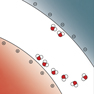
Water at functional interfaces. The structure of water—its molecular packing, orientation, organization, and electronic structure—has become central to understanding water-mediated interactions. The articles in this issue of MRS Bulletin address how the structure and dynamics of water respond in the chemical and topographical context, how these phenomena can be investigated, and their implications. The cover shows some examples of water-mediated interactions at interfaces. The top image shows a particle that goes to a water–vapor interface and sticks out the hydrophobic half on the vapor side, while the hydrophilic part is hydrated with “blue and white” water molecules in the fi rst shell. The middle image is primarily a beta-sheet protein, except for the fl exible loops. Some of the water molecules that hydrate this protein are shown in blue (oxygen) and white (hydrogen). The bottom image shows a patterned self-assembled monolayer and its hydration. See the technical theme that begins on page 1051.
Water at Functional Interfaces
Introduction
Water at functional interfaces
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1051-1053
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Other
Meet Our Authors
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1054-1055
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Water at Functional Interfaces
Research Article
Hydration layer structure at solid–water interfaces
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1056-1061
-
- Article
- Export citation
Understanding interfacial water and its role in practical applications using molecular simulations
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1062-1067
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanoparticle–protein interactions: Water is the key
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1069-1073
-
- Article
- Export citation
Water in clay nanopores
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1074-1081
-
- Article
- Export citation
Local water diffusivity as a molecular probe of surface hydrophilicity
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1082-1088
-
- Article
- Export citation
Particles at fluid–fluid interfaces: From single-particle behavior to hierarchical assembly of materials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1089-1098
-
- Article
- Export citation
Technical Feature
Research Article
Next-generation electrocaloric and pyroelectric materials for solid-state electrothermal energy interconversion
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1099-1111
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy Quarterly
Editorial
Editorial
News and analysis on materials solutions to energy challenges: www.mrs.org/energy-quarterly | www.materialsforenergy.org
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, p. 1045
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy Sector Analysis
Research Article
Solid-state batteries enter EV fray
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1046-1047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cement performance impacts integrity of oil and gas wells
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1048-1050
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
News & Analysis
Materials News
Other
GaN microrods on graphene substrates enable bendable optoelectronics devices
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, p. 1037
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hybrid device functions as self-recovering electrochromic window and self-charging battery
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1037-1038
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Giant spin-splitting revealed on SrTiO3 surface
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, p. 1038
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thinnest generator of electricity
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, p. 1039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Digital metamaterial bits for simpler optical elements
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1039-1040
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tailored flexible illusion coatings hide objects from detection
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1040-1041
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Science Policy
Other
Norway’s materials scientists are cracking the glass ceiling
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1042-1043
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
NIST releases tool for evaluating building performance: http://birdscom.nist.gov
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2014, pp. 1043-1044
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation