intercurrent infections. Pneumonia remains a common cause of death (Reference Chen, Lamberg and ChenChen et al, 2006). There is evidence that mortality is higher in people with severe dementia (53%) than in cognitively intact age-matched controls (13%) in the first 6 months after hospitalisation for pneumonia (Reference Morrison and SiuMorrison & Siu, 2000b ). The use of antibiotics to treat fevers and infections in severe dementia remains controversial. Reference Fabiszewski, Volicer and VolicerFabiszewski et al(1990) demonstrated no difference in mortality between people receiving antibiotics and those receiving only palliative care. In a controlled but non-randomised study, Reference Hurley, Volicer and VolicerHurley et al(1996) showed that treatment with antibiotics, as opposed to the use of simple antipyretics and analgesia, was associated with a worsening of dementia.
However, Reference Van der Steen, Ooms and Adervan der Steen et al (2002a) found that there was more discomfort in a group of people with dementia and pneumonia in whom antibiotics were withheld than in those treated with antibiotics. However, the same patients had higher rates of discomfort before the pneumonia and peak rates of discomfort were observed at baseline. Discomfort also seemed to be higher shortly before death when pneumonia was the final cause of death than when death had another cause. This might belie the notion that pneumonia is the ‘old man's friend’. Breathing problems were noted to be the most prominent signs. This would be predictable in pneumonia and raises two issues: first, the importance of a more global assessment of distress; second, the possibility that treatment other than antibiotics might have been beneficial (e.g. opiates to ease breathlessness).
The upshot is that the efficacy of antibiotics needs to be judged in individual specific circumstances taking into account the severity of the dementia, comorbidity, immobility, nutritional status and the person's response to the infection. In other branches of palliative care, antibiotics are sometimes used in a specifically palliative manner to ease the distress caused by infected bronchial secretions (Reference Clayton, Fardell and Hutton-PottsClayton et al, 2003). A study from The Netherlands of 706 patients suggests that physicians tend to treat most pneumonias with antibiotics: 69% with curative intent and 8% for palliative reasons (Reference Van der Steen, Ooms and Mehrvan der Steen et al, 2002b ). In the 23% where antibiotic treatment was withheld, the patients tended to have more severe dementia, more severe pneumonia, poorer food and fluid intake and were more often dehydrated. When patients are thus very close to death a natural concern is that antibiotics might simply delay death but leave the patient open to further suffering from decubitus ulcers or other consequences of very advanced inanition.
Artificial nutrition and hydration
Several things happen to a person's feeding as dementia worsens. First, just as it is common for appetite and the enjoyment of food to be reduced in terminal conditions, so too in dementia there is a loss of appetite, a loss of the experience of hunger and of the need for a routine of regular meals (Reference Watson and DearyWatson & Deary, 1997; Reference Ikeda, Brown and HollandIkeda et al, 2002). Second, there can be dyspraxic and sequencing problems that cause difficulties with the process of feeding. Third, swallowing problems become increasingly noticeable. Aspiration pneumonia becomes a concern in the more severe stages of the condition (Reference Feinberg, Ekberg and SegallFeinberg et al, 1992). It is particularly with this risk in mind that attention turns to the potential use of nasogastric and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes.
A review of the evidence, however, found no relevant randomised clinical trials comparing tube feeding and oral feeding (Reference Finucane, Christmas and TravisFinucane et al, 1999). On the basis of the available evidence the use of tube feeding in dementia did not seem to be supported. There was no good evidence to suggest that tube feeding prevented aspiration pneumonia, malnutrition, or pressure ulcers, that it reduced the risk of other infections, or that it improved survival, functional status or comfort (see Box 1).
Box 1 Review of evidence of tube feeding in patients with advanced dementia (Reference Finucane, Christmas and TravisFinucane et al, 1999)
-
• Aspiration pneumonia. No published studies to suggest tube feeding reduces risk
-
• Prevention of malnutrition. Delivering extra nutrients may not provide benefit to those in a catabolic state; additional nutrients might be beneficial in other instances, but effects might be outweighed by the adverse effects of tube feeding
-
• Improving survival. No published studies to suggest tube feeding prolongs survival in people with dementia and dysphagia
-
• Prevention of pressure ulcers. No published studies found to suggest tube feeding improves outcome for pressure sores
-
• Risks of other infections. No evidence that tube feeding reduces the risks of infection; in fact nasogastric feeding may increase the chances of sinus and middle-ear infection and PEG tubes the risk of diarrhoea, cellulitis and abscess
-
• Functional status. No published studies to support claims that tube feeding might improve functional abilities
-
• Comfort. No published studies to support claims that tube feeding might improve comfort
Indeed, the review pointed to a number of adverse effects associated with tube feeding. The most common, paradoxically, is aspiration pneumonia. In addition, peri-operative mortality rates for PEG placement are between 6 and 24% (Reference Finucane, Christmas and TravisFinucane et al, 1999). Furthermore, survival analysis of patients with dementia who are given a PEG tube suggest that 30-day mortality varies between 9.5 and 54% and 1-year mortality between 39 and 90% (Reference Sanders, Hurlstone and McAlindonSanders et al, 2004). A commentary on the ethics of tube feeding in dementia (Reference GillickGillick, 2000) suggested that, other than in special situations (e.g. where the dysphagia is likely to be a temporary phenomenon caused by something other than the general progression of the dementia), tube feeding should not be used routinely.
