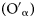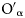A series of metal oxides (MnFeOx, MnCrOx, MnTiOx, and MnFeTiOx) supported on attapulgite (ATP) were synthesized by coprecipitation for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx with NH3. Then, they were subjected to appropriate characterizations for their properties (XRD, TEM, BET, XPS, etc.). The catalytic activity of MnFeTiOx/ATP catalyst was over 95% NOx conversion within a wide temperature window between of 175 and 300 °C, and 88% N2 selectivity. Moreover, MnFeTiOx/ATP presented excellent potassium resistance relative to the traditional V–W–Ti catalyst, and its denitration performance was significantly improved. The NOx conversion rate could be restored to nearly 90% at 210 °C after removing potassium via washing of K–MnFeTiOx/ATP. In addition, the MnFeTiOx/ATP showed better SO2 resistance and stability than the traditional V–W–Ti catalyst. Therefore, the MnFeTiOx/ATP catalyst has been proved to have broad prospects in NH3-SCR.