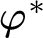When embedding data are used to argue against semantic theory A and in favor of semantic theory B, it is important to ask whether A could make sense of those data. It is possible to ask that question on a case-by-case basis. But suppose we could show that A can make sense of all the embedding data which B can possibly make sense of. This would, on the one hand, undermine arguments in favor of B over A on the basis of embedding data. And, provided that the converse does not hold—that is, that A can make sense of strictly more embedding data than B can—it would also show that there is a precise sense in which B is more constrained than A, yielding a pro tanto simplicity-based consideration in favor of B. In this paper I develop tools which allow us to make comparisons of this kind, which I call comparisons of potential expressive power. I motivate the development of these tools by way of exploration of the recent debate about epistemic modals. Prominent theories which have been developed in response to embedding data turn out to be strictly less expressive than the standard relational theory, a fact which necessitates a reorientation in how to think about the choice between these theories.