We characterize the star formation going on in the inner kiloparsec region of the galaxy NGC 1386 as derived from the analysis of a multiwavelength dataset covering the optical, near-IR and mid-IR at subarsec resolution. We detect 61 point sources, distributed in a ring of 960 pc radius around the center of the galaxy. From SED fitting we conclude that these are low mass (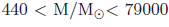 ) young clusters, with age distributed from 1 to 10 Myr, with median at 3.6 Myr. Comparison of the Hα luminosity of the clusters derived from the Hα+[N ii] narrow band image with that expected from the fitted ionizing continuum shows that a large fraction of the ionizing photons escapes from the clusters. Moreover, a large fraction of these photons escapes from the regions around the star forming ring.
) young clusters, with age distributed from 1 to 10 Myr, with median at 3.6 Myr. Comparison of the Hα luminosity of the clusters derived from the Hα+[N ii] narrow band image with that expected from the fitted ionizing continuum shows that a large fraction of the ionizing photons escapes from the clusters. Moreover, a large fraction of these photons escapes from the regions around the star forming ring.

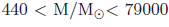 ) young clusters, with age distributed from 1 to 10 Myr, with median at 3.6 Myr. Comparison of the H
) young clusters, with age distributed from 1 to 10 Myr, with median at 3.6 Myr. Comparison of the H