No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Electron Holography of Magnetic Memory Cells
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Extract
The phase shift of an electron wave compared with a reference wave amounts to [1]
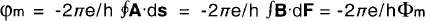
where e is the electron charge (e > 0), h is Planck's constant, A is the magnetic vector potential, B is the magnetic induction and Фm is the magnetic flux through an area F bordered by the trajectories of the two waves. The absolute value of the vector F perpendicular to this area is given by F. As a simple example we qualitatively sketch the phase shifts by a uniformly magnetized sphere. The cross section of this sphere and the magnetic field lines are shown in Fig. 1. The electron wave travels perpendicular to the paper plane. On one side of the sphere the object wave through point 1 is compared with the reference wave through point 2 and on the opposite side the wave through point 3 is compared with the one through point 4.
- Type
- Electron Holography
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America


