The quotient set of 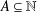 $A\subseteq \mathbb{N}$ is defined as
$A\subseteq \mathbb{N}$ is defined as 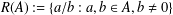 $R(A):=\{a/b:a,b\in A,b\neq 0\}$. Using algebraic number theory in
$R(A):=\{a/b:a,b\in A,b\neq 0\}$. Using algebraic number theory in 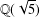 $\mathbb{Q}(\sqrt{5})$, Garcia and Luca [‘Quotients of Fibonacci numbers’, Amer. Math. Monthly, to appear] proved that the quotient set of Fibonacci numbers is dense in the
$\mathbb{Q}(\sqrt{5})$, Garcia and Luca [‘Quotients of Fibonacci numbers’, Amer. Math. Monthly, to appear] proved that the quotient set of Fibonacci numbers is dense in the 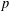 $p$-adic numbers
$p$-adic numbers 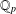 $\mathbb{Q}_{p}$ for all prime numbers
$\mathbb{Q}_{p}$ for all prime numbers 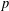 $p$. For any integer
$p$. For any integer 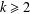 $k\geq 2$, let
$k\geq 2$, let 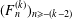 $(F_{n}^{(k)})_{n\geq -(k-2)}$ be the sequence of
$(F_{n}^{(k)})_{n\geq -(k-2)}$ be the sequence of  $k$-generalised Fibonacci numbers, defined by the initial values
$k$-generalised Fibonacci numbers, defined by the initial values 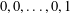 $0,0,\ldots ,0,1$ (
$0,0,\ldots ,0,1$ (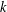 $k$ terms) and such that each successive term is the sum of the
$k$ terms) and such that each successive term is the sum of the 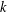 $k$ preceding terms. We use
$k$ preceding terms. We use 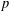 $p$-adic analysis to generalise the result of Garcia and Luca, by proving that the quotient set of
$p$-adic analysis to generalise the result of Garcia and Luca, by proving that the quotient set of 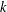 $k$-generalised Fibonacci numbers is dense in
$k$-generalised Fibonacci numbers is dense in 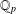 $\mathbb{Q}_{p}$ for any integer
$\mathbb{Q}_{p}$ for any integer 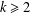 $k\geq 2$ and any prime number
$k\geq 2$ and any prime number 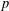 $p$.
$p$.
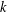 $k$-GENERALISED FIBONACCI NUMBERS IS DENSE IN
$k$-GENERALISED FIBONACCI NUMBERS IS DENSE IN 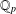 $\mathbb{Q}_{p}$
$\mathbb{Q}_{p}$