BACKGROUND
The need for translational researchers in medicine is challenged by a decline in physicians choosing research in their career pathway.Reference Hall, Mills and Lund1 One approach to reverse this trend is through cultivation of interest early in a medical trainee's career. Medical students who publish before graduation are reportedly more likely to publish after graduation, obtain a PhD or higher degree, and attain an academic position after graduation.Reference Waaijer, Ommering, van der Wurff, van Leeuwen and Dekker2–Reference Jacobsen, Raeder, Stien, Munthe and Skogen4
Research skills are a key competency in the Canadian Medical Education Directives for Specialists (CanMEDS) framework for physicians to transition to practice.Reference Frank5 However, trainees’ impressions of their research experiences are mixed. A review of the literature on medical students’ perceptions of research programs reported that students generally perceive their medical school research experiences to be positive in terms of stimulating research interest and developing scholarly research activities, but noted negative student perceptions, including too little acknowledgement, time, and faculty interaction.Reference Chang and Ramnanan6 Patel et al. performed a cross-sectional survey among 46 Canadian summer student research programs (SSRPs). Most programs (78.3%) required students to independently secure a research supervisor, 61.4% were integrated into a formal curriculum, but few (5.9%) offered an integrated clinical observership.Reference Patel, Walsh and Udell7
PURPOSE OR RATIONALE
The Summer Training and Research in Emergency Medicine (STAR-EM) 10-week program had the following primary goals for students: enrichment in research methodologies, design, and execution of a research project in conjunction with a dedicated research mentor to the point of presentation of results and manuscript preparation, and practical exposure to research in an academic emergency department (ED) through involvement in mentor-initiated projects. A secondary goal was stimulation of career interest in academic emergency medicine (EM) with a curriculum that included regular faculty interaction and clinical exposure.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INNOVATION
Five second-year Ontario medical students were recruited in early 2019 to participate in the STAR-EM program at a University of Toronto teaching hospital, from June to August, 2019.
The program had broad emergency physician (EP) engagement and was comprised of Program Director (S.M.F.) and Co-Director (D.P.) with five EP Research Faculty who served as project mentors, and 12 EP Teaching Faculty delivering academic sessions. All projects were approved by the hospital research ethics board (REB). Program curriculum was designed by the teaching faculty informed by Kern's six-step model for curriculum development.Reference Kern, Thomas, Howard and Bass8 Problem identification and general needs assessment included review of existing summer research programsReference Chang and Ramnanan6,Reference Patel, Walsh and Udell7 and literature regarding challenges to undertaking ED research.Reference McRae, Perry and Brehaut9 A research methods faculty subgroup conducted a targeted needs assessment of STAR-EM students. The goals and objectives were developed from the problem identification and needs assessment phases, which then informed the specific teaching sessions. Program evaluation by students and faculty occurred at the end of week 10.
Each weekly academic morning comprised faculty-led small group teaching of the STAR-EM curriculum, followed by group progress review of each student's project. Students were provided 10 weeks of funding and a dedicated workspace. Each student spent 1 half-day per week in the ED, shadowing an EP on duty and also identifying patients for recruitment for four ongoing mentor-initiated ED research projects. Supplemental clinical enrichment included afternoon “boot camps” each in resuscitation simulation and point of care ultrasound. The remaining time was spent on independent student project work. Project methodologies included scoping reviews, chart and electronic data-base review, and stakeholder interviews. Presentation of study results to faculty and program evaluation occurred in week 10 (see Figure 1).
