Gondi is a Dravidian language spoken by 2.2 million speakers (Census of India 1981) in the mountains and forests of four adjacent states in central India. Gondi is a chain of several dialects, some of which, at distant points, are perhaps not mutually intelligible. A major dialect division is provided by a two-step sound change: s- > h- in the west, north, and northwest and h- > 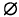 - in the south and southeast. The present article studies this two-step sound change, which is still in progress, and establishes two facts. First, contrary to the normal expectation that this sound change would be phonetically gradual and lexically abrupt (Neogram-marian type), there is evidence that it has been lexically gradual and perhaps also phonetically gradual (lexical diffusion). Second, phonetic gradualness and regularity in implementation of sound change are properties not incompatible with the mechanism of lexical diffusion. Labov's observation that s > h >
- in the south and southeast. The present article studies this two-step sound change, which is still in progress, and establishes two facts. First, contrary to the normal expectation that this sound change would be phonetically gradual and lexically abrupt (Neogram-marian type), there is evidence that it has been lexically gradual and perhaps also phonetically gradual (lexical diffusion). Second, phonetic gradualness and regularity in implementation of sound change are properties not incompatible with the mechanism of lexical diffusion. Labov's observation that s > h > 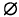 has not been reported as a lexically diffused change in many quantitative studies of Portuguese and Spanish (1981) finds a clear exception in Gondi. Under the lexical diffusion model, the regularity of a sound change is defined as the final outcome in a three-stage change of the relevant lexicon: unchanged (u), variant (u ˜ c), and changed (c). If the entire eligible lexicon passed from u to c through u ˜ c, the change would become regular. If all u ˜ c became c and for some reason no item under u became u ˜ c, the sound change would die prematurely, since the variant stage which provided the rule for the innovation would be absent. Since a regular sound change can result from either the Neogrammarian model or the lexical diffusion model, Labov's (1994:542–543) theoretical proposal of complementarity between the kinds of changes resulting from the two mechanisms calls for more studies of sound change in progress to decide the issue.
has not been reported as a lexically diffused change in many quantitative studies of Portuguese and Spanish (1981) finds a clear exception in Gondi. Under the lexical diffusion model, the regularity of a sound change is defined as the final outcome in a three-stage change of the relevant lexicon: unchanged (u), variant (u ˜ c), and changed (c). If the entire eligible lexicon passed from u to c through u ˜ c, the change would become regular. If all u ˜ c became c and for some reason no item under u became u ˜ c, the sound change would die prematurely, since the variant stage which provided the rule for the innovation would be absent. Since a regular sound change can result from either the Neogrammarian model or the lexical diffusion model, Labov's (1994:542–543) theoretical proposal of complementarity between the kinds of changes resulting from the two mechanisms calls for more studies of sound change in progress to decide the issue.
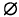 in Gondi dialects
in Gondi dialects

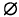 in Gondi dialects
in Gondi dialects