An opposing view, given that the results to date are based on frail people with advanced disease, might be that PEG tubes should be used sooner in dementia in order to maintain the person's nutritional state. However, there are no data to support such a view.
Recent research continues to support the more conservative approach (Reference Alvarez-Fernàndez, Garcia-Ordonez and Martinez-ManzanaresAlvarez-Fernández et al, 2005). In a study of 52 elderly nursing home residents in Australia who were cognitively intact (Reference Low, Chan and HungLow et al, 2003), using a hypothetical scenario, 69% would not agree to nasogastric tube feeding (P < 0.05) and 71% would not agree to PEG feeding (P < 0.001). Most (75%) of the respondents would agree to a modified diet (P < 0.0001) and to oral feeding despite the risk of aspiration (59.6%, P < 0.01). There is some evidence that a palliative approach and the use of advance directives can decrease the reliance on tube feeding (Reference Monteleoni and ClarkMonteleoni & Clark, 2004). Fortunately, PEG feeding is not so common in dementia in the UK. The emphasis should therefore be on conservative management of dysphagia following expert assessment (usually by a speech and language therapist) using food thickeners, with appropriate posture and careful feeding techniques. Local protocols for the training of staff can be helpful (Reference Summersall, Wight and HughesSummersall & Wight, 2006). As in the case of antibiotic use, the individual's particular medical state, the course of the dementia and judgements about quality of life seem to be more important to doctors in making such decisions, which are made on the broadest possible base and should include the family (Reference The, Pasman and Onwuteaka-PhilipsenThe et al, 2002).
Resuscitation
In severe dementia cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is unlikely to be successful. Outside hospital the chances of survival are low and CPR itself may be harmful and undignified (Reference Awoke, Mouton and ParrottAwoke et al, 1992; Reference Conroy, Luxton and DingwallConroy et al, 2006). Even with the benefits of being in hospital, CPR is three times less likely to be successful in people with cognitive impairment than in those who are cognitively intact. The success rate is similar to that found in people with metastatic cancer (Reference Ebell, Becker and BarryEbell et al, 1998).
These facts lead to some difficult decisions. The issue of CPR is often discussed with the relatives of people with severe dementia, especially within National Health Service settings where the default position is usually that CPR must be undertaken unless it is clearly documented that it should not. Since a person with dementia normally lacks the capacity to make a decision, clinicians must act in the person's best interests (Box 2). The process of assessing best interests involves talking with those near to the person, both informal family carers and formal care staff. Differences between or within the various groups involved – reflecting different knowledge, experience and background beliefs – can be difficult to acknowledge and deal with, but must be faced. The aim of capacity legislation is, in part, to provide a process for dealing with such disagreements.
Box 2 Process to assess best interests derived from the Mental Capacity Act 2005
The following must be considered, insofar as this is reasonable and practicable:
-
• all the relevant circumstances
-
• the person's past and present wishes and feelings
-
• the beliefs and values likely to influence the person's decision
-
• any other factors the person would be likely to consider
-
• the views of anyone named by the person
-
• carers or anyone with a justifiable interest in the person's welfare
-
• the donee of any lasting power of attorney
-
• any deputy appointed by the Court of Protection
-
• a mental capacity advocate (if applicable)
Against this, it has been argued that CPR should not be the default position in units looking after people with severe dementia, because it is likely to be futile and there should be no obligation on clinicians to provide futile and burdensome treatments. Moreover, if this were true, there should certainly be no obligation to hold discussions, which might themselves be burdensome, with relatives about treatments that would not be given (Reference Regnard and RandallRegnard & Randall, 2005). However, the hazards and concerns associated with having different resuscitation policies in different units has to be acknowledged. In addition, if families (or people with dementia) wish to discuss the prognosis and how things might go, clinicians would have to discuss what might or might not occur, including treatments that – for good palliative reasons – might not be given.
