A method for gyrokinetic simulation of low frequency (lower than the cyclotron frequency) magnetic compressional modes in general geometry is presented. The gyrokinetic-Maxwell system of equations is expressed fully in terms of the compressional component of the magnetic perturbation, δB∥, with finite Larmor radius effects. This introduces a “gyro-surface” averaging of δB∥ in the gyrocenter equations of motion, and similarly in the perpendicular Ampere’s law, which takes the form of the perpendicular force balance equation. The resulting system can be numerically implemented by representing the gyro-surface averaging by a discrete sum in the configuration space. For the typical wavelength of interest (on the order of the gyroradius), the gyro-surface averaging can be reduced to averaging along an effective gyro-orbit. The phase space integration in the force balance equation can be approximated by summing over carefully chosen samples in the magnetic moment coordinate, allowing for an efficient numerical implementation.

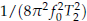 if the observation time
if the observation time 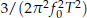 which is one order more precise than the ±1 count error induced precision of a typical frequency counter. Analysis of this method shows that the integration reduces the noise by bandwidth narrowing as in a lock-in amplifier, and no extra signal filters are needed. For a pure sinusoidal signal we find from numerical simulations that the noise-induced error in this method reaches the Cramer-Rao Lower Band (CRLB) on frequency determination. For the damped sinusoidal case of most interest, the noise-induced error is found to be within a factor of 2 of CRLB when the measurement time
which is one order more precise than the ±1 count error induced precision of a typical frequency counter. Analysis of this method shows that the integration reduces the noise by bandwidth narrowing as in a lock-in amplifier, and no extra signal filters are needed. For a pure sinusoidal signal we find from numerical simulations that the noise-induced error in this method reaches the Cramer-Rao Lower Band (CRLB) on frequency determination. For the damped sinusoidal case of most interest, the noise-induced error is found to be within a factor of 2 of CRLB when the measurement time 