No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Near Real-Time X-Ray Cone-Beam Microtomography
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Extract
Due to the penetration ability and absorption contrast mechanism, cone-beam X-ray microtomography is a powerful tool in studying 3D microstructures in opaque specimens. In contrast to the conventional parallel and fan-beam geometry, the cone-beam tomography set up is highly desirable for faster data acquisition, build-in magnification, better radiation utilization and easier hardware implementation. However, the major draw back of the cone-beam reconstruction is its computational complexity. In an effort to maximize the reconstruction speed, we have developed a generalized Feldkamp cone-beam reconstruction algorithm to optimize the reconstruction process. We report here the use of curved voxels in a cylindrical coordinate system and mapping tables to further improve the reconstruction efficiency.
The generalized Feldkamp cone-beam image reconstruction algorithm is reformulated utilizing mapping table in the discrete domain as: 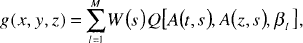 , where
, where 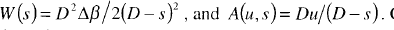 .
.
- Type
- Computational Methods for Microscopy and Microanalysis
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America