Families and carers
When a person is dying with advanced dementia the needs of families and close (informal) carers are unique (Reference Albinsson and StrangAlbinsson & Strang, 2003). As is the case with carers of people dying from cancer, families and informal carers require information and supportive listening. The difference, however, comes from the disease trajectory and from its psychosocial impact. As already mentioned, many people do not see dementia as a terminal illness, and this is itself a barrier to good-quality palliative care (Reference Sachs, Shega and Cox-HayleySachs et al, 2004). The length of many dementing illnesses, even in the moderate to severe stages, means that the process of adjustment is often long and drawn out. This has led to the notion of ‘anticipatory grief’ (Reference Sweeting and GilhoolySweeting & Gilhooly, 1990). In addition, the gradual loss of various personal attributes has been called ‘social death’ and the absence of previously cherished interactions adds to the sense of grief (Reference SweetingSweeting, 1991). The result is that the death of a person with dementia can come as a relief: whereas prior to death carers experience considerable stress and strain (Reference Diwan, Hougham and SachsDiwan et al, 2004), after death they can show remarkable resilience (Reference Schulz, Mendelsohn and HaleySchulz et al, 2003).
The practical implications are that families and informal carers require a good deal of extra support during the advanced stages of the disease. This should include not only social support (Reference Almberg, Grafstrom and WinbladAlmberg et al, 2000) but also support in facing the prospect of death (Reference Albinsson and StrangAlbinsson & Strang, 2002). Advance care planning is a way of raising some of the difficult issues that need to be faced while at the same time potentially decreasing futile or burdensome interventions (Reference HertoghHertogh, 2006). Open discussion of these issues to clear up concerns and misconceptions will usually be helpful, especially if families need to clarify their roles and responsibilities once the person with dementia is in long-term care (Reference Caron, Griffith and ArcandCaron et al, 2005).
Psychological, social and spiritual needs
There is obviously a whole other literature on the psychosocial (as opposed to physical) needs of people with dementia (Reference KitwoodKitwood, 1997). In this section we discuss psychological, social and spiritual needs.
The psychological care of people with severe dementia must not be abandoned. When individuals with dementia become immobile, aphasic and totally dependent, it is sometimes said that they ‘only’ require physical nursing. This can even be used as a reason to move a patient from a psychiatry unit to a general nursing unit in the severe stages of the disease. Such moves may be justified on other grounds, but it should not be presumed that skilled psychological approaches become wholly irrelevant. Communication remains possible and in the right hands might produce benefits (Reference Killick and AllanKillick & Allan, 2001). The possibility of lucid moments of conversation remains open (Reference Normann, Norberg and AsplundNormann et al, 2002). Even talk of ‘social death’ needs to be circumspect, because it is not at all clear – neither empirically nor conceptually – that the person or the self has died before his or her biological death (Reference Aquilina, Hughes, Hughes, Louw and SabatAquilina & Hughes, 2006). At one level this means that even in severe dementia the possibility of emotional distress (maybe even frank depression or psychosis) must be considered and treated effectively (Reference Ballard, O'Brien and SwannBallard et al, 2001b ). At another level it means that attempts to facilitate communication and understanding should be pursued into the severer stages of the disease (Reference SabatSabat, 2001).
In addition to the social support and financial advice that carers require, there needs to be greater consideration given to the prior wishes of people with dementia concerning their social care. Reference McCarthy, Addington-Hall and AltmannMcCarthy et al(1997) reported that 41% of the people with dementia died in nursing or residential care. Among those with presenile dementia in England, between 1985 and 1998 the proportion dying in hospital was about 56% (Reference Kay, Forster and NewensKay et al, 2000). In another English study (Reference Keene, Hope and FairburnKeene et al, 2001), which followed 91 people with dementia living at home when recruited, at the last interview before death 40% were still living at home, 44% were permanently living in a nursing home and 17% were living in hospital; between the last interview and death a further 14 (15%) had entered an institution permanently (i.e. almost 76% were institutionalised before death). However, most of us would prefer to die in our homes if possible. The fact that this still seems a long way off in the UK is a point that needs a good deal more consideration. There may be reasons why the person's preferred place of death is simply not practicable: perhaps he or she is living alone or with another frail or disabled partner. However, in large measure the issues are planning, resources and will.
