Article contents
Renormalization for Lorenz maps of monotone combinatorial types
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 May 2017
Abstract
Lorenz maps are maps of the unit interval with one critical point of order 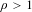 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}>1$ and a discontinuity at that point. They appear as return maps of sections of the geometric Lorenz flow. We construct real a priori bounds for renormalizable Lorenz maps with certain monotone combinatorics and a sufficiently flat critical point, and use these bounds to show existence of periodic points of renormalization, as well as existence of Cantor attractors for dynamics of infinitely renormalizable Lorenz maps.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}>1$ and a discontinuity at that point. They appear as return maps of sections of the geometric Lorenz flow. We construct real a priori bounds for renormalizable Lorenz maps with certain monotone combinatorics and a sufficiently flat critical point, and use these bounds to show existence of periodic points of renormalization, as well as existence of Cantor attractors for dynamics of infinitely renormalizable Lorenz maps.
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2017
References
- 1
- Cited by




