The fertilisation calcium wave in sea urchin eggs triggers the onset of development. The wave is an explosive increase in intracellular free calcium concentration 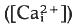 that begins at the point of sperm entry and crosses the egg in about 20 s. Thimerosal is a sulphydryl reagent that sensitises calcium release from intracellular stores in a variety of cell types. Treatment of unfertilised eggs with thimerosal causes a slow increase
that begins at the point of sperm entry and crosses the egg in about 20 s. Thimerosal is a sulphydryl reagent that sensitises calcium release from intracellular stores in a variety of cell types. Treatment of unfertilised eggs with thimerosal causes a slow increase 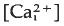 that results eventually in a large, spontaneous calcium transient and egg activation. At shorter times after thimerosal treatment, egg activation and the calcium transient can be triggered by calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels, a form of calcium-induced/calcium release (CICR). Thimerosal treatment also reduces the latency of the fertilisation calcium response and increases the velocity of the fertilisation wave. These results indicate that thimerosal can unmask CICR in sea urchin eggs and suggest that the ryanodine receptor channel based CICR may contribute to explosive calcium release during the fertilisation wave.
that results eventually in a large, spontaneous calcium transient and egg activation. At shorter times after thimerosal treatment, egg activation and the calcium transient can be triggered by calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels, a form of calcium-induced/calcium release (CICR). Thimerosal treatment also reduces the latency of the fertilisation calcium response and increases the velocity of the fertilisation wave. These results indicate that thimerosal can unmask CICR in sea urchin eggs and suggest that the ryanodine receptor channel based CICR may contribute to explosive calcium release during the fertilisation wave.