Article contents
Atomic Structure and Bonding of Epitaxial CU Films on (1120) A-Al203
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Extract
Thin Cu films were grown on single crystalline 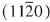 α-Al2O3 by molecular beam epitaxy at a substrate temperature of T = 800°C. The nominally 100 nm thin film consists of islands, which have diameters of 0.5-1 μm. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) were applied to obtain information about the atomic and electronic structure of the interface. HRTEM studies were performed on the Jeol JEM ARM 1250 operated at 1250 kV (point resolution of 0.12 nm). Analytical studies were conducted on a dedicated scanning TEM (VG HB 501) operated at 100 kV and equipped with a parallel EELS (Gatan 666).
α-Al2O3 by molecular beam epitaxy at a substrate temperature of T = 800°C. The nominally 100 nm thin film consists of islands, which have diameters of 0.5-1 μm. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) were applied to obtain information about the atomic and electronic structure of the interface. HRTEM studies were performed on the Jeol JEM ARM 1250 operated at 1250 kV (point resolution of 0.12 nm). Analytical studies were conducted on a dedicated scanning TEM (VG HB 501) operated at 100 kV and equipped with a parallel EELS (Gatan 666).
HRTEM of the Cu/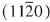 Al2O3-interface shows an atomically abrupt interface and reveals an epitaxial orientation relationship (1120)s[0001]s || (111)Cu <211>Cu (S denotes sapphire) (FIG.l). Close-packed planes and directions in both crystals are parallel to each other resulting in misfits of 2% and 7% in <211>Cu- and <110>Cu-directions, respectively. The interface is not coherent, but in both directions no misfit dislocations are detectable.
Al2O3-interface shows an atomically abrupt interface and reveals an epitaxial orientation relationship (1120)s[0001]s || (111)Cu <211>Cu (S denotes sapphire) (FIG.l). Close-packed planes and directions in both crystals are parallel to each other resulting in misfits of 2% and 7% in <211>Cu- and <110>Cu-directions, respectively. The interface is not coherent, but in both directions no misfit dislocations are detectable.
- Type
- Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy (EELS) and Imaging
- Information
- Microscopy and Microanalysis , Volume 6 , Issue S2: Proceedings: Microscopy & Microanalysis 2000, Microscopy Society of America 58th Annual Meeting, Microbeam Analysis Society 34th Annual Meeting, Microscopical Society of Canada/Societe de Microscopie de Canada 27th Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania August 13-17, 2000 , August 2000 , pp. 182 - 183
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America
References
1. Egerton, R. F., Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy, Plenum Press: New York (1996)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
2. Möllejans, H. and Bruley, J., Ultramicroscopy 53, (1994) 351CrossRefGoogle Scholar
3. Stadelmann, P., Ultramicroscopy 21, (1987) 131CrossRefGoogle Scholar
4. We acknowledge Dr. Bruley, J. who provided the reference spectrum of CuAl2. This work is financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).Google Scholar
- 2
- Cited by


