Increasing evidence suggests that the UK population is iodine insufficient(Reference Vanderpump, Lazarus and Smyth1, Reference Bath and Rayman2). Iodine is essential for the infant's brain development during pregnancy and lactation and iodine deficiency is the most preventable cause of brain damage worldwide. This study aimed to assess the iodine status of breastfeeding mothers in the area of Glasgow, UK.
Recruitment for the survey took place in Greater Glasgow, UK, during June–July 2013 and February-March 2014. Dietary habits were recorded using a validated iodine-specific food frequency questionnaire(Reference Combet and Lean3). Urinary iodine concentration (UIC) was measured using the Sandell-Kolthof colorimetric method on casual spot samples, and corrected for creatinine excretion.
A total of 168 breastfeeding mothers were recruited during summer 2013 (n = 103) and winter 2014 (n = 65). Mean age was 34 years (SD 4). They were mainly non-smokers (98%) with a normal BMI of 22·7 (IQR 20·7–25·7). There was no vegan, and only 1·8% reported using iodised salt. Median age of the babies was 26 weeks (IQR 15–35).
The median population UIC was 79 μg/l (IQR 43–120), lower than the WHO recommended threshold for lactation (100 μg/l), indicating mild iodine insufficiency. Although 63% of the participants consumed supplements, less than half (45%) contained iodine. Average iodine intake was 150 μg/day (IQR 105–196), 169 μg/day (IQR115–196) including supplements. Only 19% and 11% of mothers reached the intake threshold (≥250 μg/day) with and without supplements, respectively. Women who consumed iodised supplements were more likely to have sufficient iodine intake (p = 0·002) but there was no difference in UIC (p = 0·6) or UIC corrected for creatinine excretion (p = 0·8) between those consuming supplements or not. Similarly, no difference was seen between summer and winter samples or mothers with younger and older babies (>6 months) for UIC, dietary or total iodine intake. UIC corrected with creatinine was higher in the winter sample (p < 0·001).
Milk was the main source of dietary iodine, contributing toward 38% of the dietary iodine intake, with higher consumption in those with sufficient total iodine intake (p < 0·001).
While older and well educated, this sample still did not achieve the recommended iodine intake, and the population UIC was below the threshold for sufficiency. The use of supplements may be able to improve the iodine status of lactating women.
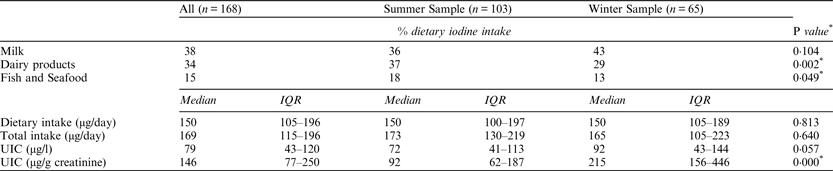
Mann-Whitney U test, *p < 0·05, statistically significant difference between summer and winter samples.


