Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 May 2022
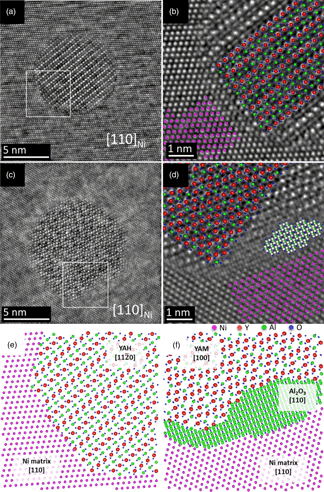
Nanocrystalline oxides are mainly responsible for Ni-base oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) superalloys excellent thermo-mechanical properties. To establish the microstructural correlations between the metallic matrix and various oxide dispersoids, we report here the atomic-scale structure and chemistry of the complex nano-oxide dispersoids. Ultrahigh-resolution Cs-aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) based techniques have been used to resolve nano-dispersoids in the Alloy 617 ODS. These nano-oxides, interestingly, possess a variety of high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) contrasts, that is, bright, dark, and bi-phases. Both the light and heavy atoms have been found to be present in Y–Al–O complex-oxide nanostructures in varying quantities and forming a characteristic interface with the metallic matrix. In overcoming the limitation of conventional STEM-HAADF imaging, the integrated differential phase-contrast imaging technique was employed to investigate the oxygen atoms along with other elements in the dispersoids and its interface with the matrix. The most intriguing aspect of the study is the discovery of a few atoms thick Al2O3 interlayer (shell) around a monoclinic Y–Al–O core in the Ni-matrix. On the other hand, when the dispersoid is a hexagonal type Y–Al–O complex, the interface energy is already low, maintaining a semi-coherent interface and it was devoid of a shell.
Present Address: Indian Institute of Technology-Madras, Chennai 600 036, India.