Article contents
Observation of Meyer-Neldel rule in amorphous films of Ge1–xSe2Pbx
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 January 2009
Abstract
Electrical conductivity was performed on amorphous thin films of
Ge1–xSe2Pbx (with x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8) as a
function of temperature in the range 300–450 K. The experimental results
indicate that the conduction is through thermally activated process having two
conduction mechanisms. In the first region at high-temperatures range, the
values of $\sigma _{o}$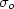 suggest that the dominant conduction of charge
carriers changes from the extended states to the localized states in the
band tails at composition x = 0.8. The experimental results have also been
analyzed using Meyer-Neldel Rule. The other one appears in the low
temperatures region and the conductivity has been analyzed using Mott's
variable range hopping conduction. Mott's parameters were calculated for
Ge1–xSe2Pbx films.
suggest that the dominant conduction of charge
carriers changes from the extended states to the localized states in the
band tails at composition x = 0.8. The experimental results have also been
analyzed using Meyer-Neldel Rule. The other one appears in the low
temperatures region and the conductivity has been analyzed using Mott's
variable range hopping conduction. Mott's parameters were calculated for
Ge1–xSe2Pbx films.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2008
References
- 4
- Cited by




