Article contents
Inversion Domain Boundaries in Ain and GaN Thin Films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Extract
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), multislice image simulation and multiple dark field TEM imaging techniques have been used to investigate the structure of extended defects in AlN and GaN thin films grown on (0001) α-Al2O3 by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). AlN layers were grown directly on the (0001) sapphire. In the case of GaN thin films, 300-500 Å AlN buffer was deposited first.
Cross-sectional TEM revealed the presence of domain boundaries in these Ill-nitride films. In this study we investigated these defects by multiple dark field imaging technique and proved some of them to be IDBs lying in 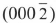 planes. The multiple dark field images of several adjacent domains of AlN film are shown in Fig. 1 (a, b). The images were obtained exactly in [11
planes. The multiple dark field images of several adjacent domains of AlN film are shown in Fig. 1 (a, b). The images were obtained exactly in [11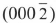 0] zone of AlN using (0002) and (000
0] zone of AlN using (0002) and (000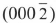 ) reflections.
) reflections.
- Type
- Microscopy of Semiconducting and Superconducting Materials
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America
References
fn01. Dovidenko, K., et al, J. Appl. Phys., 79 (5), (1996) 2439.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
fn02. Sereels, R. et al., Phys. Stat. Sol. B, 58, (1973) 277.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
fn03. Dovidenko, K., et al, Proceedings of Materials Research Society (1997), in press.Google Scholar
fn04. Westwood, A.D., Notis, M.R., J. Amer. Ceram. Soc, 74 (6), (1991) 1226.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
fn05. Northrup, J.E., Neugebauer, J., Romano, L.T., Phys. Rev. Lett., 77, (1996) 103.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
fn06. Romano, L.T., Northrup, J.E., O'Keefe, M.A., Appl. Phys. Lett., 69, (1996) 2394.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
fn07. Wu, X.H. et al, J. Appl. Phys., 80, (1996) 3238.Google Scholar
- 1
- Cited by


