Article contents
Gravitational-Like Lens Based on Graphene Ripple
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 August 2015
Abstract
We conducted a semiclassical study on carrier movement in curved graphene. A previous attempt was made to show that curved graphene is a readily available and cheap laboratory material used to study general relativity effects, especially if the electron energies satisfy 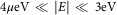 ${\rm 4}\:\mu {\rm eV}\,\ll\,\left| E \right|\,\ll\,{\rm 3}\:{\rm eV}$
. Furthermore, a gravitational-like lens can be constructed based on a special graphene ripple; this lens has neither chromatic nor cometic aberration. One can design an ideal electron lens using a graphene ripple.
${\rm 4}\:\mu {\rm eV}\,\ll\,\left| E \right|\,\ll\,{\rm 3}\:{\rm eV}$
. Furthermore, a gravitational-like lens can be constructed based on a special graphene ripple; this lens has neither chromatic nor cometic aberration. One can design an ideal electron lens using a graphene ripple.
- Type
- Equipment and Software Development
- Information
- Copyright
- © Microscopy Society of America 2015
References
- 1
- Cited by