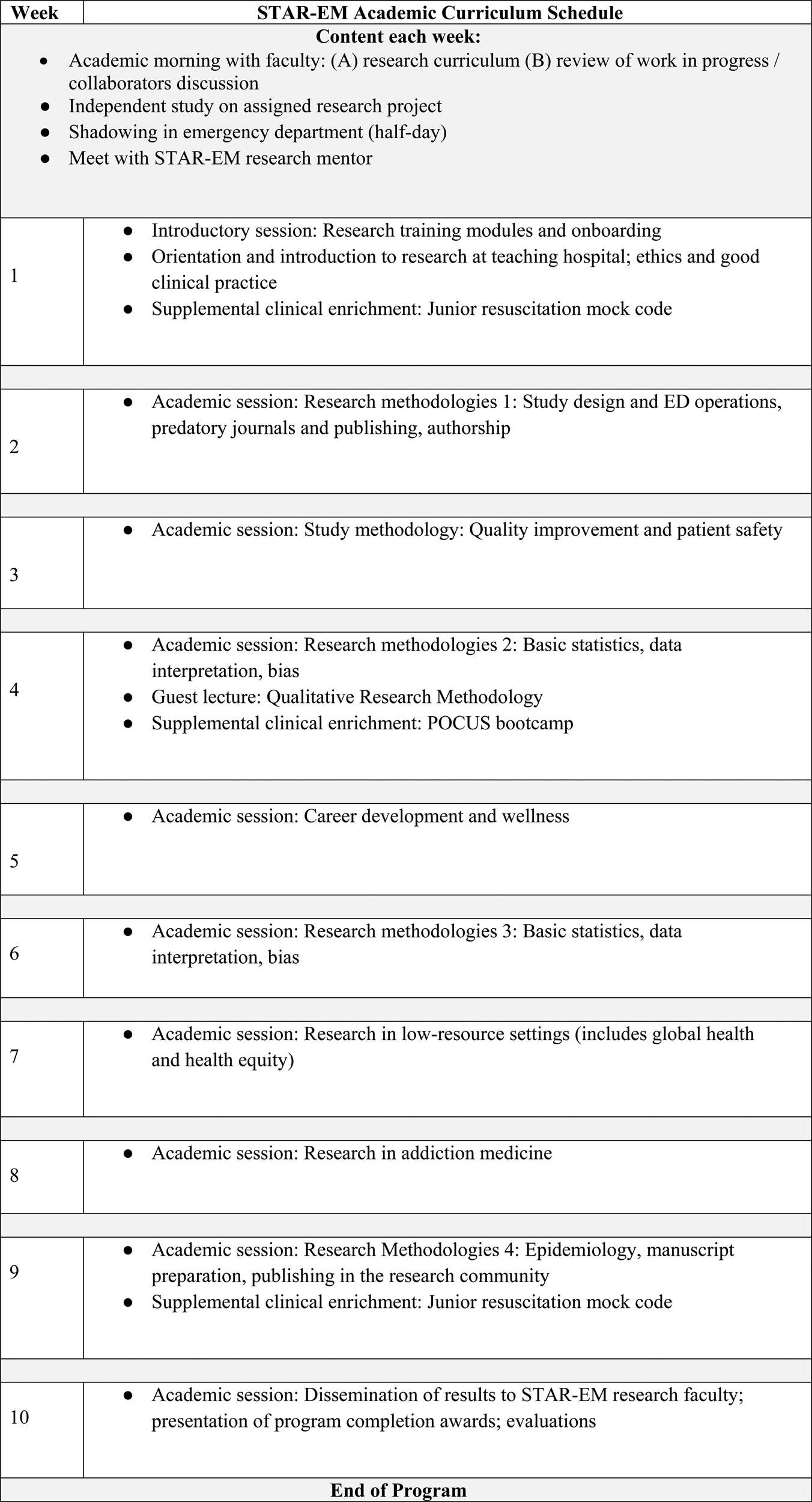
Figure 1. STAR-EM academic curriculum outline.
Program evaluation was informed by Kirkpatrick's model of learning evaluation: reaction, learning, behavioral change, organizational performance.Reference Kurt10 At the reactions and learning level, student evaluations reflected a uniform impression that course material and mentorship were each excellent (100%; n = 5). At the level of behavioral change, interest in pursuing academic EM as a career was identified by all students. At the level of organizational performance, faculty researchers who served as mentors rated the program as very effective (80%; N = 4) or somewhat effective (20%; n = 1) in terms of enhancing their own research productivity and scholarly output. Scholarly output included acceptance of at least one abstract for presentation at a national scientific meeting for four of five students. Outcomes could not be measured at this stage of the innovation; however, longitudinal follow-up of participants over several cohorts could inform whether or not this program truly promotes a career in academic EM.
DISCUSSION
Research programs for medical trainees have cited lack of protected time, availability of resources, inaccessibility of research mentors, and lack of acknowledgment as barriers to research.Reference Chang and Ramnanan6 The STAR-EM program was successful in cultivating EM research interest and skills in undergraduate medical trainees, and supporting research engagement among ED clinicians. Future program evaluation will include focus groups for qualitative assessment of program effectiveness and recommendations for change, and longitudinal assessment of student career path and engagement with research.
LIMITATIONS
Resources required included student funding and faculty participation in research mentorship and delivery of curriculum. Most academic departments in Canada do not have 12 research faculty to support a 5 student curriculum. Collaboration between institutions could enable economy of scale. Curriculum delivery by other sites will be facilitated with future on-line publication of STAR-EM content. Program evaluation by students and staff was anonymous but surveyed small groups, and is vulnerable to response bias.
SUMMARY
The STAR-EM program goes beyond the traditional summer research program goal of having a student complete and disseminate a scholarly project. This innovation provides a comprehensive research curriculum using the expertise of several faculty, but also includes clinical opportunities and deliberate mentorship toward a career in academic EM. This program has the potential to increase the number of physicians choosing Clinician Investigator career pathway for their career.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Joel Lexchin for his contributions to the STAR-EM program and to the manuscript.



