No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
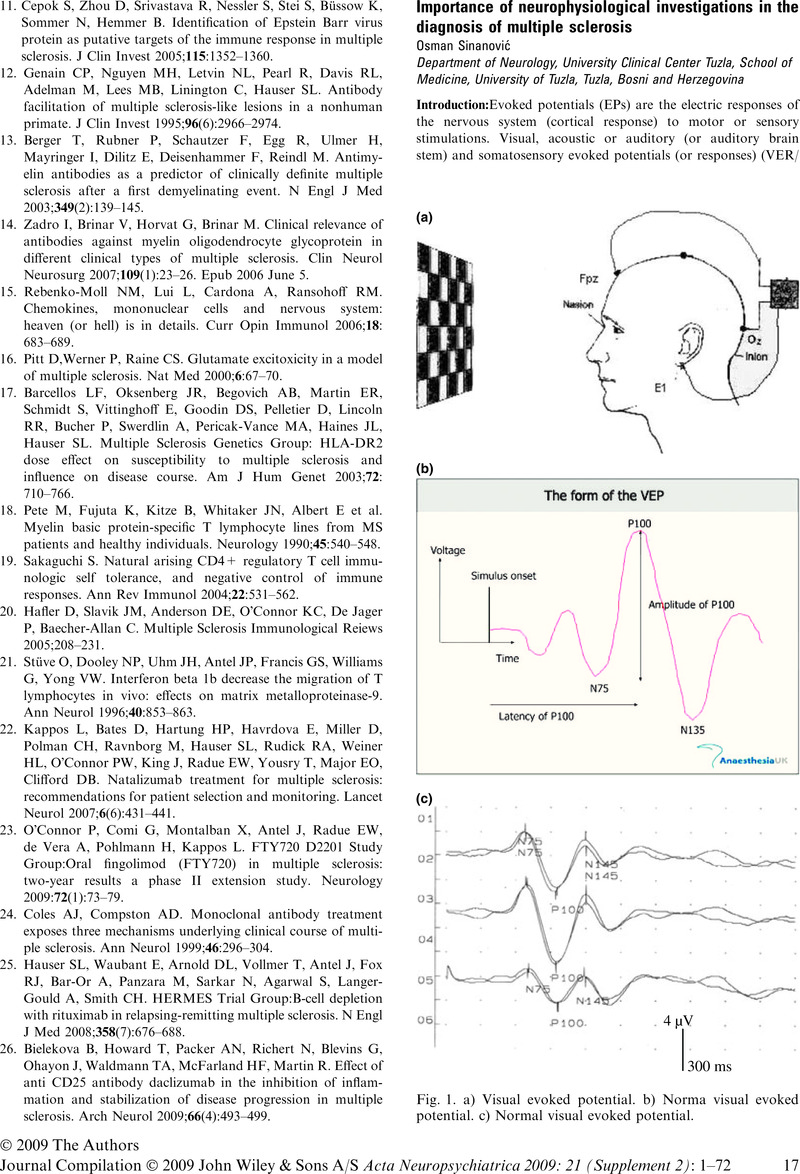
Importance of neurophysiological investigations in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 June 2014
Abstract
An abstract is not available for this content so a preview has been provided. Please use the Get access link above for information on how to access this content.
- Type
- Main Theme: Multiple Sclerosis
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S
References
References:
1.Misulis, EK. Spehlmann's Evoked Potential Primer. Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, 1994.Google Scholar
2.Chiappa, HK, Hill, AR. Pattern-Shift Visual Evoked Potentials: Interpretation. In: Chiappa, HK (ed). Evoked Potentials in Clinical Medicine. Lippincot-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, 1997:95–146.Google Scholar
3.Odom, JV, Bach, M, Barber, C, Brigell, M, Marmor, MF, Patrizia Tormene, A, Holder, GE. Visual evoked potentials standard (2004). Doc Ophtal 2004;108: 115–123.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
4.Barbato, L, Rinalduzzi, S, Laurenti, M, Ruggieri, S, Accornero, N.Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1994;2:169–172.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
5.Ellis, JS. Clinical Neurology: Essential Concepts. Butterwort Heinemann: Oxford, 1998.Google Scholar
6.Weinstock-Guttman, B, Baier, M, Stockton, Ret al.Pattern reversal visual evoked potentials as a measure of visual pathway pathology in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 2003; 9(5):529–534.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
7.Fischer, C, Andre-Obadia, N, Mauguiere, F. Diagnostic criteria of multiple sclerosis: electrophysiological criteria. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2001:157(8-9 Pt 2):974–980.Google ScholarPubMed
8.McDonald, WI, Compston, A, Edan, G, Goodkin, D, Hartung, HP, Lublin, FD, McFarland, HF, Paty, DW, Polman, CH, Reingold, SC, Sandberg-Wollheim, M, Sibley, W, Thompson, A, van den Noort, S, Weinshenker, BY, Wolinsky, JS. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2001;50(1):121–127.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
9.Polman, CH, Reingold, SC, Edan, G, Filippi, M, Hartung, HP, Kappos, L, Lublin, FD, Metz, LM, McFarland, HF, O'Connor, PW, Sandberg-Wollheim, M, Thompson, AJ, Weinshenker, BG, Wolinsky, JS. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann Neurol 2005;58(6):840–846.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
10.Miller, DH, Newton, MR, van der Poel, JC, du Boulay, EP, Halliday, AM, Kendall, BE, Johnson, G, MacManus, DG, Moseley, IF, McDonald, WI. Magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve in optic neuritis. Neurology 1988;38(2):175–179.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
11.Sinanović, O. Visual and auditory evoked potentials in multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and brain steam vascular lesions. Radovi (Akademije nauka Bosne i Hercegovine). Knjiga 3. 2004;101–112.Google Scholar
13.Drislane, FW. Use of evoked potentials in the diagnosis and follow-up of multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurosci 1994, 2(3-4):196–201.Google ScholarPubMed
14.Walsh, P, Kane, N, Butler, S. The clinical role of evoked potentials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2005;76 (Suppl 2):ii16–22.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
15.Alshuaib, WB. Progression of visual evoked potential abnormalities in multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 2000;40(4): 243–252.Google ScholarPubMed
16.Fraser, C, Klistorner, A, Graham, S, Garrick, R, Billson, F, Grigg, J. Arch Neurol 2006;63(6):847–850.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
17.Sater, RA, Rostami, AM, Galetta, S, Farber, RE, Bird, SJ. Serial evoked potential studies and MR imaging in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 1999;171:79–83.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
18.Turker, H, Terzi, M, Bayrak, O, Cengiz, N, Onar, M, Us, O. Visual evoked potentials in different diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and neeurobehcet's disease. Tohoku J Exp Med 2008;216(2):109–116.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
19.Djuricic, V, Djuricic, S, Jolic, M. Diagnostic value ofmultimodal evoked potential in patients with multiple sclerosis. Int Cong Ser 2005;1278:160–162.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
20.Rico, A, Audoin, B, Franques, J, Eusebio, A, Reuter, F, Malikova, I, Ali Cherif, A, Pouget, J, Pelletier, J, Attarian, S. Motor evoked potentials in clinically isolated syndrome suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 2009;15(3): 355–362.CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed


