Article contents
High-Deposition-Rate a-Si:H Through VHF-CVD of Argon-Diluted Silane
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2011
Abstract
We discuss various ways to produce hydrogenated amorphous silicon, a-Si:H, at a high deposition rate. We also present results of our recent study on the structural properties of a-Si:H films deposited at high rates using argon (Ar) dilution of silane in a 50-MHz glow discharge. The results of the depositions with Ar dilution are compared to films deposited from pure silane, SiH4. The deposition rate rd is changed by varying the rf power Prf into the discharge. We focus on the Prf-dependence of the hydrogen (H) bonding configuration and total H content in the film. It is observed that rd saturates at 14 Å/s for pure SiH4, and at 22 Å/s for Ar-diluted SiH4 deposition. Upon increase of Prf the H bonding configuration changes from mostly isolated H to mostly clustered H, and back to mostly isolated H. It is argued that Ar* metastable atoms play an important role in the growth mechanism at intermediate Prf, whereas at high Prf ion bombardment through Ar+ and 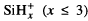 ions becomes crucial. Two high-rate a-Si:H films are incorporated in thin-film transistors, TFTs. We present their characteristics before and after illumination with calibrated light. It is shown that a-Si:H TFTs with a saturation mobility of 0.7 cm2/Vs can be fabricated, with the complete intrinsic layer deposited at 20 Å/s.
ions becomes crucial. Two high-rate a-Si:H films are incorporated in thin-film transistors, TFTs. We present their characteristics before and after illumination with calibrated light. It is shown that a-Si:H TFTs with a saturation mobility of 0.7 cm2/Vs can be fabricated, with the complete intrinsic layer deposited at 20 Å/s.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1997
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by