If people with dementia have discussed their preferred place of care at an early stage, along with attendant possible practical problems, it is more likely that supportive services could be planned in advance. But the crucial step is that attention should be paid to the wishes of the person with dementia. In the UK the process of ensuring that all people die as they would wish has been encouraged by the adoption of the Gold Standards Framework (GSF; Reference ThomasThomas, 2003), the Liverpool Care Pathway (Reference Ellershaw and WilkinsonEllershaw & Wilkinson, 2003) and the Preferred Place of Care Plan (http://www.cancerlancashire.org.uk/ppc.html). There is no reason to suppose that similar frameworks and pathways might not work in dementia care (see National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence & Social Care Institute for Excellence, 2006). In individual cases it is possible to provide enough resources to support a person's wish to stay at home, but this often depends on a good deal of determination on the part of the carer. The local services, from the general practitioner to the specialist team (e.g. both old age psychiatry and palliative care), must be willing to provide support.
The personal dimensions of spirituality and faith have tended to be ignored by medical practitioners. Palliative care has helped to lead a returning awareness and respect for such issues (Reference Speck, Higginson and Addington-HallSpeck et al, 2004). People with mental health problems are also concerned with spirituality and are responsive to the attributes of faith (Reference DeinDein, 2004). Spiritual perspectives help to illuminate the nature of personhood in dementia (Reference Allen, Coleman, Hughes, Louw and SabatAllen & Coleman, 2006). Many people have religious beliefs that can be helpful to the way they experience dementia (Reference DavisDavis, 1989). People with dementia and their carers seem to benefit from spiritual support (Reference Dinning and HughesDinning, 2006). Furthermore, the emphasis on the spiritual dimension helps to bring out the extent to which a condition such as dementia, and our approach to it, must be broader than suggested by the narrowness of a purely biomedical model (Reference Downs, Small and FroggattDowns et al, 2006). Dementia can raise deep, existential issues to do with our lives and relationships, so the possibility of spiritual advice and support should be open to all.
Conclusions
There is an increasing interest in palliative care in dementia and much good work goes on (largely unnoticed) in the field. However, there are questions about how best to provide good-quality palliative care for people with dementia in a manner that becomes embedded as good practice. There is a need, therefore, for continuing debate and research. None of the issues is straightforward. Moreover, this field amply demonstrates the extent to which clinical decisions are often ethical decisions. The ethical imperative must be to maintain or improve the quality of life, even at its end (Reference Hughes and BaldwinHughes & Baldwin, 2006). This aspiration helps to drive the palliative care movement. It should also be a potent motivating force in psychiatric practice wherever the care of dying patients is commonplace.
Declaration of interest
None.
MCQs
-
1 The palliative care approach:
-
a has a good evidence base for adoption for dementia
-
b ensures routine access to hospice care for people dying with dementia
-
c can be equated with good-quality person-centred dementia care
-
d suggests that antibiotics should be used more frequently in severe dementia
-
e emphasises the involvement of families over and above the importance of spiritual care.
-
-
2 Barriers to good-quality palliative dementia care include:
-
a the realisation that dementia is a life-shortening condition
-
b the lack of advance care planning
-
c good prognostication in dementia
-
d failure to recognise the relevant issues in the literature
-
e failure to recognise the need for improvement in terms of services.
-
-
3 Pain in severe dementia:
-
a is easily recognised
-
b is always treated effectively
-
c is the sole cause of distress
-
d can be managed by a stepped-care approach
-
e is reliably detected by pain assessment tools.
-
-
4 Concerning treatment in severe dementia:
-
a when there is a fever, antipyretics and analgesia may be a better response than antibiotics
-
b as dementia advances, PEG feeding becomes almost mandatory
-
c the odds in favour of successful CPR are significantly better than those seen in metastatic cancer
-
d the requirement for skilled nursing lessens as dementia worsens
-
e bladder and bowel problems are uncommon.
-
-
5 The correct approach to people with severe dementia:
-
a is to favour biological treatments over psychosocial interventions
-
b is to avoid complementary therapy at all costs
-
c is to avoid attempts to communicate with the person, on the grounds that he or she is socially dead
-
d is to avoid antidepressant medication at all costs
-
e is to recognise the increasing support required by family carers as the disease progresses.
-
MCQ answers
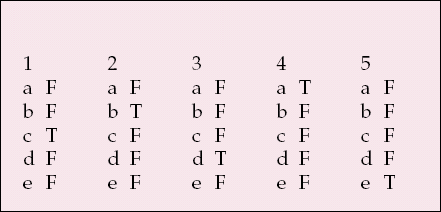
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | F | a | F | a | F | a | T | a | F |
| b | F | b | T | b | F | b | F | b | F |
| c | T | c | F | c | F | c | F | c | F |
| d | F | d | F | d | T | d | F | d | F |
| e | F | e | F | e | F | e | F | e | T |





eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.