Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 April 2021
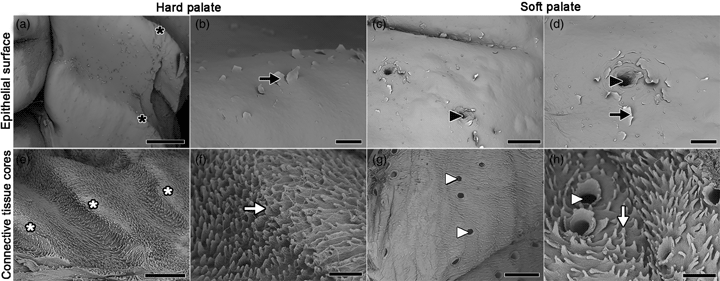
The palate is a fundamental region in food swallowing and presents different adaptations in species. This research aimed to describe structural and ultrastructural characteristics of the palatine epithelium and the connective tissue cores (CTCs) of ten red-rumped agoutis (Dasyprocta leporina—Linnaeus, 1758) using macroscopic, light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. We found nine palatine ridges in the diastema and hard palate, and a smooth surface in the soft palate. Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with projections of lamina propria and soft palate had gland clusters. Epithelial removal revealed CTCs with a conical shape with high density in the hard palate and the sides of the soft palate. Near the CTCs were nerve fibers in the hard palate, and the soft palate had muscular tissue below the gland clusters. The structural and ultrastructural characteristics enable stability of the hard palate and fixation to the soft palate sides, while the soft palate center has greater mobility thus assisting in food swallowing. We concluded that structural characteristics are similar to other mammals, although the morphology of agouti's palate differs in the amount and disposition of palatine ridges, and the conical CTC's morphology.