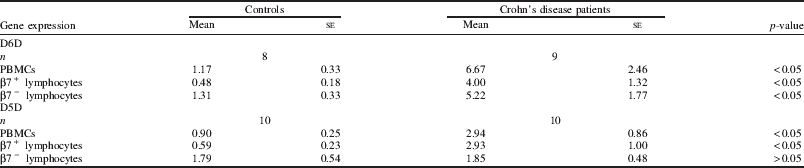
Crohn's disease (CD) is a long-term condition that causes inflammation of the lining of the digestive system. Inflammation can affect any part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the back passage, but most commonly occurs in the last section of the small intestine (ileum) or the large intestine (colon)( Reference Fiorino, Bonifacio, Malesci, Balzarini and Danese 1 ). Two rate-limiting enzymes, delta-6 desaturase (D6D) and delta-5 desaturase (D5D), are involved in the production of the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)( Reference Xiang, Rahman, Ai, Li and Harbige 2 ). Fatty acid metabolism is involved in the immune response and inflammation processes( Reference Harbige 3 ) in patients with CD. Fatty acid changes may be relevant to the clinical course of CD( Reference Westcott, Mattacks, Windsor, Knight and Pond 4 ). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) may be a useful, easily available and sensitive marker of the response of D5D and D6D genes to CD. The β7 integrin family of adhesion molecules on circulating lymphocytes may play a significant part in trafficking and localisation to the gut in CD( Reference Meenan, Spaans, Grool, Pals, Tytgat and van Deventer 5 ). The present study compared the expression of the D6D and D5D genes in PBMCs, β7+ and β7− lymphocytes between CD patients and healthy controls. Ten patients with recently diagnosed CD and ten healthy controls were studied. The expression of D6D and D5D genes in PBMCs was higher in CD patients than in healthy controls (Table). The patients with CD also had higher expression of D6D and D5D genes in β7+ lymphocytes than healthy controls (Table). Furthermore, the expression of D6D gene in β7− lymphocytes was higher in CD patients than healthy controls (Table). However, no significant differences were found in D5D gene expression of β7− lymphocytes between CD patients and healthy controls (Table). These results may indicate that the higher D6D and D5D genes expression in PBMCs, β7+ and (or) β7− lymphocytes in patients with CD is required to promote active desaturation of LA to maintain arachidonic acid (AA, C20:4ω-6) levels which we have previously reported are severely depleted in lymphocytes in CD and are essential for the functions of these cells( Reference Harbige 3 , Reference Westcott, Mattacks, Windsor, Knight and Pond4 ).