Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 June 2022
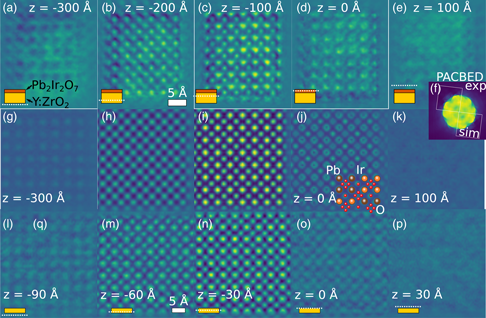
Increasing interest in three-dimensional nanostructures adds impetus to electron microscopy techniques capable of imaging at or below the nanoscale in three dimensions. We present a reconstruction algorithm that takes as input a focal series of four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy (4D-STEM) data. We apply the approach to a lead iridate, Pb $_2$Ir
$_2$Ir $_2$O
$_2$O $_7$, and yttrium-stabilized zirconia, Y
$_7$, and yttrium-stabilized zirconia, Y $_{0.095}$Zr
$_{0.095}$Zr $_{0.905}$O
$_{0.905}$O $_2$, heterostructure from data acquired with the specimen in a single plan-view orientation, with the epitaxial layers stacked along the beam direction. We demonstrate that Pb–Ir atomic columns are visible in the uppermost layers of the reconstructed volume. We compare this approach to the alternative techniques of depth sectioning using differential phase contrast scanning transmission electron microscopy (DPC-STEM) and multislice ptychographic reconstruction.
$_2$, heterostructure from data acquired with the specimen in a single plan-view orientation, with the epitaxial layers stacked along the beam direction. We demonstrate that Pb–Ir atomic columns are visible in the uppermost layers of the reconstructed volume. We compare this approach to the alternative techniques of depth sectioning using differential phase contrast scanning transmission electron microscopy (DPC-STEM) and multislice ptychographic reconstruction.
Current address: Ian Holmes Imaging Centre, Bio21 Molecular Science and Biotechnology Institute, the University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC 3052, Australia.