No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Transmission Electron Microscopy Study of Tin Oxide Thin Films Deposited on the Sapphire Substrate
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Extract
Thin films of tin oxide (SnO2) with the rutile structure are the subject of many investigations due to their potential applications, such as gas sensing devices, lithium batteries cathodes and solar cells. There is a growing interest in the development of gas sensors using SnO2 thin films due to their high surface to volume ratio. Previous studies have shown that the gas sensing properties of SnO2 are very dependent on the microstructure and that doping elements can greatly influence their electrical properties. In this paper we present transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studies of the microstructure and crystal defects of SnO2 thin films.
Tin oxide films 5 nm in thickness were deposited on the 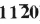 surface of sapphire (A12O3) by pulsed laser ablation of ceramic SnO2 targets. The film microstructure was studied using X ray diffraction, atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Defects were studied using high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM).
surface of sapphire (A12O3) by pulsed laser ablation of ceramic SnO2 targets. The film microstructure was studied using X ray diffraction, atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Defects were studied using high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM).
- Type
- Films and Coatings
- Information
- Microscopy and Microanalysis , Volume 6 , Issue S2: Proceedings: Microscopy & Microanalysis 2000, Microscopy Society of America 58th Annual Meeting, Microbeam Analysis Society 34th Annual Meeting, Microscopical Society of Canada/Societe de Microscopie de Canada 27th Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania August 13-17, 2000 , August 2000 , pp. 442 - 443
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America


